When applying for the MCAT, understanding how the test scoring works is absolutely vital. A high score on the MCAT is your gateway to your choice of medical school since higher scores tend to have a positive impact on your med school application. This in turn increases your chances of getting an acceptance into a school of your choice.
In this article, we have composed a complete guide for candidates and premed students that are new to the MCAT. The article also covers the scoring basics of the MCAT exam.
What are the Four Sections of MCAT and their Format?
The Medical College Admission Test, or widely known as MCAT is a 7.5 hour exam administered by Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC). It is a multiple-choice, computer-based standardized exam that is a requirement for admissions in medical schools in the USA and Canada.
It is one of the essential requirements for med school admission, along with your academic record and other supporting material.
Apart from testing the candidates’ qualifications, the MCAT also examines the candidates’ proficiency in basic skills of science, for instance, organic chemistry, biology, physics, etc. It also tests critical analysis and reasoning skills.
The MCAT consists of four sections that integrate multiple topics, meaning that the subjects are not tested independently. This integrated content is further divided into four sections which are given below. Out of these four sections, three are science sections and one is based on reading and comprehension.
Biological and Biochemical Foundations of Living Systems (Bio-Biochem)
This section consists of questions from the concepts covered in Biology and Biochemistry. Common biochemical topics that are covered are amino acids, metabolism, DNA, etc. On the other hand, concepts tested for biology are cardiology, immunology, genetics, and more.
The time allocated to this section is 95 minutes, and candidates are required to answer 59 questions in the time limit. There are also 10 passages.
Out of the total questions, 44 are passage-based questions, while the remaining 15 are separate questions. While this section widely tests biology and biochemistry, there are a few questions about organic and general chemistry.
Chemical and Physical Foundations of Living Systems (Chem/Phys)
The Chem/Phys section follows the same pattern as the previous one. The time limit and number of questions are the same. This section tests concepts of chemistry and physics, for instance, forces, translational motion, fluids, thermodynamics, and much more.
Out of 59 questions, a significant amount goes to physics and general chemistry. Alongside these, we have biochemistry which is also a significant portion in this section.
Just like the previous section, 15 questions are independent of the passage, while the rest are related to the passages given from scientific journals.
Psychological, Social, and Biological Foundations of Behavior (Psych-Soc)
The Psych-Soc section also consists of 59 questions. However, as the name indicates, the topics tested in this section are different. Many test-takers have stated that this section is a combination of the other science sections and the CARS section.
Psychological concepts tested in this section include identity, development, learning, and psychological disorders.
On the other hand, common concepts tested for sociology are social structures, discrimination, inequality, and demographics. This section is really important as it ensures that the future physicians and doctors will be able to treat diverse populations with a variety of social and cultural issues.
Critical Analysis and Reasoning Skills (CARS)
This section, as its name indicates, is a bit different from the rest. While the other three test scientific concepts, this assesses basic comprehension and reading skills and requires no prior knowledge.
The total time allotted for this is 90 minutes and candidates have to solve 53 passage-based questions. There are 9 passages provided.
Commonly tested topics for this section range from ethics to religion to anthropology to political science. The passages are taken from various journals and magazines and are often long and challenging.
With the help of these passages, three skills are assessed which are necessary for medical students. They include foundations of comprehension, reasoning beyond the text, and reasoning within the text.
Here is a summary of all 4 sections of the MCAT Exam along with their format:
Section | Number of Questions | Time Allotted |
|---|---|---|
Bio-Biochem | 59 | 95 min |
Chem/Phys | 59 | 95 min |
Psych-Soc | 59 | 95 min |
CARS | 53 | 90 min |
TOTAL TIME | 230 | 6 hours, 15 minutes |
MCAT Scoring Explained
The number of the correct answers, otherwise known as Raw Score, is the basis of MCAT scoring.
The scoring ranges from a low of 118 points to the highest of 132, with 125 as a midpoint for each section.
Incorrect answers are scored the same way. Thus it leaves no room for a penalty for guessing.
It is also important to note that the admission committee only uses the scaled scores as the MCAT component for admission.
To understand the scoring process better, here’s a look at the report one will receive after the MCAT exams. You will see different elements that describe your performance.
Here’s the sample MCAT Score Report from Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC):
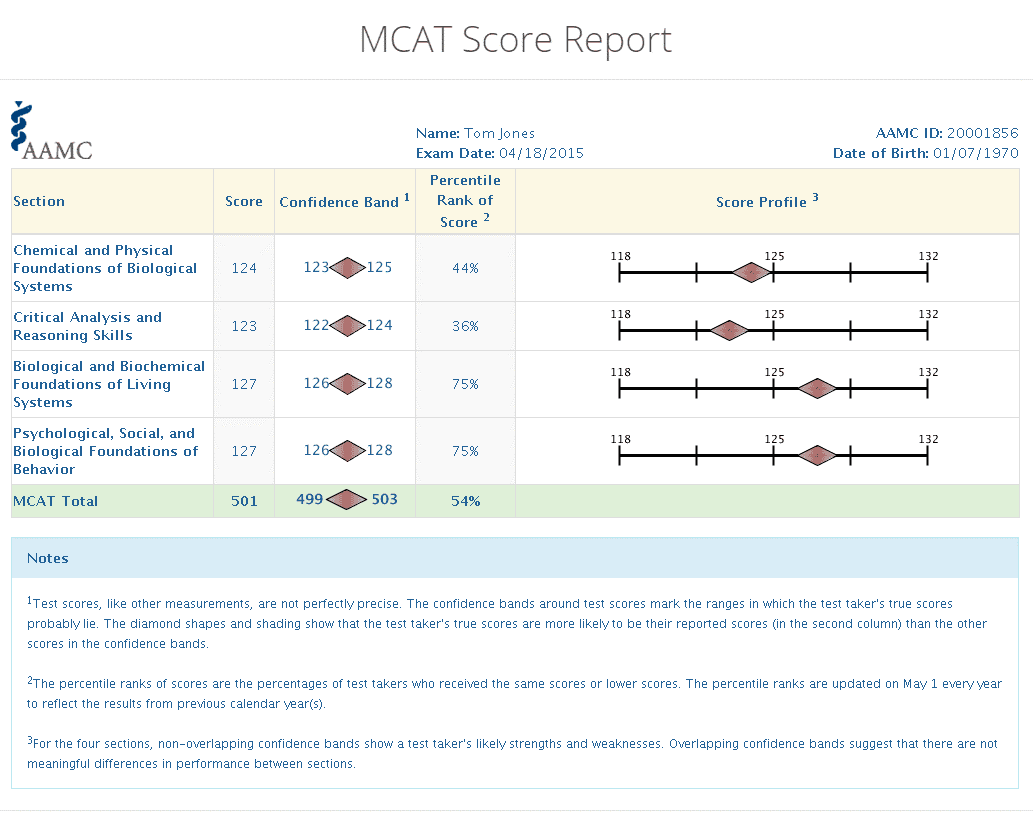
You will receive five scores.
Four of these scores are section scores, and the last one is your total combined score.
Let’s look at the overall score first. The overall score is one total score, that is, the sum of your scores in all 4 sections and this ranges from 472-to 528. Here 500 is the midpoint of the range.
Next, each of the four sections is worth 132 raw points with 118 being the lowest score. 125 is the midpoint in this region. And this range is visible under the score profile in your report.
Raw score, here, means scores you get based on the number of correct questions.
Percentile rank and confidence band are also a part of the MCAT report. The confidence band indicates the range where your score lies in all sections. Whereas, percentile rank shows your progress compared to other competitors.
For example, the percentile rank of total score indicates that the exam taker’s total score is better than 54% of other exam takers. Let’s look at the example scores given below:
Raw Score | Scaled Score | Percentile Score |
|---|---|---|
58-59 | 132 | 99.99% |
56-57 | 131 | 99.1% |
53-55 | 130 | 97.6% |
50-52 | 129 | 94.3% |
46-49 | 128 | 88.2% |
42-45 | 127 | 82.7% |
37-41 | 126 | 71.7% |
32-36 | 125 | 50.0% |
27-31 | 124 | 45.2% |
22-26 | 123 | 34.8% |
18-21 | 122 | 23.1% |
14-17 | 121 | 15.5% |
10-13 | 120 | 10.8% |
6-9 | 119 | 5.3% |
0-5 | 118 | 0.0% |
Is the MCAT Graded on a Curve?
MCAT scores are NOT curved.
That means, your MCAT score does not depend on when you take the exam and who takes it with you. Normally, the classroom exams are graded on a curve.
That means a small percentage in the class gets an A grade and an F grade, while the rest of the students get B or C. Hence, there exists a bell curve that depends on the average curve.
MCAT is scaled such that scores have the same meaning and do not change based on when you take the exam, and it is only reflective of how you did in each section. So the bottom line? MCAT is not graded on a curve.
How and Where Do I Apply Based on My MCAT Score?
The first step before applying to any medical school is to research it. That will give you a better insight into how you need to score to get accepted into that particular school.
But keep in mind that, while you should aim to get a high score, your MCAT score is not the only factor considered. We’ve briefly discussed these factors in the above section.
Following guidelines on where to apply based on your score is very general as it depends on your state residence, GPA, and other factors too, that can bring about changes, but some general points are:
How are the MCAT Scores Used in the Admission Process?
MCAT is a necessary test that requires minimum scores specific to medical schools to ensure your chance of getting accepted.
To ensure whether you are a good fit for that particular medical school, the admission committee uses both your MCAT score and will look for a particular set of skills they deemed fit for successful students.
Along with MCAT scores, information about the following factors are also observed:
Thus, having a good GPA and higher MCAT scores benefits your application and increases your chance among the competitors. Other than that, if you’ve taken multiple exams, the school will consider all the exam results and attempts.
Additional FAQs – MCAT Scoring
Is My GPA Important in MCAT?
With a good GPA and equally good MCAT scores, the probability of getting admission is higher. Hence, it may not be the only criteria, but it is equally important.
What is the Perfect MCAT Score?
Although anything above 517 is a good score, if you have a high GPA, it increases your chances of getting into medical school.
What is the Passing Score for MCAT?
However, it is recommended to get a higher MCAT score as this makes it easier to get admission to the college of your choice - the higher the score, the better your chances of acceptance are.
When Will I Receive My MCAT Scores?
Hence, the long waiting time. However, during this time, students can submit their concerns regarding exam questions and testing conditions.
How Many Times Can I Take the MCAT?
Two consecutive years: up to 4 times
Lifetime: up to 7 times
But remember, not appearing on the testing voids is still counted against you.
MCAT scores may not be the only important part of getting into medical school, but it is crucial where your overall application is considered.
That is why giving enough time to prepare for the exam and doing your best should be your priority as this empirical approach can maximize your chances of getting in.


 To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these
To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these 
