As you prepare for the MCAT, comprehending functional groups is a prerequisite for understanding organic chemistry. Although you are unsure of the specific questions that will be asked on the MCAT, the exam certainly includes questions about MCAT organic chemistry functional groups.
While MCAT organic chemistry functional groups seem too technical and challenging, answering these questions will be easier if you start with the basics to understand what they are and how they work.
If you are studying for the MCAT and want to know more about the different organic chemistry functional groups, that is exactly what this page is for. Please keep reading.
What are MCAT Organic Chemistry Functional Groups?
The ability to swiftly identify the most frequent functional groups will become increasingly crucial as you study organic chemistry because they are the crucial structural components that determine how organic molecules react.
A functional group in organic chemistry is a substituent or moiety in a molecule that triggers the molecule's distinctive chemical processes.
No matter how the rest of the molecule is made up, the same functional group will experience the same or a similar set of chemical events. It means, for instance, that alcohol will behave the same whether it is a component of methyl-alcohol, ethyl-alcohol, or isopropyl-alcohol.
This permits the design of chemical synthesis, the systematic prediction of chemical reactions, and the behavior of chemical molecules. Other functional groups close by can affect a functional group's reactivity.
Retrosynthetic analysis can be used to design organic synthesis by using functional group interconversion.
Additionally, these functional groups frequently operate as the main basic or acidic sites in a compound, which increases their propensity to act as a site for various organic processes.
What are the Different Functional Groups in Organic Chemistry?
While recognizing functional groups can tremendously help break down any substance into its fundamental features and probable reactions, novel organic compounds may initially seem intimidating. The key is to analyze what each compound is made up of.
Here is a list of the seven different MCAT organic chemistry functional groups to help you understand them better:
Hydroxyl Functional Group Structure
Methyl Functional Group
Methyl functional groups, which have a core carbon atom linked to three hydrogen atoms, are very stable. Therefore, even in the presence of extremely potent acids or bases, the functional group itself is often non-reactive.
Despite having a stable conformation, methyl groups can participate in "methylation" reactions, which entail moving the complete functional group to a different molecule.
Processes, including epigenetics, gene expression, liver detoxification, and neurotransmitter production, all depend on this enzyme-mediated response.
Methyl Functional Group Structure
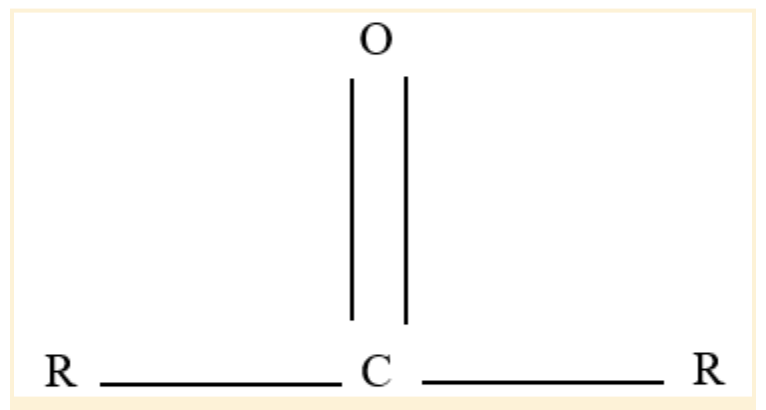
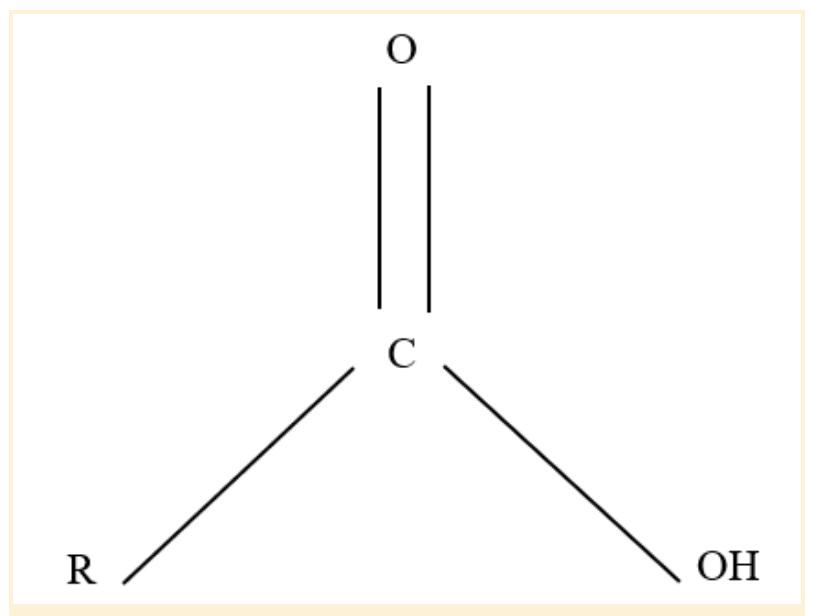
Carbonyl Functional Group
An oxygen atom and a carbon atom are double-bonded to form a functional group known as a carbonyl group or C=O.
In organic chemistry, it is perhaps the most significant functional group. The main constituents of these molecules, which are an essential component of organic chemistry, are aldehydes, ketones, and carboxylic acids.
As a component of numerous larger functional groups, it is present in many kinds of organic molecules. The term "carbonyl compound" is frequently used to describe a compound with a carbonyl group.
Carbon monoxide, which functions as a ligand in inorganic or organometallic complexes, can also be referred to as a carbonyl.
Carbonyl Functional Group Structure
Carboxyl Functional Group
The carboxyl group is an organic functional group in chemistry composed of a single carbon atom connected to a hydroxyl group and double-bound to an oxygen atom. It can also be thought of as a carbonyl group with a hydroxyl group (O-H) joined to the carbon atom (C=O).
Carboxyl groups' -OH group releases their hydrogen atom, causing them to ionize. As a result, the H+, a free proton, is discharged.
Carboxyl groups, afterward, make excellent acids. There is a negative charge on the oxygen atom when hydrogen departs the group, which it shares with the other oxygen atom. This property makes the carboxyl stable even when oxidized.
Carboxyl Functional Group Structure
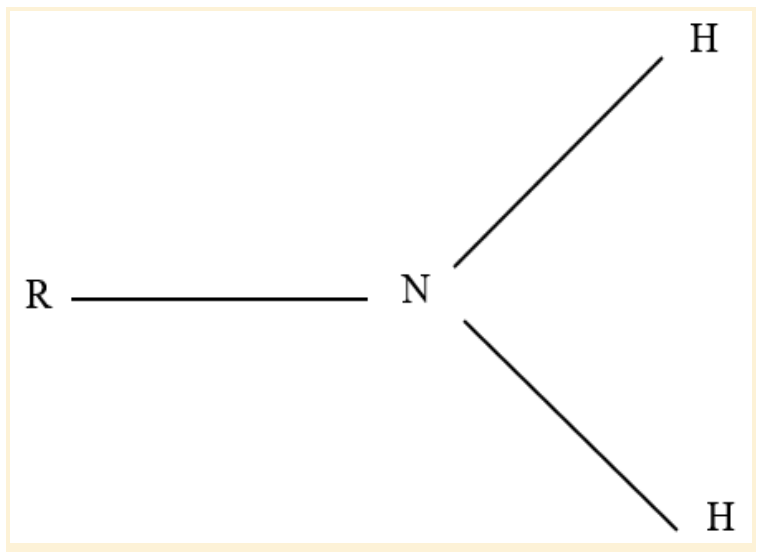
Amino Functional Group
An alkaline or basic group makes up the amino functional group. It is frequently found in proteins, amino acids, and the nitrogenous building blocks for DNA and RNA.
The amino group is NH2, but when exposed to acid, it picks up a proton and changes to NH3+.
A nitrogen atom is joined to two hydrogen atoms to form an amino group. For example, an amine is a chemical compound that has an amino functional group. Sometimes, amine groups are used to refer to amino groups.
Any nitrogen-containing group with a lone pair is an amine. An amino group is a nitrogen atom with a lone pair and at least two hydrogen atoms attached to it.
A primary amine is also an amino group. When something is primary, it only has one non-hydrogen bond.
Amino Functional Group Structure
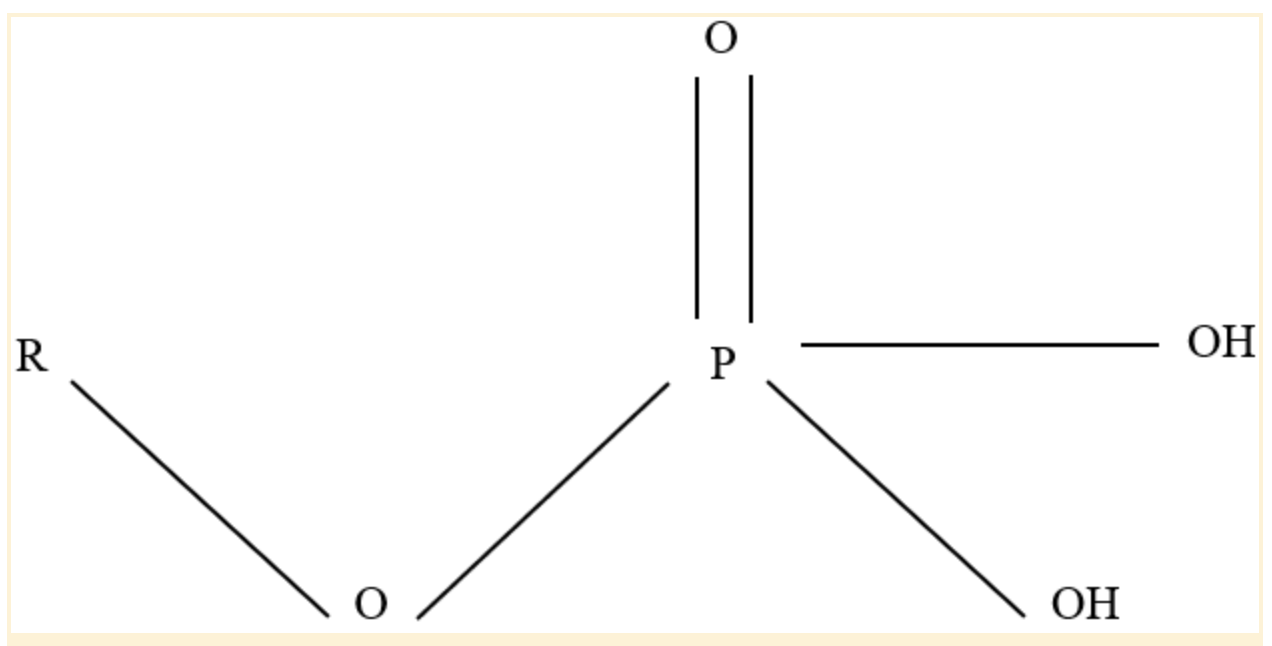
Phosphate Functional Group
Four oxygen atoms and one phosphorus atom combine to form the chemical compound phosphate, which has the formula PO43-. It is referred to as a phosphate functional group when it is joined to a carbon-containing molecule.
Polar covalent connections are produced because the oxygen atoms are more electronegative than phosphorus.
Because of this, these oxygen atoms can create hydrogen bonds with neighboring hydrogen atoms that also have a positive charge (hydrogen atoms bound to another electronegative atom). Additionally, having a negative charge, phosphate groups can participate in ionic bonding.
It can be found in molecules like adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which gives organisms energy, and in the genetic material DNA and RNA.
Phospholipids, which make up the cell membrane, can be formed from phosphates. In ecosystems, phosphate is also a crucial resource, particularly in freshwater settings.
Phosphate Functional Group Structure
Sulfhydryl Functional Group
A sulfur atom is joined to a hydrogen atom to form the functional group known as sulfhydryl.
Chemistry terminology uses "-thiol" as a suffix and "mercapto-" or "sulfanyl" as a prefix to designate the sulfhydryl group, also known as a thiol.
For soft metals, thiols have a strong affinity. Moreover, sulfhydryls are crucial in biochemistry because disulfide bonds enable the functional connection of essential amino acids in secondary, tertiary, or quaternary protein structures.
Cysteine, an amino acid, contains sulfhydryl groups.
Two cysteine residues may attach together and form a disulfide bridge, also known as cystine if they are located adjacent to one another.
An illustration of a post-translational alteration is the creation of a disulfide bond. Although it can be advantageous to protein structure, it might make it challenging to precisely establish a protein's sequence using the Edman sequencing method.
Sulfhydryl Functional Group Structure
Do You Need to Memorize Functional Groups for the MCAT?
As mentioned earlier, the MCAT organic chemistry functional groups are crucial for the MCAT.
You need to devote time and effort to studying them during your MCAT preparation. And while we have been mentioning that the MCAT is not merely a test of memory recall, it is worth noting that to answer the MCAT organic chemistry functional groups questions, you need to be able to remember what they are.
In addition, aside from memorizing their components and structure, you need to have a solid grasp of what they are and how and why they function. You need to understand why these MCAT organic chemistry functional groups are essential for the human body.
It is important that aside from memorizing the different MCAT organic functional groups. – also make it a point that you fully comprehend their importance in how the human body works.
How Can I Remember Functional Groups in Organic Chemistry?
With many terms, definitions, and equations to remember for the MCAT chemistry and the entire MCAT, you cannot help but feel overwhelmed. However, since these are essential concepts that are required for the MCAT, you need to memorize and study them.
Here are some of the best and most effective ways on how to remember the MCAT organic chemistry functional groups:
Use Mnemonic Devices
Most MCAT test-takers agree that employing mnemonics to remember the different MCAT organic chemistry functional groups is effective. While there are ready-made mnemonic devices around, you can also make your own to suit your preference.
Ensure that aside from memorizing these functional groups, you fully understand the entirety of the concepts required.
Try MCAT Flashcards
MCAT flashcards are also an excellent way to help you remember the different MCAT organic chemistry functional groups. You can choose to use paper or digital flashcards.
To help you maximize the use of MCAT flashcards, you must use them regularly anytime and anywhere you have the opportunity. Also, remove the flashcards you have fully mastered to give way to concepts you need to improve on.
Draw Things Out
You can best recall and remember the MCAT organic chemistry functional groups if you draw how they are structured. However, with a lot of chemical compounds required, it could be challenging to rely just on your memory.
This is a strategy that has yielded good results for most MCAT test-takers. Keeping a notebook solely for the MCAT organic chemistry functional group is a good idea. It may also be beneficial to practice simple reactions with them which will help with pattern recognition and identification.
Place MCAT Organic Chemistry Functional Group Drawings in Strategic Places
Simply draw all functional groups on a piece of paper and pin it to a wall in strategic locations in your place. It could be your bedroom, kitchen, living room, or even your car.
Every day, observe the functional group whenever you have a moment. Then, check to see if you wrote it accurately.
If you do this attentively for at least three days with the proper focus, you will be able to remember the MCAT organic chemistry functional groups easily.
How to Draw, Recognize and Name MCAT Organic Chemistry Functional Groups?
The MCAT organic chemistry functional groups may seem complicated and hard to master.
However, if you know the tips and techniques on how to identify or even name them, answering MCAT questions related to them is a breeze.
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC, typically pronounced eye-you-pack) has developed a system for naming organic molecules.
The IUPAC method helps identify relatively tiny, straightforward organic compounds, but biomolecules are frequently rather large and complex; they are not typically utilized for these purposes.
However, it is advisable (even for biologists) to get familiar with the IUPAC system's fundamental components and be able to create straightforward structures using IUPAC nomenclature.
Finding the longest straight chain of carbon atoms, known as the "parent chain," is the first step in naming an organic compound. The simplest straight-chain alkane structures will be discussed first. Both C2H6 and CH4 are known as gases.
Remember them, as they serve as the foundation for the remainder of the IUPAC nomenclature system. The table below continues with the names of longer straight-chain alkanes (and are widely used in naming biomolecules as well).
1 carbon: methane
2 carbons: ethane
3 carbons: propane
4 carbons: butane
5 carbons: pentane
6 carbons: hexane
7 carbons: heptane
8 carbons: octane
9 carbons: nonane
10 carbons: decane
To be able to name the MCAT organic chemistry functional groups correctly, you also need to familiarize yourself with the prefixes that come with them.
The prefixes “di”, “tri”, and “tetra” are applied when there are several substituents.
For instance, the parent chain name of alcohols has the suffix "ol" and a number indicating the location of the hydroxyl group. One is used to identify ketones.
Aldehydes finish in "al," carboxylic acids in "oic acid," and carboxylates in "oate," all of which are groups that can only be found on a terminal carbon and for which a locating number is not required.Additional FAQs – MCAT Organic Chemistry Functional Groups
How Hard is Organic Chemistry on the MCAT?
While there are a lot of terms, definitions, and compounds to memorize, as long as you employ the best and proven tips and techniques, answering MCAT questions about them is not a problem.
You also have to remember not to focus on memorization alone, as the MCAT is not a test of recall. Instead, you are assessed more on how you can apply the MCAT organic chemistry concepts to contexts where relevant.
What Percentage of the MCAT is Organic Chemistry Functional Groups?
It is certain that out of these 12 questions, a few (or more) will require your knowledge and skills about the MCAT organic chemistry functional groups.
Additional Reading:
- MCAT Organic Chemistry Practice Questions
- Alcohols and Ethers on the MCAT
- Aldehydes and Ketones on the MCAT
- Bonding on the MCAT
- Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives on the MCAT
- Isomers on the MCAT
- Laboratory Techniques and Separations on the MCAT
- Nitrogen Containing Compounds on the MCAT
- Phosphorus Containing Compounds on the MCAT
- Organic Chemistry Nomenclature on the MCAT
- Nucleophiles and Electrophiles on the MCAT
- Spectroscopy on the MCAT
- Redox Reactions Organic Chemistry on the MCAT





 To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these
To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these