Imagine you are an assembly worker manufacturing cars. With your help, the machines make the process much quicker. Your job is to also regulate the number of cars being made. Without your help, the machines cannot stop or start assembling car parts together, resulting in an excess or not enough cars that meet consumer demands.
In a similar manner to assembly line machines, enzymes act to increase the rate at which metabolism occurs; however, this must be regulated. These processes are regulated by metabolites to increase or decrease the activity of enzymes so that an adequate amount of product can be made to meet metabolic demands.
Now that we have gone over an analogy of the regulation of metabolism, we can dive a little further into the key terms, definitions, and pathways that will be important for the MCAT.
Let’s get started!
Regulation of Metabolism on the MCAT: What You Need to Know
The regulation of metabolism will show up in the Bio/Biochem section of the MCAT.
Introductory biochemistry accounts for 25% of the Biological and Biochemical Foundations of Living Systems section (Bio/Biochem) and 25% of the Chemical and Physical Foundations of Biological Systems section (Chem/Phys).
In this section, your understanding of negative and positive feedback mechanisms, which enzymes are regulated, and under what conditions will be fundamental to answering these questions.
Important Sub-Topics - Regulation of Metabolism
Allosteric and Hormonal Regulation of Carbohydrate Metabolism
Enzymes of carbohydrate metabolism must be regulated through feedback pathways. Products that are produced downstream have the ability to modulate the activity of enzymes upstream.
This is either completed through a positive feedback or negative feedback mechanism. The former involves a stimulation of an earlier step which promotes the production of a downstream product, while the latter involves the suppression of an earlier step which inhibits downstream products.
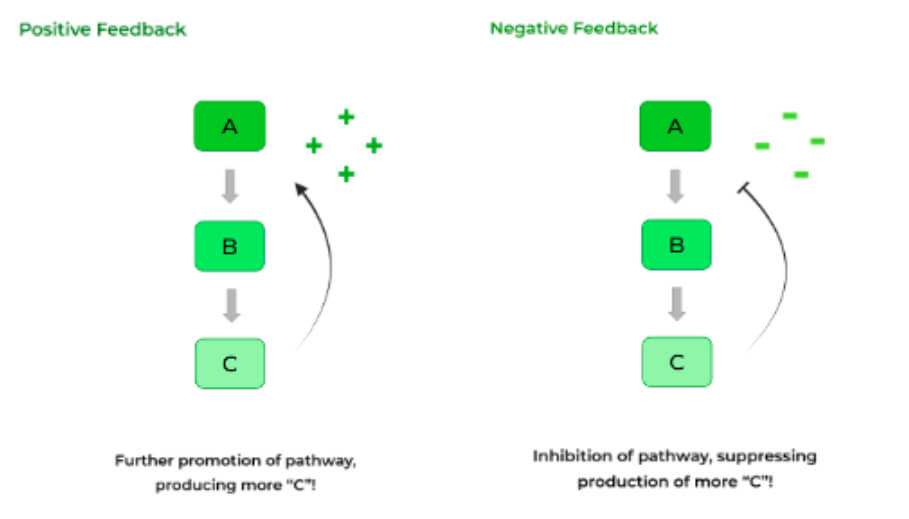
There are several molecules and hormones that are of particular importance on the MCAT which participate in the feedback, allosteric regulation of enzymes in carbohydrate metabolism.
Full Study Notes : Allosteric and Hormonal Regulation of Carbohydrate Metabolism on the MCAT
For more in-depth content review on allosteric regulation of enzymes in carbohydrate metabolism, check out these detailed lesson notes created by top MCAT scorers.
Important Definitions and Key Terms - Regulation of Metabolism
Term | Definition |
|---|---|
Allosteric regulation | When a regulatory molecule (either an activator or inhibitor) binds to an enzyme on a site that is not the active site. |
Positive feedback loop | When the physiological system reinforces the changes that are occurring to increase the products of a reaction. |
Negative feedback loop | When the physiological system inhibits the changes that are occurring to decrease the products of a reaction. |
Additional FAQs - Regulation of Metabolism on the MCAT
What is the regulation of metabolism?
What are the four major mechanisms of metabolic regulation?
1. Substrate availability
→ This is the concentration of substrate available. Increased substrate available may
activate enzymes required for their metabolism.
2. Allosteric enzyme regulation
→ When a regulatory molecule (either an activator or inhibitor) binds to an enzyme
on a site that is not the active site.
3. Covalent enzyme modification
→ Enzyme-catalyzed changes to an enzyme, which includes the addition or removal
of chemical groups of a synthesized protein.
4. Regulation of enzyme synthesis
→ Involves the activation or repression of gene transcription of specific enzymes.
What do I need to know about metabolic pathways on the MCAT?
How much of glycolysis do you need to know for the MCAT?
However, if you have the bandwidth, memorize all enzymes and products of glycolysis, this will only help you. There are some discrete questions that may test you on the products of other enzymes in glycolysis.
Additional Reading Links – Regulation of Metabolism on the MCAT
Additional Reading: Biochemistry Subjects on the MCAT:
- Biological Membranes on the MCAT
- Carbohydrate Metabolism on the MCAT
- Carbohydrate Structure on the MCAT
- DNA and RNA on the MCAT
- Enzymes on the MCAT
- Lipids and Lipid Metabolism on the MCAT
- Non-Enzymatic Proteins on the MCAT
- Amino Acids Peptides Proteins on the MCAT
- Biotechnology on the MCAT
- Bioenergetics on the MCAT







 To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these
To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these 
