In organic chemistry, protecting groups prevent certain functional groups from reacting while performing a reaction on another part of the molecule. Protection reactions of alcohols are a common practice to achieve selective transformations.
I. Basics of Protection Reactions
A. What are Protection Reactions?
Protection reactions involve temporarily masking a reactive group to prevent it from participating in unwanted reactions. Once the desired transformation is complete, the protective group is removed to regenerate the original functional group.
B. Why Protect Alcohols?
Alcohols (compounds containing -OH groups) can be highly reactive, making them susceptible to various chemical reactions. Protecting alcohols helps in:
- Preventing unwanted reactions: Protecting the -OH group allows selective reactions on other molecule parts.
- Improving reaction yields: With the -OH group protected, the desired reactions proceed more smoothly.
II. Common Alcohol Protecting Groups
A. Silyl Ethers
Silyl ethers are a popular choice for protecting alcohols due to their stability and ease of removal.
1. Formation
To protect an alcohol using a silyl ether, a silyl chloride (like trimethylsilyl chloride, TMSCl) is used in the presence of a base such as triethylamine (TEA).
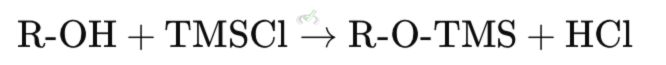
Explanation: In this reaction, the alcohol (R-OH) reacts with trimethylsilyl chloride (TMSCl) to form a silyl ether (R-O-TMS) and hydrochloric acid (HCl). The base (TEA) helps neutralize the HCl formed.
2. Removal
The silyl ether can be removed by treating it with a fluoride source, such as tetra-n-butylammonium fluoride (TBAF).
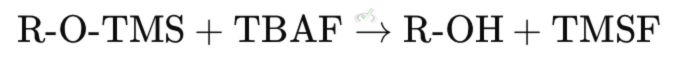
Explanation: In this reaction, the silyl ether (R-O-TMS) reacts with TBAF to regenerate the original alcohol (R-OH) and produce trimethylsilyl fluoride (TMSF).
B. Acetals and Ketals
Acetals and ketals protect alcohols by forming stable cyclic structures, particularly useful in acidic conditions.
1. Formation
An alcohol reacts with an aldehyde or ketone in the presence of an acid catalyst to form an acetal or ketal.
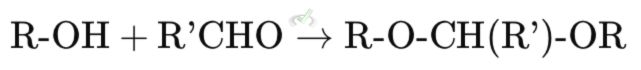
Explanation: In this reaction, an alcohol (R-OH) reacts with an aldehyde (R'CHO) to form an acetal (R-O-CH(R')-OR). The acid catalyst helps in this transformation.
2. Removal
Acetals and ketals can be removed by hydrolysis under acidic conditions, regenerating the original alcohol.
Explanation: In this reaction, the acetal (R-O-CH(R')-OR) reacts with water (H₂O) under acidic conditions to regenerate the original alcohol (R-OH) and the aldehyde (R'CHO).
C. Benzyl Ethers
Benzyl ethers are another option for protecting alcohols, particularly stable under basic and neutral conditions.
1. Formation
To form a benzyl ether, the alcohol reacts with benzyl chloride (BnCl) in the presence of a base.
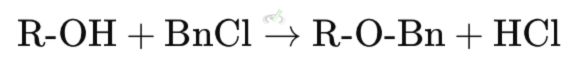
Explanation: In this reaction, the alcohol (R-OH) reacts with benzyl chloride (BnCl) to form a benzyl ether (R-O-Bn) and hydrochloric acid (HCl).
2. Removal
The benzyl group can be removed by hydrogenolysis, using hydrogen gas and a palladium catalyst.
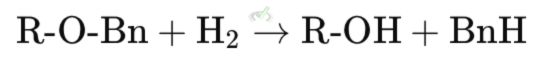
Explanation: In this reaction, the benzyl ether (R-O-Bn) is converted back to the original alcohol (R-OH) using hydrogen gas (H₂) and a palladium catalyst. This produces toluene (BnH) as a by-product.
D. Additional Protecting Groups
Other protecting groups include:
- Methoxymethyl (MOM) ethers: Formed using chloromethyl methyl ether (MOMCl) and removed with acid.
- Tetrahydropyranyl (THP) ethers: Formed using dihydropyran (DHP) and removed with acid.
- p-Methoxybenzyl (PMB) ethers: Formed using p-methoxybenzyl chloride (PMBCl) and removed with acid or oxidation.
III. Applications of Protection Reactions
A. Synthesis of Complex Molecules
Protection reactions are essential in the multi-step synthesis of complex organic molecules. By selectively protecting and deprotecting alcohols, chemists can build intricate molecular architectures. It can also help them achieve selective functionalization.
B. Pharmaceutical Industry
In drug synthesis, protecting groups help ensure the stability of sensitive functional groups. It also allows for the selective modification of specific parts of the drug molecule.
C. Natural Product Synthesis
Natural products often have multiple functional groups. Protecting alcohols enables selective reactions necessary for constructing these complex structures.
IV. Bridging Concepts: Protection Reactions Beyond Alcohols
Protection reactions are not limited to alcohols. They can be applied to other functional groups, such as:
- Amines: Protecting groups like Boc (tert-butyloxycarbonyl) are used for amines.
- Carbonyls: Acetals and ketals can protect carbonyl groups in aldehydes and ketones.
Understanding the principles of protection reactions in alcohols provides a foundation for learning about protecting other functional groups. This knowledge is crucial for mastering complex synthetic pathways in organic chemistry.
V. Wrap-Up and Key Terms
Protection reactions are a crucial tool in organic chemistry. They allow chemists to selectively modify molecules without interference from reactive groups like alcohols. By understanding the formation and removal of protecting groups and their applications in various fields, one can master complex synthetic routes essential for research and industry applications.
Key Terms
- Protecting Group: A chemical group used to mask a reactive site in a molecule temporarily.
- Silyl Ether: A protecting group formed from silyl chlorides and alcohols, removable with fluoride sources.
- Acetal/Ketal: Cyclic protecting groups for alcohols, formed with aldehydes or ketones, removable by acidic hydrolysis.
- Benzyl Ether: A stable group for protecting against alcohols, removable by hydrogenolysis.
- Hydrogenolysis: A reaction involving the cleavage of a bond using hydrogen gas and a catalyst.
- Tetra-n-butylammonium Fluoride (TBAF): A reagent used to remove silyl ethers.
- Multi-Step Synthesis: A complex process in organic chemistry where multiple reactions are performed sequentially to obtain a final product.
VI. Practice Questions
Sample Practice Question 1
What is the purpose of protecting alcohol in organic synthesis?
A. To prevent the alcohol from reacting.
B. To increase the number of reactions.
C. To change the chemical structure.
D. To make the alcohol more reactive.
Ans. A
The primary purpose of protecting alcohol in organic synthesis is to prevent it from reacting with other reagents or functional groups in the molecule.
Sample Practice Question 2
Which reagent is commonly used to remove a silyl ether-protecting group?
A. Sodium hydroxide (NaOH)
B. Hydrochloric acid (HCl)
C. Tetra-n-butylammonium fluoride (TBAF)
D. Benzyl chloride (BnCl)
Ans. C
Tetra-n-butylammonium fluoride (TBAF) is commonly used to remove silyl ether-protecting groups. Silyl ethers are often used to protect alcohols, and TBAF effectively cleaves the silicon-oxygen bond, regenerating the original alcohol. The fluoride ion in TBAF attacks the silicon atom, breaking the bond and forming the free alcohol and a silyl fluoride by-product. This reagent is preferred because it works under mild conditions and provides a high yield of the deprotected alcohol.Tetra-n-butylammonium fluoride (TBAF) is commonly used to remove silyl ether-protecting groups. Silyl ethers are often used to protect alcohols, and TBAF effectively cleaves the silicon-oxygen bond, regenerating the original alcohol. The fluoride ion in TBAF attacks the silicon atom, breaking the bond and forming the free alcohol and a silyl fluoride by-product. This reagent is preferred because it works under mild conditions and provides a high yield of the deprotected alcohol.







 To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these
To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these 
