Human behavior involves looking at various aspects. This includes attraction, aggression, attachment, and social support.
These elements influence how we form relationships, react to others, and provide or seek support. Let's explore these concepts in depth and understand their importance.
I. Understanding Inherent Attraction
Inherent attraction refers to the natural draw we feel towards certain people. This can be due to physical appearance, personality traits, or shared interests.
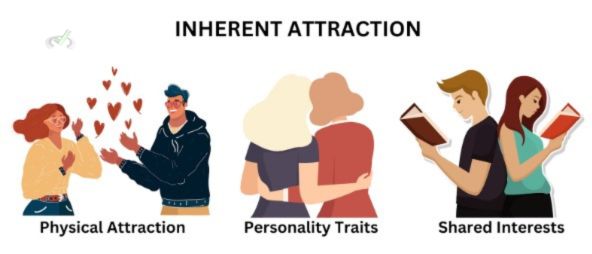
Physical Attraction
Physical attraction is when we are drawn to someone based on their looks. This is often the first thing we notice about someone because our brains are wired to respond to visual cues quickly.
For example, you might feel more comfortable around people with friendly smiles or expressive eyes. Evolutionary theories suggest that physical traits like symmetry and health indicators are found attractive because they signal good genes and fertility.
Personality Traits
We are also attracted to people with certain personality traits. Traits such as kindness, humor, and confidence can make someone more appealing to us.
For example, having a friend who is always there to make you laugh or help you out can build strong bonds. This attraction is because positive traits often make interactions more enjoyable and fulfilling.
Shared Interests
Sharing common hobbies or interests can also enhance attraction. When you enjoy similar activities, spending time together and building a connection is easier.
For instance, if you both love playing soccer or reading books, you have more to talk about and do together. Cultural differences can influence what interests are shared. This affects how attraction forms in different societies.
II. Understanding Aggression
Aggression is behavior aimed at causing harm or pain to others. It can be physical or verbal and arises from various situations and emotions.
Types of Aggression
- Physical Aggression: This involves harming others through physical force. For example, hitting or pushing someone.
- Verbal Aggression: This includes using words to hurt someone, such as name-calling or yelling.
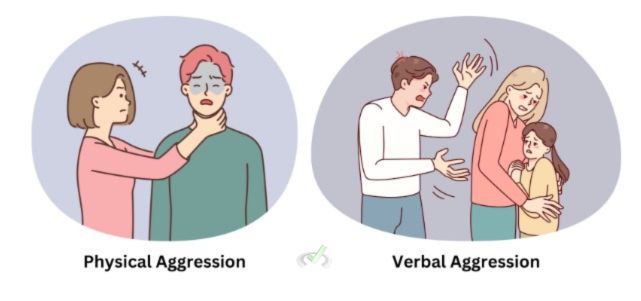
Causes of Aggression
Aggression can be caused by frustration, anger, or a need to dominate. For instance, if someone feels threatened, they might act aggressively to protect themselves.
The frustration-aggression hypothesis suggests that frustration or blocking a goal can lead to aggressive behavior. Society and the media can also influence aggressive behavior by normalizing violence.
Effects of Aggression
Aggressive behavior can lead to negative outcomes like damaged relationships, fear, and even legal consequences. For example, frequent arguments and physical fights can cause long-term damage to friendships or family bonds.
It is important to learn how to handle conflicts without resorting to aggression. Anger management techniques, such as deep breathing and talking about feelings, can help reduce aggressive responses.
III. Understanding Attachment
Attachment is the emotional bond we form with others, starting from infancy. This bond influences our relationships throughout life.
Types of Attachment
- Secure Attachment: This occurs when caregivers are responsive and supportive. Individuals with secure attachment feel confident and comfortable in relationships. For example, a child with secure attachment feels safe to explore their environment, knowing they can return to a caring caregiver.
- Insecure Attachment: This happens when caregivers are inconsistent or neglectful. It can lead to anxiety and difficulty in forming healthy relationships. Children with insecure attachment might be clingy or avoidant, fearing abandonment or rejection.
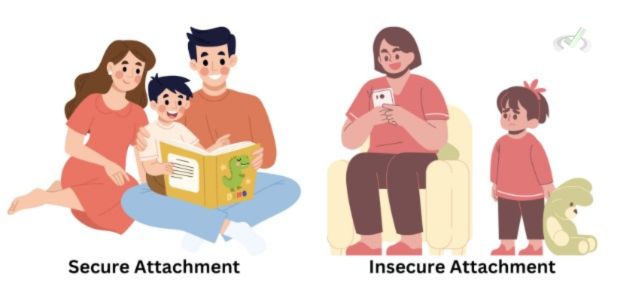
Importance of Attachment
Strong attachment bonds provide a sense of security and support. They help in emotional regulation and social development.
For example, securely attached children are often more confident and better at handling stress. Attachment theory, developed by John Bowlby and Mary Ainsworth, shows that early relationships with caregivers shape future relationships and emotional health.
IV. Understanding Social Support
Social support refers to the assistance we get from others. It can be emotional, instrumental (practical help), or informational.
Types of Social Support
- Emotional Support: This involves showing empathy, care, and concern. For example, a friend comforting you when you're sad.
- Instrumental Support: This includes practical help like lending money or helping with tasks. For instance, helping a neighbor with groceries.
- Informational Support: This means providing advice or information. For example, guiding a friend on how to solve a problem.
V. Benefits of Social Support
Strong social support can improve mental health, enhance coping skills, and increase feelings of belonging. Knowing you have friends and family to rely on can make stressful situations more manageable.
Social support can buffer against stress, meaning it helps protect you from the adverse effects of stress. It also important in health outcomes, like faster recovery from illness and reduced risk of mental health issues.
VI. Bridge/Overlap
Studying inherent attraction, aggression, attachment, and social support connects to other important areas in sociology and psychology.
Interpersonal Relationships
Understanding these concepts helps explain how we form and maintain relationships. For example, it's important to recognize secure attachment. This can guide better parenting practices and improve relationship counseling.
Conflict Resolution
Knowing about aggression and its causes can help develop strategies to resolve conflicts peacefully. For instance, teaching anger management can reduce aggressive behaviors. Hence, it is important in therapeutic settings.
Mental Health
Social support is important in mental well-being. Positive social interactions can reduce stress and improve overall health. This links to the study of psychological well-being and disorders.
Social Identity
Attachment and attraction influence how we see ourselves within social groups. Understanding these dynamics can help explain behaviors in different cultural contexts. For example, social support systems can vary widely across cultures, impacting how people seek and give help.
Biological Basis of Behavior
Neurobiological factors influence attraction and aggression. For example, hormones like oxytocin can enhance bonding and attachment. Meanwhile, imbalances in neurotransmitters like serotonin can increase aggression.
Developmental Psychology
Attachment theories highlight the impact of early relationships on later development. This theory is developed by John Bowlby and Mary Ainsworth. It is crucial for understanding human growth and development.
VII. Wrap Up/Key Terms
Let's summarize the key points:
- Inherent Attraction: The natural draw towards others based on looks, personality, or interests.
- Aggression: Behavior intended to harm others, either physically or verbally.
- Attachment: The emotional bond formed with others, influencing relationships throughout life.
- Social Support: Assistance from others, including emotional, instrumental, and informational support.
VIII. Practice
Test your understanding with these questions:
Sample Practice Question 1
What is a secure attachment?
A. Feeling anxious in relationships.
B. Having responsive and supportive caregivers.
C. Forming bonds only with friends.
Ans. B
Secure attachment occurs when caregivers are consistently responsive and supportive. This leads to confidence and comfort in relationships.
Sample Practice Question 2
Which is an example of instrumental support?
A. Offering advice.
B. Offering advice.
C. Showing empathy.
Ans. B
Instrumental support involves practical help, such as lending money or assisting with tasks.








 To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these
To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these 
