Have you ever wondered how magnets can move objects without touching them? Or how do magnets attract each other?
The answer lies in the principle that all magnetism depends on current, the flow of electric charge. Magnetic fields exert forces on moving charges, which in turn exert forces on other magnets with moving charges.
I. Introduction to Magnetic Forces on Moving Charges
Magnetic forces are among nature's most fundamental forces. They are as crucial as electrostatic (Coulomb) forces but more complex.
The magnetic force depends on several factors. This includes the magnitude and direction of the charge's movement and the magnetic field.
The magnetic force on a moving charge is given by:

This formula shows that the force depends on the charge's speed, the strength of the magnetic field, and the angle between the charge's movement and the field.
II. Properties of Magnetic Fields
Magnetic fields have unique properties that determine their behavior and effects. Understanding these properties helps us comprehend how magnetic forces act on moving charges.
Magnetic Field Strength
Magnetic field strength, or magnetic flux density, is measured in teslas (T). It indicates the force experienced by a moving charge or a magnetic material in the field. The magnetic field strength BB can be calculated using the equation:

Direction of Magnetic Fields
The direction of a magnetic field is the direction at which the north pole of a compass needle points when placed in the field. Magnetic fields flow from the north pole to the south pole of a magnet. For example, the Earth's magnetic field flows from the geographic south to the north pole.
Magnetic Field Lines
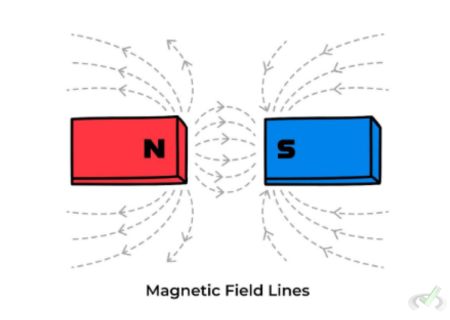
Magnetic field lines are visual representations that show the direction and strength of magnetic fields. They form closed loops, starting at the north pole and ending at the south pole of a magnet.
The closer the lines are, the stronger the magnetic field. These lines never intersect each other because that would imply two different directions for the magnetic field at the same point, which is impossible.
Uniform Magnetic Fields
In some situations, magnetic fields are uniform, meaning they have the same strength and direction everywhere. An example is the magnetic field between two parallel magnetic poles. The equation for a uniform magnetic field is:

III. Behavior of Magnetic Fields on Moving Charges
Magnetic fields interact with moving charges in specific ways, and several principles help explain these interactions.
Lorentz Force
The Lorentz Force describes the force experienced by a moving charge in a magnetic field. The formula is:

For example, if a charge of 1 coulomb moves at 2 meters per second through a magnetic field of 3 teslas at an angle of 90 degrees, the force is:

Right-Hand Rule
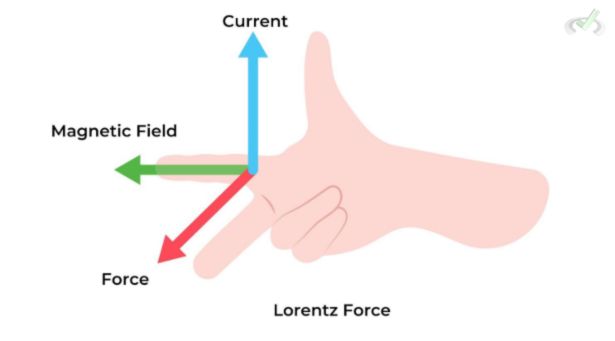
The Right-Hand Rule helps determine the direction of the force on a moving charge in a magnetic field. Point your thumb in the direction of the velocity of the positive charge. Then, your fingers pointed toward the magnetic field and your palm in the direction of the force.
Magnetic Flux
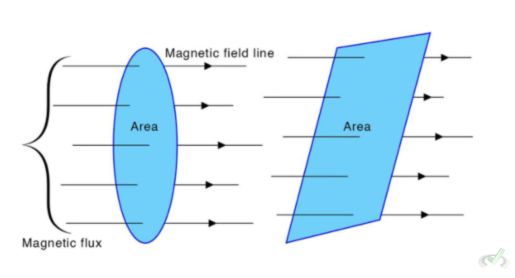
Magnetic flux (Φ) is the total magnetic field passing through a given area. It helps determine the strength of the interaction between a magnetic field and a moving charge. The formula for magnetic flux is:

IV. Applications of Magnetic Forces on Moving Charges
Magnetic forces have various applications in various fields, from technology to medicine.
Electric Motors
Electric motors transform electrical into mechanical energy using magnetic forces. They work by passing a current through a coil in a magnetic field, creating a force that spins the coil. This spinning motion powers many devices, from household appliances to industrial machinery.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
MRI machines utilize magnetic fields and radio waves. They create detailed images of the inside of the body.
The strong magnetic fields align the hydrogen atoms in the body, and radio waves disrupt this alignment. When the atoms realign, they emit signals that create images of tissues and organs.
Particle Accelerators
Particle accelerators use magnetic fields to propel charged particles to high speeds and direct them to collide with targets. These collisions help scientists study the fundamental particles and forces in the universe.
The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) is one of the most famous particle accelerators. Its magnetic fields are used to control the direction and speed of particles with high precision.
V. Connecting Magnetic Forces to Broader Scientific Concepts
Magnetic forces are fundamental in various scientific fields, influencing phenomena from light behavior to the Earth's magnetosphere dynamics.
Magnetic Forces and Electromagnetic Waves
Magnetic forces are closely related to electromagnetic waves, such as light. Electromagnetic waves are generated by moving electric charges. It creates changing electric and magnetic fields propagating through space.
Understanding magnetic forces helps explain how these waves interact with matter. It enables technologies like wireless communication.
Magnetic Forces and Earth’s Magnetosphere
The Earth's magnetosphere is a region where the Earth's magnetic field dominates the behavior of charged particles. This magnetic shield protects us from harmful solar wind particles. Understanding magnetic forces helps scientists study space weather and its effects on satellites and power grids.
Electromagnetic Induction
Electromagnetic induction generates an electric current by changing the magnetic field. This principle is used in transformers and generators to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Faraday's Law of Induction describes this phenomenon. It states that the induced voltage in a coil is proportional to the rate of change of the magnetic flux.

Understanding electromagnetic induction helps explain how electric generators produce electricity. It also details how transformers change the voltage of electric power in transmission lines.
VI. Wrap-Up and Key Terms
Understanding magnetic forces on moving charges involves grasping several key concepts and principles. Let's review.
Key Terms
- Magnetic Field Strength: Measure the force experienced by a charge in the field.
- Direction of Magnetic Fields: Direction a compass needle points.
- Magnetic Field Lines: Visual representation showing field strength and direction.
- Lorentz Force: Describes the force on a moving charge in a magnetic field.
- Right-Hand Rule: Method to determine the direction of the magnetic force.
- Magnetic Flux: Total magnetic field passing through a given area.
- Faraday's Law: Describes how a change in magnetic flux can induce an electric current.
VII. Practice Questions
Sample Practice Question 1
What measures the force on a charge in a magnetic field?
A. Magnetic Flux
B. Magnetic Field Strength
C. Lorentz Force
D. Right-Hand Rule
Ans. C
Lorentz Force measures the force on a moving charge in a magnetic field.
Sample Practice Question 2
Which rule helps determine the direction of the force on a moving charge in a magnetic field?
A. Coulomb's Law
B. Magnetic Flux
C. Right-Hand Rule
D. Faraday's Law
Ans. C
The Right-Hand Rule helps determine the direction of the magnetic force on a moving charge.







 To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these
To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these 
