I. What is the Pentose Phosphate Pathway?
We hate to make this analogy, but when compared to the other various pathways we’ve covered involving carbohydrate metabolism, the pentose phosphate pathway is like that forgotten middle child: still there, but sometimes get’s glanced over.
While it may be looked over as it’s one of the pathways that doesn’t begin with a “-gly” or “-glu” prefix, it’s still without a doubt an important metabolic pathway to be briefly familiar with come test day, the key word being “briefly”, meaning to focus on the high yield topics!
We believe that the best way to approach this topic is to focus and highlight the outcomes and importance of the pentose phosphate pathways as opposed to the specific enzymes, as this is most likely how the MCAT will test you on this topic!
II. Pentose Phosphate Pathway
Let’s run it back and start with a quick overview of the PPP! We want to preface that not all of the enzymes are included because we want to focus on the most important enzymes!
A. Pentose Phosphate Pathway Overview
The pentose phosphate pathway allows for the oxidation of glucose-6-phosphate to products such as ribulose-5-phosphate and NADPH which can then be used to generate other molecules including nucleotides, fatty acids, and glutathione.
In the first step, an incoming glucose-6-phosphate is oxidized to 6-phosphogluconolactone via glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, the rate limiting enzyme of the reaction, while also reducing NADP+ to NADPH.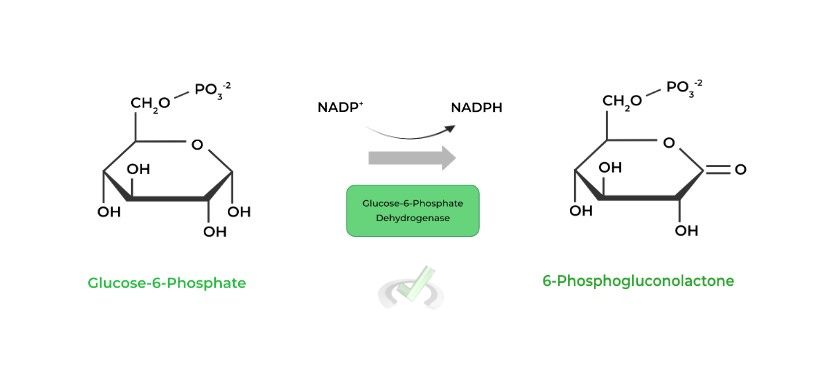
6-phosphogluconolactone is then converted to 6-phosphogluconate via the lactonase enzyme. 6-phosphogluconate is then finally oxidized to ribulose-5-phosphate, via 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase while also reducing NADP+ to NADPH.
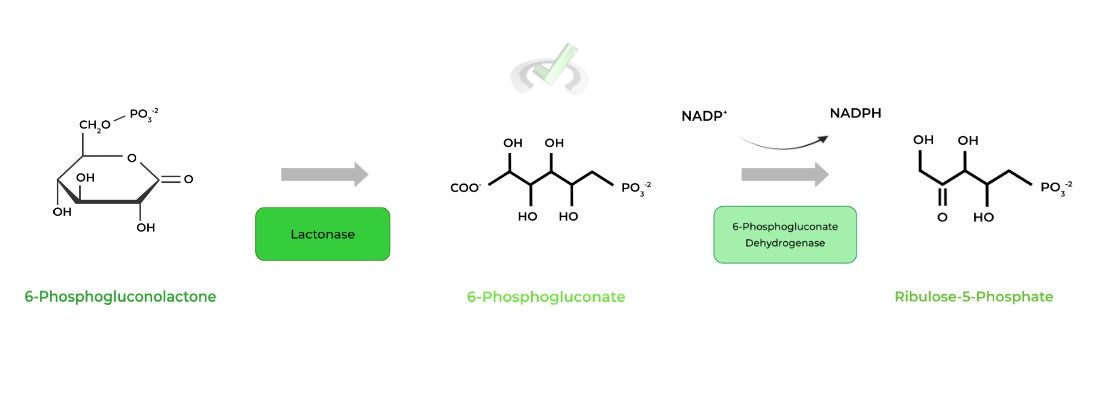
The end result of this pathway allows for the generation of 2 NADPH molecules and a ribulose-5-phosphate which are important molecules needed in various other reactions as well touch on in a bit.
For us, we really believe it’s best just to memorize the dehydrogenase enzymes (glucose-6-phosphate and 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase) for this pathway as these are the most high yield enzymes to know!!
B. Important Products of the Pentose Phosphate Pathway
As mentioned above, we believe that the most important takeaways from the pentose phosphate pathway are the molecules produced and how they’re important for other physiological processes!
While it is important to memorize the substrates and enzymes involved in the pathway (especially the dehydrogenase enzymes!), make this more of a priority when reviewing for your MCAT prep!
I. NADPH
Don’t confuse this with NADH, this has an extra phosphate group! The main importance of NADPH post-pentose phosphate pathway is their requirement in fatty acid synthesis and the formation of glutathione!
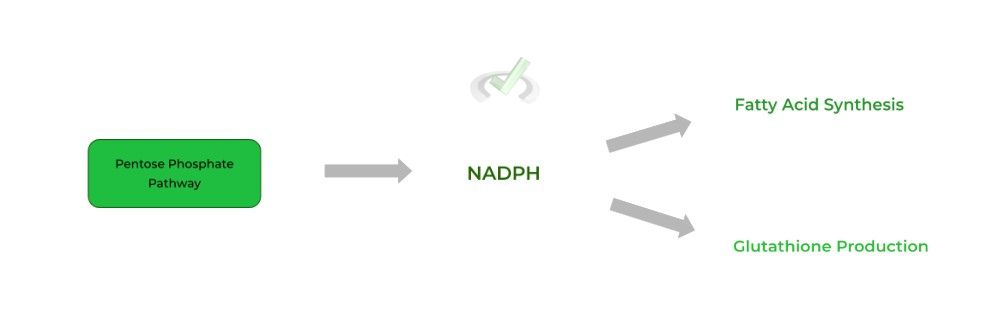
While fatty acids are self-explanatory, glutathione may require a more in depth explanation: one of the main roles of glutathione in the body is to act as an antioxidant to protect against harmful oxidative stress!
II. Ribulose-5-Phosphate
As the main product of the pentose phosphate pathway, this molecule can be isomerized to ribose-5-phosphate via ribose-5-phosphate isomerase.
From here, ribose-5-phosphate can be used as a starting point to synthesize nucleotides needed for replication, transcription, etc!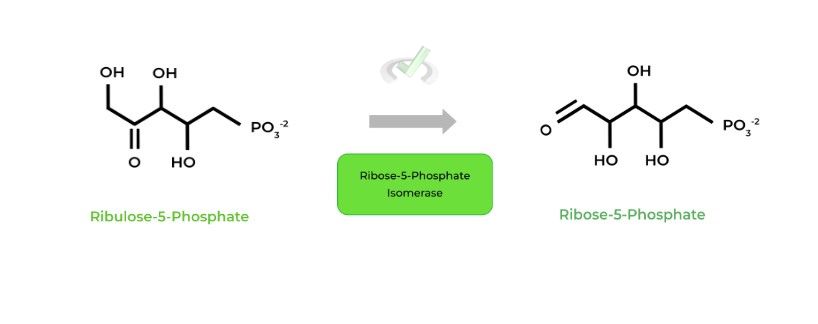
III. Bridge/Overlap
As mentioned above, NADPH is an important molecule needed for the production of glutathione, an important molecule that combats oxidative stress. What is oxidative stress anyway and why is it so harmful to the human body? Let’s quickly learn some of the basics regarding oxidative stress!
I. Oxidative Stress
The accumulation of various reactive oxygen species (ROS) eventually leads to oxidative stress. Some of these reactive oxygen species you may be familiar with include hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), hydroxyl radicals (OHᐧ), and superoxide radicals (O2-ᐧ).
Some major physiological consequences of oxidative stress on cells include DNA damage, disruption of cell membrane integrity, and apoptosis, which can contribute to various diseases including cancer, atherosclerosis, COPD, etc.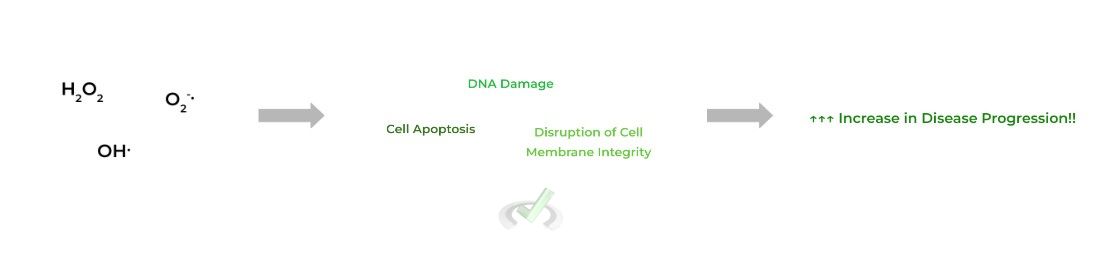
III. Wrap Up/Key Terms
Let’s take this time to wrap up & concisely summarize what we covered above in the article!
A. Pentose Phosphate Pathway Overview
This pathway allows for the oxidation of glucose-6-phosphate to ribulose-5-phosphate and NADPH which are important molecules needed for processes including nucleotide synthesis, fatty acids, and glutathione.
An incoming glucose-6-phosphate is first oxidized to 6-phosphogluconolactone while also reducing NADP+ to NADPH, via glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase.
6-phosphogluconolactone is then converted to 6-phosphogluconate via lactonase. 6-phosphogluconate is finally oxidized to ribulose-5-phosphate, while also reducing another NADP+ to NADPH via 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase.B. Important Products of the Pentose Phosphate Pathway
As mentioned above, the most important takeaway from the pentose phosphate pathway are not the enzymes (though they are important!), but the products as they serve as required molecules for various other reactions!
I. NADPH
Make sure not to confuse this for NADH! This molecule is an important requirement for processes such as fatty acid synthesis and glutathione generation!
Glutathione is an important antioxidant which aids in protecting the body from oxidative stress, which results from the accumulation of reactive oxygen species.
II. Ribulose-5-Phosphate
This precursor molecule can be isomerized to ribose-5-phosphate via ribose-5-phosphate isomerase. From here, ribose 5-phosphate can be utilized as a precursor to synthesize various other nucleotides!
V. Practice
Take a look at these practice questions to see and solidify your understanding!
Sample Practice Question 1:
A mutation results in the deficiency of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase for an individual. Which of the following processes would be affected?
I. ATP Synthesis
II. DNA Replication
III. Protection Against Reactive OxygenS Species
A. I only
B. III only
C. I and III
D. I, II, and III
Ans. D
This question is a little tricky, as it requires you to put together various amounts of information and content. Recall that NADPH is required for the generation of glutathione, which is important for protecting against reactive oxygen species as it’s an antioxidant.
Ribulose-5-phosphate can be isomerized to ribose-5-phosphate, which can then be utilized for nucleotide synthesis. However, while we think of nucleotides as dealing with DNA replication, they also involve nucleotide triphosphates such as ATP!
Sample Practice Question2:
Presumably, at which stage of the cell cycle should the pentose phosphate pathway be highly promoted and activated?
A. G1
B. S
C. G2
D. M
Ans. B
Recall that the S phase of the cell cycle results in DNA replication (hence the term “S” for DNA synthesis). As such, it should be expected that the PPP should be highly active during this phase as one of the possible outcomes following the pathway is nucleotide synthesis!
This is because of the generation of ribulose-5-phosphate and eventually ribose-5-phosphate, which can then be a precursor for nucleotide synthesis.







 To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these
To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these 
