When people think of some of the important dietary molecules and minerals that are for the body, minerals such as sodium, calcium, and potassium come to mind. However, one that may not come up but is of equal importance is phosphorus!
As we’ll see in the upcoming sections, phosphorus is an important dietary mineral as it’s found in many forms throughout the body performing different, but important functions. From being a source of energy to bone growth, this is without a doubt an important dietary nutrient!
This chapter overview should get you comfortable with the common phosphorus containing compounds as well as their basic characteristics. Let’s get started!
Phosphorus Containing Compounds on the MCAT: What You Need to Know
Topics on organic chemistry will be tested on the Chem/Phys and the Bio/Biochem section of the MCAT and can appear both as passage based and fundamental discrete questions.
Luckily, this is one of the topics that isn’t highly emphasized and tested upon! Similar to other topics, this concept is really more about application, meaning that you’ll use the content learned from this section to help you with understanding of other topics and problems!
Introductory organic chemistry accounts for 15% of the content covered in the Chemical and Physical Foundations of Biological Systems and 5% of the content covered in the Biological and Biochemical Foundations of Living Systems.
Important Sub-Topics: Phosphorus Containing Compounds
As mentioned above, the content covered in this section is more about application toward understanding other topics! As such, don’t worry too much about memorizing but more so about how you can use what you learn to help you approach other topics and problems!
1. Organic and Inorganic Phosphates
Before getting into the difference between organic and inorganic phosphates, let's first give a brief definition! A phosphate is basically a functional group characterized by a central phosphorus atom bonded to 4 oxygen atoms – 1 bond is a double bond, while the remaining 3 are single bonds.
Though we usually describe phosphate as an ion, we can also think of it as being a derivative of phosphoric acid! Depending on the pH range, the hydrogen can be deprotonated, which gives us the anionic form.
When differentiating between an organic and inorganic phosphate, look to whether the phosphate group is attached to a carbon backbone! Some examples of organic phosphates are nucleotides such as the ever so common energy source, ATP!
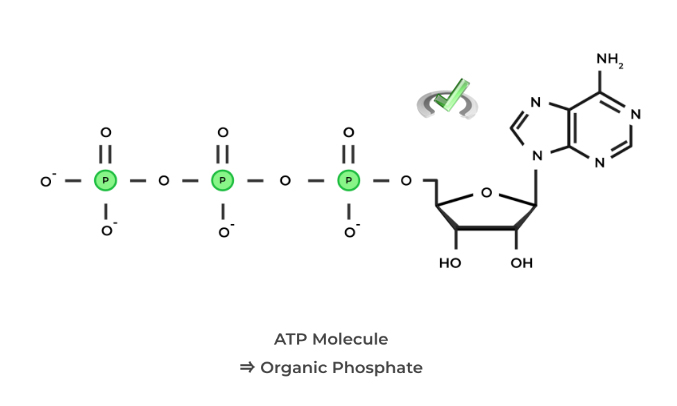
Inorganic phosphates are phosphates not bound to a carbon backbone and are usually free in solution. We can actually now make a distinction between kinases and phosphorylases based on the definitions of organic and inorganic phosphates.
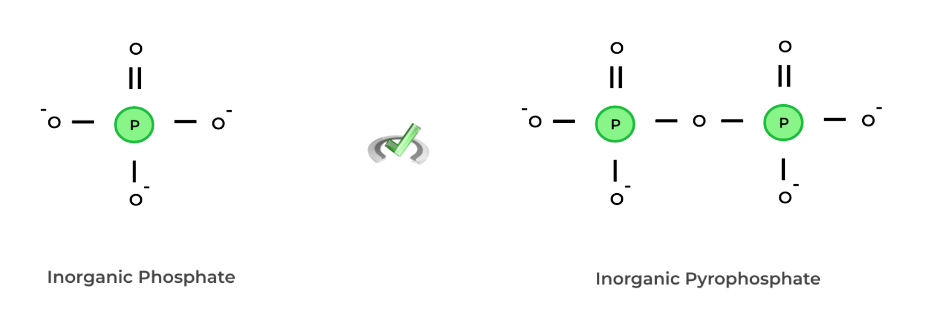
Kinases are enzymes that allow for phosphorylation by the transfer of an organic phosphate group from an organic molecule (such as ATP, GTP) to another molecule. Phosphorylases allow for phosphorylation via the addition of a free, inorganic phosphate from the solution.
Full Study Notes : Organic and inorganic phosphates
For more in-depth content review on organic and inorganic phosphates as well as their differences, check out these detailed lesson notes created by top MCAT scorers.
2. Properties of Phosphorus Containing Compounds
There are 2 main characteristics that are important to note when talking about phosphorus containing compounds: 1) their negative charge and 2) high energy bonds (only if multiple phosphate groups are bound together).
Phosphate groups by themselves have a negative charge and can apply that negative charge when attached to other molecules! A great example of this is in the phosphate backbone of DNA!
Because the backbone of DNA is composed of phosphate groups connected by phosphodiester bonds, the backbone is negatively charged. As such, most amino acids in the DNA binding domain of transcription factors are positively charged!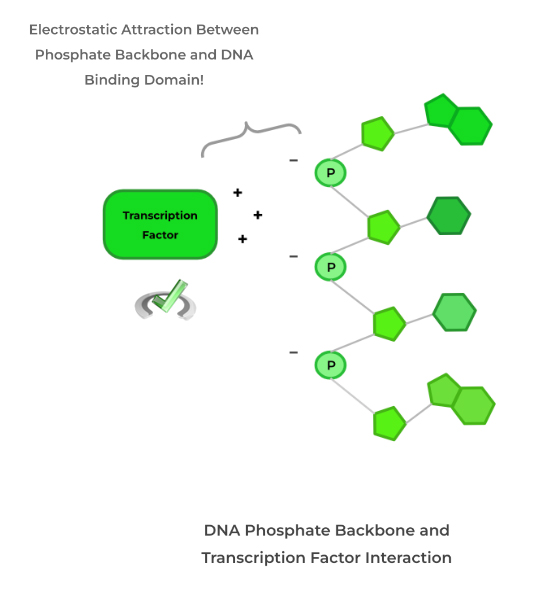
In addition, if there are multiple phosphate groups bonded together, such as in ATP and GTP, high energy bonds are generated, which when broken, release a lot of energy! This is seen in ATP hydrolysis as the hydrolyzing of one phosphate group to ADP is highly exergonic, releasing about 34 kj of energy per mole.
ADP is a lot more stable and energetically favorable than ATP because you reduce the electrostatic repulsion that occurs between the adjacent phosphate groups, just like how 2 same pole magnets want to repel each other!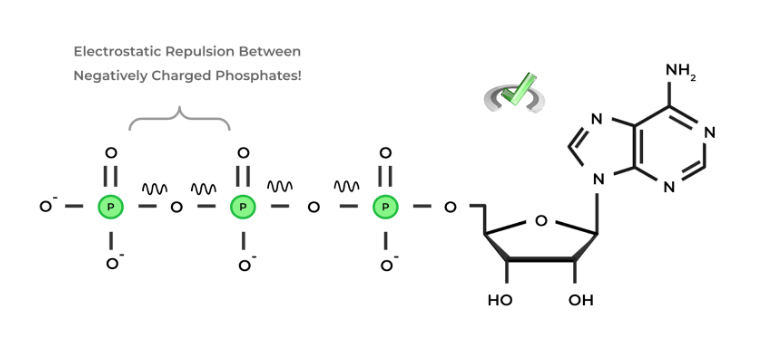
As you’ll see in our bioenergetics articles, we can actually use the energy released by this reaction to power other endergonic reactions so that when summed together, the overall reaction is exergonic!
Full Study Notes : Properties and characteristics of phosphorus containing compounds
For more in-depth content review on properties and characteristics of phosphorus containing compounds, check out these detailed lesson notes created by top MCAT scorers.
Important Definitions and Key Terms
Below are some high yield definitions and key terms to refer to when reviewing concepts and ideas about phosphorus containing compounds in organic chemistry!
Term | Definition |
|---|---|
Phosphate | A functional group containing a central phosphorus atom bonded to 4 oxygens – 3 single bonds and 1 double bond |
Phosphoric Acid | Fully protonated form of phosphate |
Organic Phosphate | A phosphate which is connected to a carbon backbone molecule; Some examples include nucleotides such as ATP and GTP |
Inorganic Phosphate | A phosphate which is not bound to a carbon backbone molecule and usually exists free in solution |
Additional FAQs - Phosphorus Containing Compounds on the MCAT
What Compounds Contain Phosphorus?
How Many Phosphorus Compounds Are There? – MCAT
In addition, inorganic phosphate is an important component of hydroxyapatite which makes up a significant portion of the bone matrix.
Where Are Phosphate Compounds Found? – MCAT
In addition, as mentioned above, phosphate is also found in the bone as it contributes to the hydroxyapatite bone matrix!
What Organic Molecule is Phosphorus Usually Found In? – MCAT
What Molecule is an Organic Phosphate? – MCAT
What Does Phosphoric Acid Do? – MCAT
Additional Reading -- Organic Chemistry Topics:
- Aldehydes and Ketones on the MCAT
- Bonding on the MCAT
- Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives on the MCAT
- Isomers on the MCAT
- Laboratory Techniques and Separations on the MCAT
- Nitrogen Containing Compounds on the MCAT
- Alcohols and Ethers on the MCAT
- Organic Chemistry Nomenclature on the MCAT
- Nucleophiles and Electrophiles on the MCAT
- Spectroscopy on the MCAT
- Redox Reactions Organic Chemistry on the MCAT







 To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these
To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these 










 reviews on TrustPilot
reviews on TrustPilot