You walk into a room full of people. Everyone is quietly listening to a speaker at the front. Naturally, you also become quiet and attentive.
This behavior isn't random; it's a result of socialization. Socialization shapes how we act and interact within society by teaching us what is considered "normal" behavior.
I. What is Normative Behavior?
Normative behavior refers to typical or expected actions within a particular group or society. These behaviors are learned through socialization.
Socialization is the process of learning a society's norms, values, and behaviors. Norms are the rules and expectations by which a society guides its members' behavior. Values are deeply held beliefs about what is good, right, and appropriate.

Examples of Normative Behavior
- Greeting Others: In many cultures, it's normal to say "hello" or shake hands when meeting someone. In some cultures, bowing is a standard greeting instead of shaking hands.
- Waiting in Line: In most places, people wait their turn rather than pushing ahead.
- Using Manners: Saying "please" and "thank you" is expected and shows politeness.
II. The Role of Socialization in Establishing Normative Behavior
Socialization is how we learn the norms and rules of our society. It begins in childhood and continues throughout our lives. There are several critical agents of socialization:
Family
Family is the first and most important agent of socialization. Parents teach children basic norms and values, like sharing and respecting others.
Schools
Schools play a crucial role in socialization by teaching children discipline, cooperation, and the importance of education. Teachers and peers influence how children behave and interact. Schools also have a hidden curriculum. This hidden curriculum includes the unspoken norms, values, and beliefs conveyed in the classroom, like punctuality and respect for authority.
Peer Groups
Peer groups, or friends, are significant in shaping behavior, especially during adolescence. Peers can reinforce positive behaviors, like studying hard, or negative ones, like skipping school.
Media
TV, the internet, and social media provide information about societal norms and behaviors. It can influence how we dress, speak, and act.
Workplaces
Employees learn professional norms and behaviors in the workplace, such as punctuality and teamwork, which are necessary for career success. Workplace culture also plays a role in shaping behavior and expectations.

III. How Normative Behavior is Enforced
Normative behavior is maintained through various mechanisms that encourage conformity and discourage deviance.
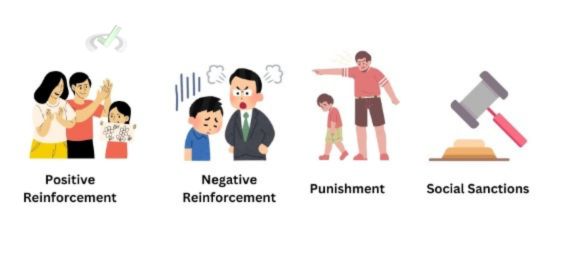
Positive Reinforcement
Positive reinforcement involves rewarding behavior that conforms to societal norms. For example, praising a child for saying "thank you" encourages them to continue using good manners.
Negative Reinforcement
Negative reinforcement involves removing an unpleasant consequence when the desired behavior occurs. For example, a teacher might stop scolding students once they finish their homework on time.
Punishment
Punishment discourages unwanted behavior by applying negative consequences. For example, a child might be given a time-out for hitting a sibling, teaching them that such behavior is unacceptable.
Social Sanctions
Social sanctions are reactions from others that encourage conformity. These can be formal, like a fine for breaking the law, or informal, like disapproving looks from peers.
IV. Bridge/Overlap: The Importance of Normative Behavior in Society
Normative behavior is crucial for the smooth functioning of society. It helps maintain order and predictability, allowing people to interact harmoniously.
Building Social Cohesion
Normative behavior builds social cohesion by creating a sense of belonging and shared understanding. When people follow societal norms, they feel connected to their community.
Facilitating Communication
Common behaviors and norms make communication easier. For example, knowing how to greet someone properly helps avoid misunderstandings and fosters positive relationships.
Enhancing Cooperation
When people follow norms, it promotes cooperation and trust. For instance, driving on the correct side of the road prevents accidents and ensures smooth traffic flow.
Reducing Conflict
Adhering to norms reduces conflict by setting clear expectations for behavior. For example, waiting in line prevents arguments about who gets served first.
Connections to Other MCAT Topics
Normative behavior links to other important areas of psychology and social sciences, such as:
- Mental Health: Understanding social norms can help mental health professionals provide better care by considering how cultural norms influence behavior and attitudes.
- Cognitive Development: Socialization impacts cognitive development by teaching problem-solving skills and moral reasoning.
- Behavioral Skills: Learning norms and values enhances interpersonal skills crucial for personal and professional success.
V. Wrap Up/Key Terms
Let’s summarize what we've covered about normative behavior and socialization:
Key Terms
- Normative Behavior: Actions that are considered typical or expected within a society.
- Socialization: The process of learning a society's norms, values, and behaviors.
- Agents of Socialization: Key influencers in learning norms, such as family, schools, peer groups, media, and workplaces.
- Positive Reinforcement: Encouraging desired behavior through rewards.
- Negative Reinforcement: Encouraging desired behavior by removing negative consequences.
- Punishment: Discouraging unwanted behavior through negative consequences.
- Social Sanctions: Reactions from others that encourage conformity to norms.
VI. Practice
Sample Practice Question 1
Which of the following is NOT an agent of socialization?
A. Family
B. Schools
C. Peer Groups
D. Gravity
Ans. D
Gravity is a natural force and not an agent of socialization, which involves people and institutions that influence behavior.
Sample Practice Question 2
What is an example of positive reinforcement?
A. Scolding a child for running inside the house
B. Praising a student for completing their homework
C. Ignoring bad behavior
D. Giving a time-out for hitting
Ans. B
Positive reinforcement involves rewarding good behavior, which encourages it to continue. Praising a student for homework completion is a reward that reinforces the behavior.







 To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these
To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these 
