Socialization is how individuals learn and adopt their culture's values, norms, and behaviors. Understanding how we develop our sense of self and function in society is crucial. Let's explore the main theories of socialization to understand this process better.
I. Understanding Socialization
Socialization involves learning from various sources, including family, peers, schools, and media. It's how we develop our personalities and understand our roles in society.
Family

Family is often the first agent of socialization. Parents and siblings teach us basic norms and values, like manners and language. For example, parents might teach children to say "please" and "thank you.
Family structures, such as single-parent or extended families, can influence socialization. Parenting styles, authoritative, authoritarian, or permissive, also shape children's behavior and attitudes.
Peers

Peers become significant during adolescence. Friends influence our behavior and help us learn social skills. For instance, peer groups can shape interests in music, fashion, and hobbies.
Peer pressure can have a strong impact, encouraging behaviors to fit in with the group, which can be positive or negative. Understanding how to navigate peer influence is a crucial part of social development.
Schools

Schools play a crucial role in socialization by teaching academic knowledge and social norms. For example, schools teach the importance of punctuality and following rules.
The hidden curriculum includes the unspoken values and behaviors taught in school. This includes teamwork and competition, which also significantly influences students' socialization. These lessons prepare students for their future roles in the workplace and society.
Media

Media, including TV, internet, and social networks, provide a wide range of information and cultural norms. For example, media can influence our views on gender roles and lifestyle choices.
Media literacy, or critically analyzing media messages, is essential in understanding and resisting negative influences. Media shapes our perceptions of reality. It can also reinforce stereotypes or promote positive social change.
II. Theories of Socialization
Several critical theories explain how socialization occurs. Let's delve into some of the main ones:
1. The Looking-Glass Self (Charles Horton Cooley)

This theory suggests that our self-image is shaped by how we think others see us.
Key Points:
- We imagine how we appear to others.
- We imagine their judgment of us.
- We develop our self-concept based on these judgments.
For example, if people treat us as intelligent and capable, we start seeing ourselves that way. However, if we perceive negative judgments, it can lead to low self-esteem and self-worth. This process is continuous and influences our interactions and self-perception throughout life.
2. Role-Taking (George Herbert Mead)

Mead's theory focuses on the development of the self through social interaction. He introduced the concept of "role-taking."
Key Points:
- Children learn to take the perspective of others through play and games.
- They move from simple imitation to understanding complex social roles.
- The self has two parts: the "I" (spontaneous and autonomous) and the "Me" (socialized aspect).
For example, children playing "house" practice understanding the roles of parents and children. Role-taking develops in stages, starting with simple imitation in early childhood.
It progresses to understanding multiple roles and perspectives in adolescence, which helps children develop empathy and social skills.
3. Psychoanalytic Theory (Sigmund Freud)
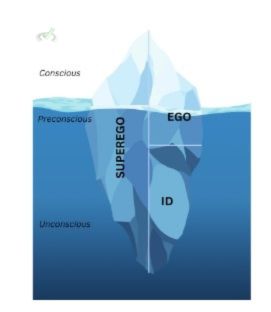
Freud's theory emphasizes the influence of early childhood experiences and unconscious motives on socialization.
Key Points:
- The personality is divided into three parts: the id (instinctual drives), the ego (rational part), and the superego (moral standards).
- Socialization helps balance these parts.
- Early family interactions are crucial for developing a healthy personality.
For example, how parents manage a child's aggressive impulses can shape their social behavior. If a child's needs are consistently unmet, it can lead to fixation and impact their personality development. Freud's theory highlights early experiences' importance and lasting impact on behavior and relationships.
4. Social Learning Theory (Albert Bandura)

Bandura's theory highlights the role of observation and imitation in learning.
Key Points:
- People learn by watching others and imitating their behavior.
- Reinforcement and punishment influence whether behaviors are repeated.
- This theory introduces the concept of "self-efficacy," or belief in one's ability to succeed.
For example, children might learn to share by watching their parents do it and receiving praise for doing the same. Vicarious reinforcement, where individuals learn by observing the consequences of others' actions, is also crucial. For instance, rewarding a peer for good behavior can encourage others to imitate that behavior.
5. Cognitive Development Theory (Jean Piaget)

Piaget's theory explains how children's thinking develops in stages and affects their understanding of the social world.
Key Points:
- Children go through four stages: sensorimotor, preoperational, concrete operational, and formal operational.
- Each stage represents a different level of cognitive ability.
- Socialization is linked to cognitive development as children learn to understand and navigate social norms.
For example, during the concrete operational stage, children learn to see things from others' perspectives, which aids in socialization. This development allows children to understand rules and cooperate with others.
It lays the foundation for complex social interactions. Piaget's theory underscores the link between cognitive growth and social learning.
III. Bridge/Overlap
The study of socialization theories connects to various important areas in sociology and psychology. These are also crucial for MCAT preparation.
Interpersonal Relationships
Understanding socialization helps explain how we form and maintain relationships. For example, social learning theory can explain how relationship behaviors are modeled and imitated.
Developmental Psychology
Theories like Piaget's Cognitive Development Theory highlight the stages of development and their impact on social learning. This is crucial for understanding human growth and development.
Mental Health
Early socialization experiences, as described by Freud's Psychoanalytic Theory, can significantly impact mental health. Understanding these influences can help in developing therapeutic approaches.
Cultural Norms
Socialization is key to understanding how cultural norms and values are passed down. For instance, role-taking theory shows how children learn to adopt societal roles through interaction.
Behavioral Sciences
Social learning theory and reinforcement are foundational in behavioral sciences. They help explain how behaviors are acquired and maintained.
Clinical Settings
Understanding these theories is vital for developing treatment plans and interventions in clinical settings. For example, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) incorporates principles from social learning theory. This help patients change negative behaviors and thoughts.
Biological Basis of Behavior
Neurobiological factors influence socialization. For example, hormones like oxytocin play a role in bonding and attachment. Meanwhile, neurotransmitters like dopamine and serotonin are involved in reward and mood regulation and affect social behaviors.
IV. Wrap Up/Key Terms
Let's summarize the key points:
- Socialization: The process through which individuals learn and adopt their culture's values, norms, and behaviors.
- Looking-Glass Self: The theory that our self-image is shaped by how we think others see us.
- Role-Taking: Mead's concept involves learning to understand and adopt the roles of others.
- Psychoanalytic Theory: Freud's theory emphasizes early childhood experiences and unconscious motives.
- Social Learning Theory: Bandura's theory highlights observation and imitation in learning.
- Cognitive Development Theory: Piaget's theory explains the stages of cognitive development and their impact on social learning.
V. Practice
Test your understanding with these questions:
Sample Practice Question 1
What is the main idea of the looking-glass self-theory?
A. We learn through imitation.
B. Our self-image is shaped by how we think others see us.
C. Socialization happens in stages.
Ans. B
The looking-glass self-theory suggests that we develop our self-concept based on our perception of others' judgments.
Sample Practice Question 2
Which theory emphasizes the role of observation and imitation in learning?
A. Psychoanalytic Theory
B. Social Learning Theory
C. Cognitive Development Theory
Ans. B
Social Learning Theory highlights the importance of observing others and imitating their behavior to learn.







 To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these
To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these 









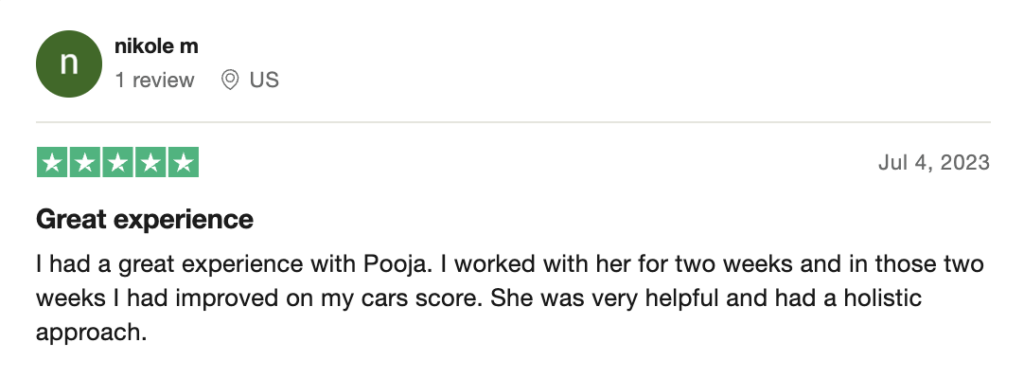
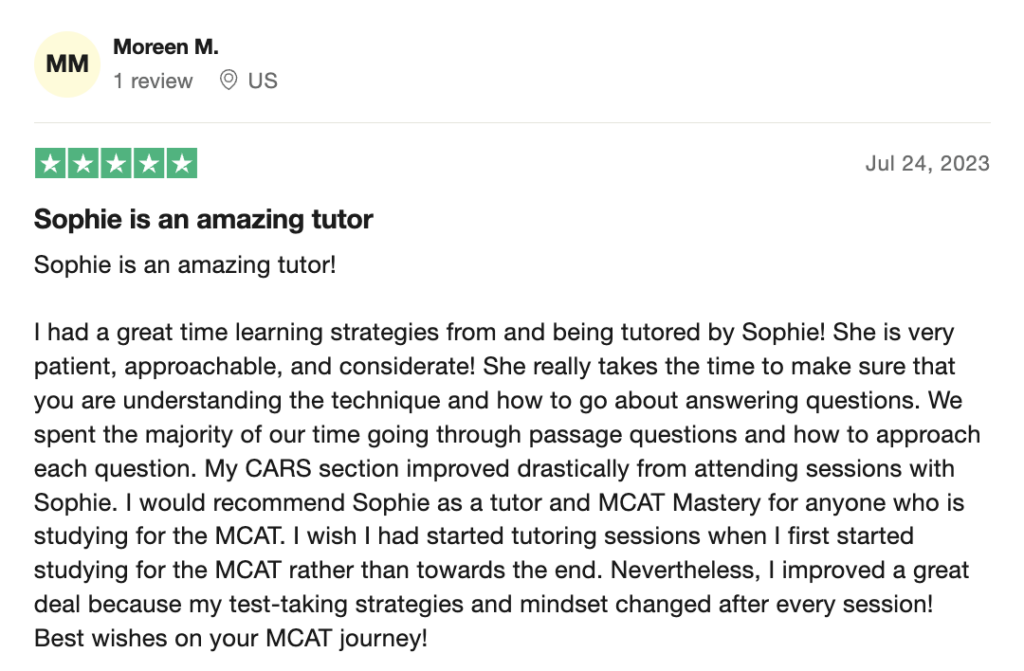

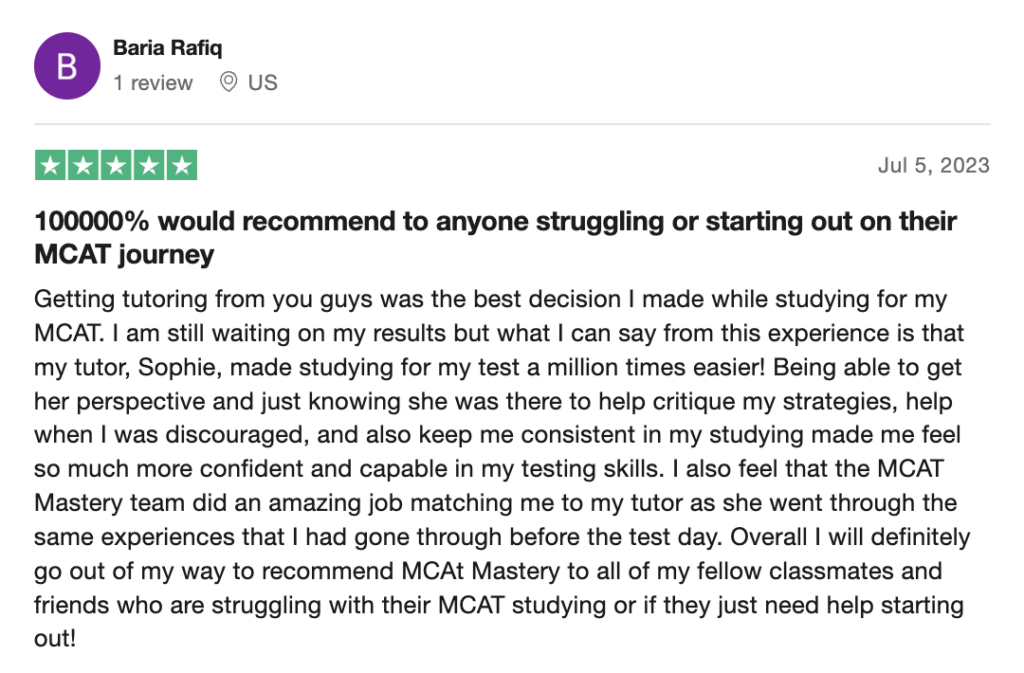
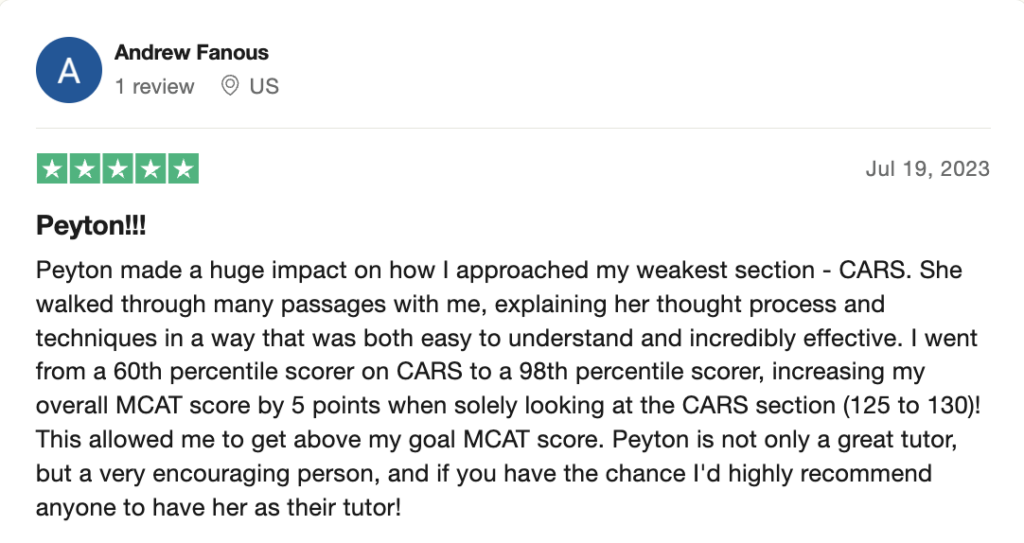
 reviews on TrustPilot
reviews on TrustPilot