At the beach, you watch waves roll in from the ocean. Some waves are larger, and others are faster. This observation introduces you to the fascinating world of waves in physics.
Waves are not limited to water; they are present in sound, light, and space. Understanding the characteristics of waves helps us grasp many natural phenomena and technological applications.
I. Introduction to Waves
Waves are disturbances that transport energy from one place to another without moving matter. They can travel through different mediums, such as air, water, or space. The study of waves includes understanding their properties and behaviors.
Types of Waves
Waves come in different forms, primarily mechanical and electromagnetic. Each type has distinct characteristics and propagation requirements.
1. Mechanical Waves: These waves needs a medium to travel through, like sound waves moving through air or water waves in the ocean.
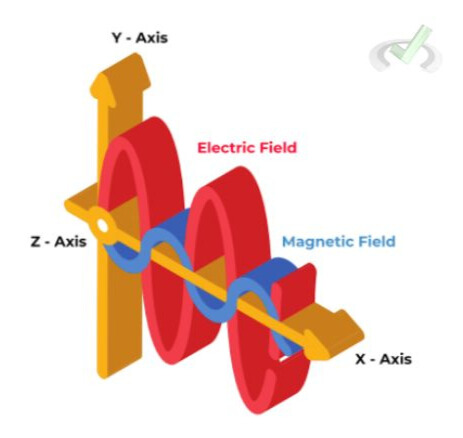
2. Electromagnetic Waves: These waves, like light and radio waves, do not need a medium and can travel through a vacuum.
II. Key Properties of Waves
Understanding the key properties of waves, such as wavelength, frequency, amplitude, speed, and phase, is essential in physics. Each property helps us describe how waves behave and interact with their environment.
Wavelength and Frequency
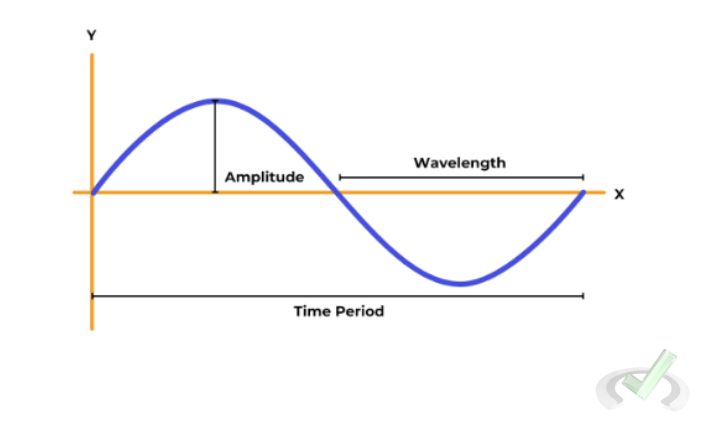
- Wavelength: The distance between a wave's consecutive peaks (or troughs). It is usually measured in meters (m).
- Frequency: The number of waves that pass a given point in one second. It is measured in Hertz (Hz).
For example, if you are watching ocean waves, the wavelength is the distance between the peaks of two waves. The frequency is how many waves pass by you in one second. These two properties are related. As the wavelength increases, the frequency decreases also, and vice versa.
Amplitude
Amplitude is the height of the wave from its midpoint to its peak. This property is directly related to the energy or intensity of the wave.
Higher amplitude means more energy. For instance, louder sounds have higher amplitudes. In simpler terms, the amplitude is like the height of a wave. The taller the wave, the more energy it has.
Speed
The speed of a wave is a critical property that determines how quickly a wave travels through a medium. Different waves travel at different speeds depending on the medium.
Moreover, the speed at which the wave travels through a medium. For example, sound travels faster in water than in air. The medium and the type of wave determine the speed of a wave. The formula for wave speed is:
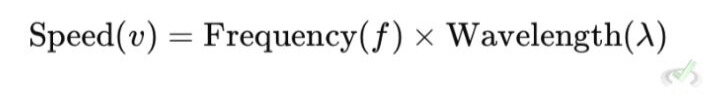
Phase
Phase describes the position of a point in time on a wave cycle. Understanding how waves interact with each other is crucial.
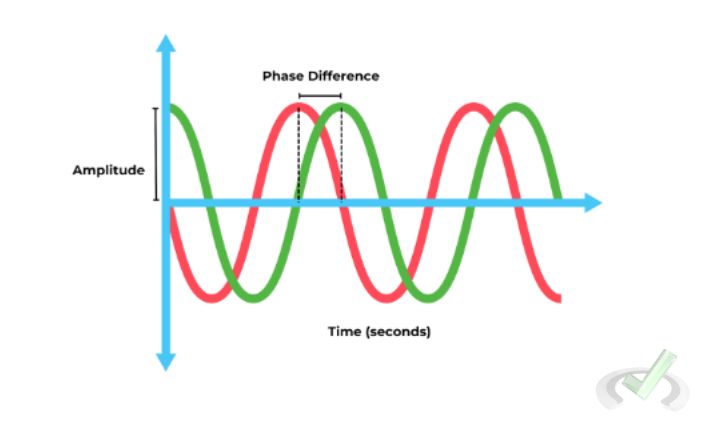
Two waves are in phase if their peaks and troughs align. They are out of phase if they do not. This concept is important in understanding wave interference.
III. Behavior of Waves
The behavior of waves can be observed in various phenomena, such as reflection, refraction, diffraction, and interference. These behaviors explain how waves interact with surfaces and mediums.
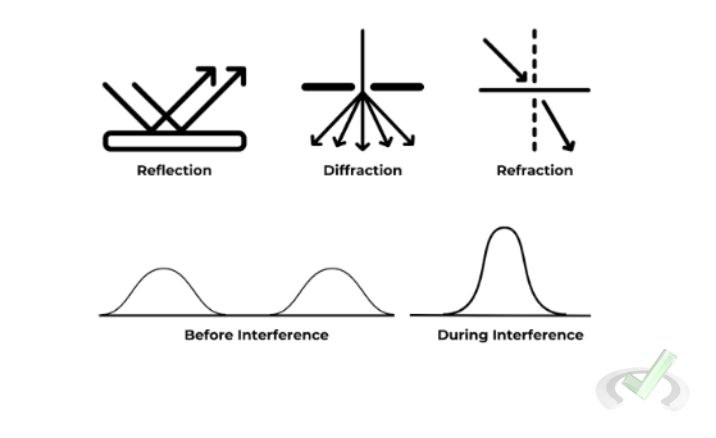
Reflection
Reflection occurs when a wave hits a surface and bounces back. The law of reflection states that the angle at which the wave hits the surface equals the angle at which it reflects. This principle explains why we can see ourselves in a mirror.
Refraction
Refraction occurs when waves pass from one medium to another, causing them to bend. This bending happens due to a change in the wave's speed. For example, a straw looks bent in a glass of water due to refraction.
Diffraction
Diffraction is when the waves bend around the edges of an obstacle or through an opening. This property allows waves to spread out after passing through narrow gaps. It explains why we can hear someone speaking even if they are around a corner.
Interference
Interference happens when two waves meet and combine to form a new wave pattern. This can result in two types of interference:
- Constructive interference occurs when waves add up to make a larger amplitude.
- Destructive interference occurs when waves cancel each other out.
IV. Applications of Wave Characteristics
Wave characteristics have various applications in communication, medicine, and everyday technology. These applications demonstrate the practical importance of understanding wave behavior.
Communication
Waves play a crucial role in communication technologies. They transmit signals to various devices and systems.
Example: Radio waves transmit television, radio, and mobile phone signals. Fiber optic cables utilize light waves to transmit data quickly and efficiently.
Medicine
Waves are used in diagnostic imaging and medical treatments. Different types of waves provide other benefits in medical applications.
Example: Ultrasound applies sound waves to create images of the inside of the body. Meanwhile, X-rays use electromagnetic waves to view bones and other internal structures.
Everyday Technology
Many everyday devices rely on the principles of wave behavior. Understanding waves allows for the development of various technologies.
Example: Microwaves use electromagnetic waves to heat food. Remote controls use infrared waves to send signals to televisions.V. Deeper Insights into Wave Phenomena
Wave characteristics are connected to broader scientific concepts, making them relevant to various fields of study.
The Electromagnetic Spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum includes all types of electromagnetic radiation, from radio waves to gamma rays. Each type has different wavelengths and frequencies, which affect how it interacts with matter.
Quantum Mechanics
Waves play a critical role in quantum mechanics. Particles like electrons display both wave-like and particle-like properties, known as wave-particle duality. This is fundamental in understanding how matter behaves at very small scales.
Acoustics
Studying sound waves, or acoustics, helps us design better concert halls and hearing aids. Understanding how sound waves work with each other with different materials allows us to control and manipulate sound.
VI. Wrap-Up and Key Terms
Understanding wave characteristics involves several key concepts and principles. Let's review:
Key Terms:
- Wavelength: Distance between successive peaks of a wave.
- Frequency: Number of wave cycles that pass a point in one second.
- Amplitude: The height of a wave related to its energy.
- Speed: How fast the wave travels through a medium.
- Reflection: Bouncing of waves off a surface.
- Refraction: Bending of waves as they change mediums.
- Diffraction: Bending of waves around obstacles or openings.
- Interference: Combining of waves to form new patterns.
VII. Practice Questions
Sample Practice Question 1
What happens when waves change speed as they pass from one medium to another?
A) Reflection
B) Refraction
C) Diffraction
D) Interference
Ans. B
Refraction is the bending of waves due to a change in speed as they move from one medium to another.
Sample Practice Question 2
Which property describes the height of a wave from its midpoint to its peak?
A) Frequency
B) Wavelength
C) Amplitude
D) Speed
Ans. C
Amplitude is the height of a wave from its midpoint to its peak, indicating the wave's energy.







 To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these
To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these 










 reviews on TrustPilot
reviews on TrustPilot