Entropy is a fundamental concept in chemistry that deals with a system's degree of disorder or randomness. It's crucial to understand how and why chemical reactions occur.
I. Introduction to Entropy
Entropy is a measure of the disorder in a system. In simple terms, it's how spread out or chaotic the energy and particles are.
Definition and Basic Concepts
- Entropy (S): A thermodynamic property that quantifies a system's disorder or randomness. It's related to the number of possible arrangements (microstates) of particles.
The second Law of Thermodynamics: States that the total entropy of an isolated system can never decrease over time. It always increases in spontaneous processes.
Microstates and Statistical Mechanics
- Microstates: Different ways particles can be arranged while maintaining the same overall energy.
Boltzmann Equation: S=kB ln W, where kB is Boltzmann's constant, and W is the number of microstates. This equation shows that more possible arrangements (higher W) mean higher entropy.
II. Entropy in Chemical Reactions
Entropy plays a crucial role in determining the spontaneity of a chemical reaction.
Spontaneous Processes
A spontaneous process occurs without external intervention. For a process to be spontaneous, the total entropy change (ΔSuniverse) must be positive, including the system and its surroundings.
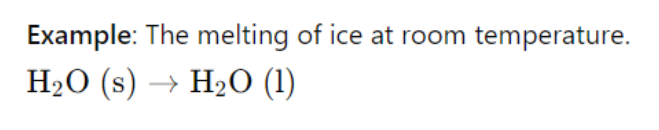
III. Factors Affecting Entropy
Several factors influence the entropy of a system:
1. Temperature
As temperature increases, entropy increases because particles move more vigorously and spread out.
2. Phase Changes
Solids have the least entropy, followed by liquids, and gases have the most entropy.
Example: Ice melting into water increases entropy.
3. Number of Particles
More particles usually mean higher entropy.
Example: Dissolving salt in water increases entropy because the salt dissociates into ions.
IV. Entropy Changes in Reactions
When chemical reactions occur, the entropy of the system changes.
1. Entropy Change (ΔS\Delta SΔS)
The change in entropy (ΔS\Delta SΔS) can be positive or negative depending on the reaction.
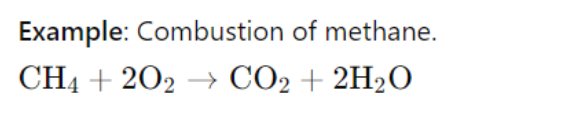
In this reaction, the entropy increases because the products (CO₂ and H₂O) are more disordered than the reactants.
2. Gibbs Free Energy (GGG)
Gibbs Free Energy (G) combines enthalpy (H) and entropy (S) to predict the spontaneity of a process.

V. Bridge/Overlap
Understanding entropy helps in grasping other concepts in chemistry, such as:
Energy Changes in Biochemical Reactions
In metabolic pathways, such as ATP hydrolysis, entropy changes significantly. The breakdown of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) into ADP (adenosine diphosphate) and inorganic phosphate releases energy and increases entropy, driving many biological processes.
ATP→ADP+Pi
Entropy and Enzyme Catalysis
Enzymes lower the activation energy of reactions, allowing them to proceed faster. While enzymes organize the substrate into a more ordered state (lower entropy), the overall process leads to a greater increase in entropy in the surroundings, making the reactions more favorable.
Thermodynamic Stability of Biomolecules
The stability of proteins and nucleic acids is closely related to entropy changes during folding and binding. For example, when a protein folds, its entropy decreases because it becomes more ordered. However, the process releases water molecules into the surroundings, increasing the entropy and driving the folding process.
VI. Wrap-Up and Key Terms
Understanding entropy and its implications in chemical reactions is essential for mastering many areas of chemistry. By recognizing how entropy affects the spontaneity of reactions, phase changes, and biological processes, students can better predict and control chemical behavior. This knowledge is not only vital for academic success but also for practical applications in various scientific fields.
- Entropy (S): Measure of disorder.
- Spontaneous Process: A process that occurs without external force.
Gibbs Free Energy (G): Determines spontaneity of reactions.
VII. Practice Questions
Sample Practice Question 1
What happens to the entropy when ice melts into water?
A. Decreases
B. Increases
C. Stays the same
D. It cannot be determined
Ans. B
When ice (solid water) melts into liquid water, the molecules gain more freedom of movement. Water molecules are in a structured lattice in the solid state, but in the liquid state, they move more randomly. This increase in randomness or disorder means that the system's entropy increases during melting.
Sample Practice Question 2
In the reaction N2+3H2→2NH3, what happens to the entropy?
A. Increases
B. Decreases
C. Stays the same
D. It cannot be determined
Ans. B
In this reaction, four molecules of gas (1 molecule of N2N2 and three molecules of H2H2) combine to form two molecules of NH3NH3 gas. Since the number of gas molecules decreases, the system's overall disorder (or entropy) decreases as well. Fewer gas molecules mean less randomness in the system, leading to decreased entropy.







 To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these
To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these 








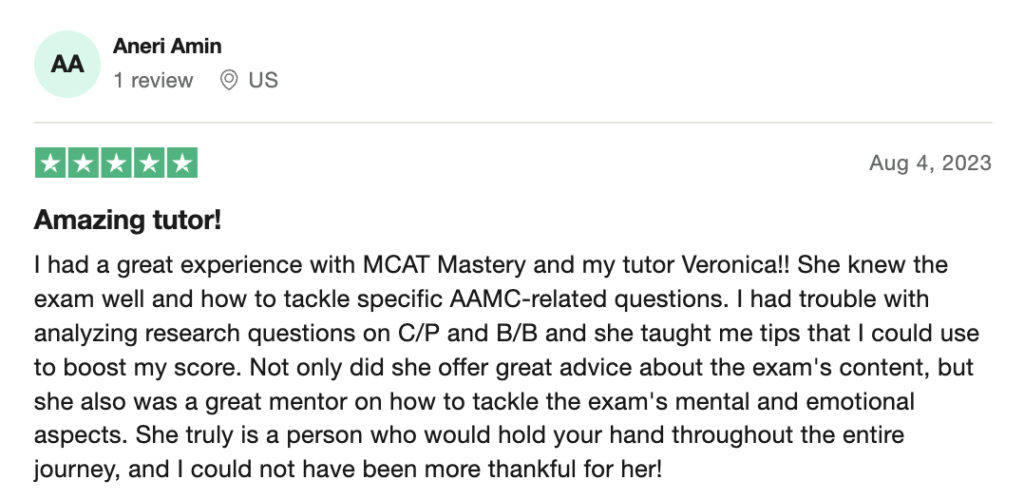

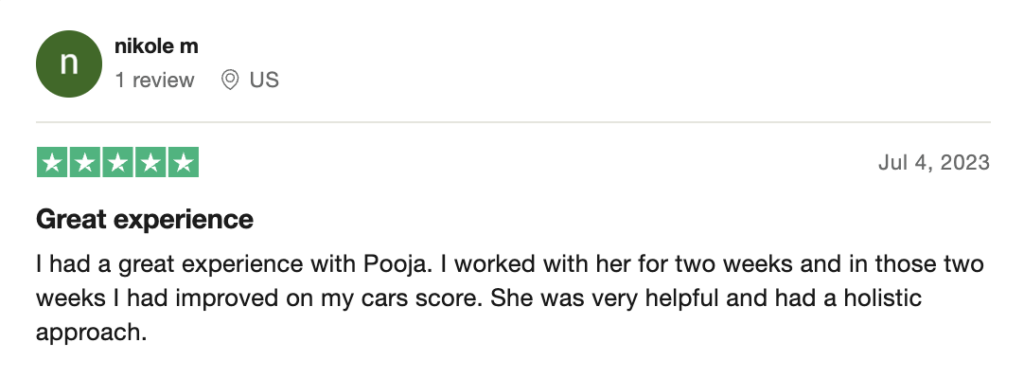
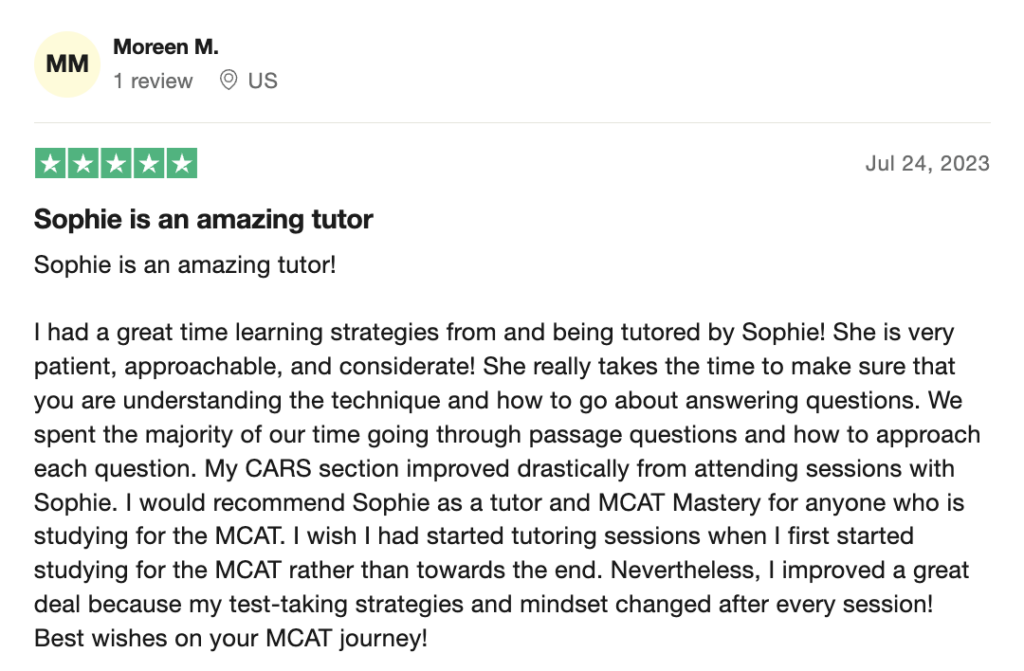

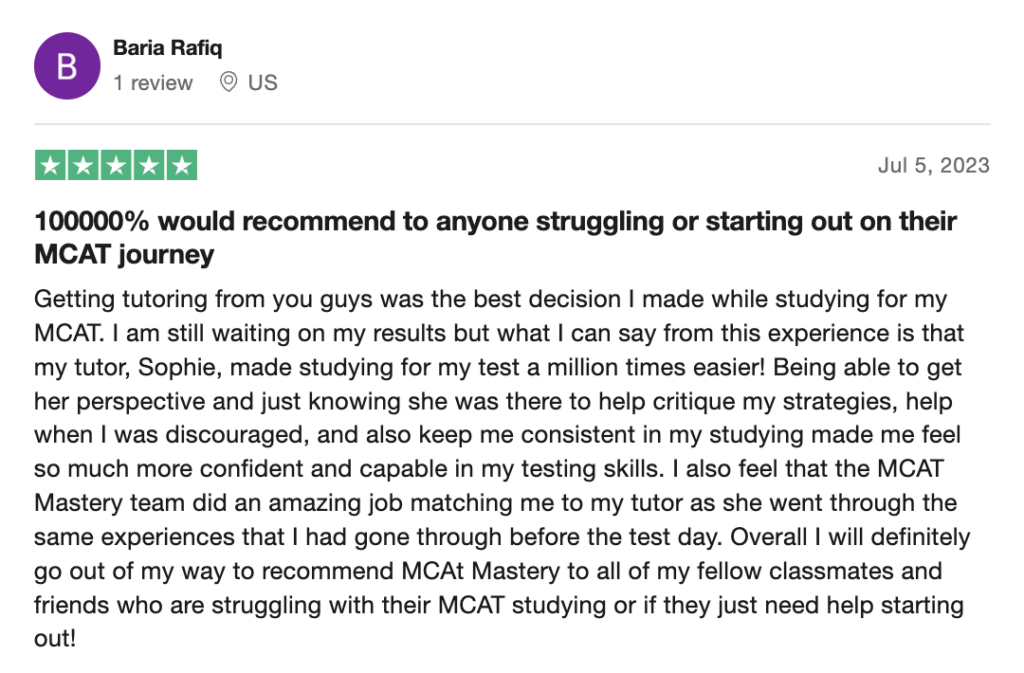
 reviews on TrustPilot
reviews on TrustPilot