Understanding acids and bases is essential in chemistry. Acids and bases undergo dissociation, which affects their strength. This guide will explain the dissociation process, how it relates to acid/base strength, and key concepts in an easy-to-understand manner.
I. Introduction to Acid/Base Dissociation
Dissociation in the context of acids and bases involves the separation of molecules into ions when dissolved in water. For acids, this means releasing hydrogen ions (H+\text{H}^+H+), and for bases, it means releasing hydroxide ions (OH−\text{OH}^-OH−). Water, a polar solvent, stabilizes these ions, facilitating dissociation.
Acid Dissociation (HA → H⁺ + A⁻)
- Example: Hydrochloric acid (HCl) dissociates in water to form H⁺ and Cl⁻.
HCl → H⁺ + Cl⁻
Base Dissociation (BOH → B⁺ + OH⁻)
- Example: Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) dissociates in water to form Na⁺ and OH⁻.
NaOH → Na⁺ + OH⁻
II. Understanding Acid and Base Strength
The strength of an acid or base depends on how completely it dissociates in water. Strong acids and bases dissociate completely, while weak acids and bases only partially dissociate.
Strong Acids and Bases
- Strong Acid: Completely dissociates in water.
- Example: Sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄)
H₂SO₄ → 2H⁺ + SO₄²⁻
- Strong Base: Completely dissociates in water.
- Example: Potassium hydroxide (KOH)
KOH → K⁺ + OH⁻
Weak Acids and Bases
- Weak Acid: Partially dissociates in water.
- Example: Acetic acid (CH₃COOH)
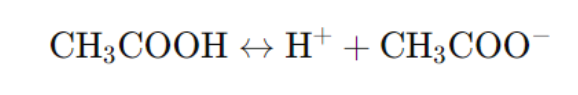
- Weak Base: Partially dissociates in water
- Example: Ammonia (NH₃)
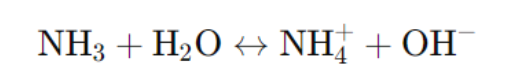
III. Factors Affecting Dissociation
Several factors, including concentration, temperature, and the nature of the solvent, influence the dissociation of acids and bases.
Concentration
- Higher concentration can increase the number of ions in the solution.
Temperature
- Increasing temperature can increase the dissociation of weak acids and bases.
Nature of the Solvent
- Water is a common solvent that facilitates dissociation due to its polarity, stabilizing the ions formed during dissociation.
IV. Important Concepts and Equations
Understanding pH, pOH, and ionization constants is crucial for grasping acid and base strength.
pH and pOH
- pH: Measures the concentration of hydrogen ions (H⁺).
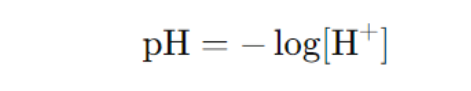
- pOH: Measures the concentration of hydroxide ions (OH⁻).
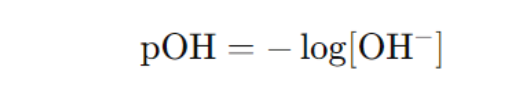
Relation Between pH and pOH
pH + pOH = 14
Ionization Constants
Ka (Acid dissociation constant): Indicates the strength of a weak acid.
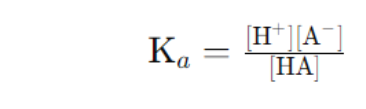
- Kb (Base dissociation constant): Indicates the strength of a weak base.
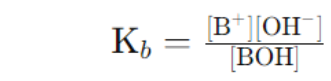
V. Applications and Examples
The concepts of acid and base dissociation have various practical applications, including buffer solutions, titration curves, and biological relevance.
Buffer Solutions
- Buffer: Resists changes in pH upon adding small amounts of acid or base.
- Example: Acetic acid (CH₃COOH) and its conjugate base, sodium acetate (CH₃COONa), form a buffer.
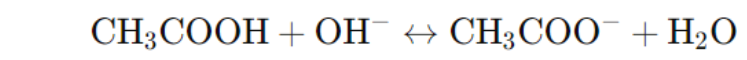
- Buffers work by neutralizing added acids or bases. The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation (pH=pKa+og([HA]/[A⁻])) helps calculate the pH of buffer solutions.
Titration Curves
- Used to determine the concentration of an acid or base in a solution.
- Strong acid vs. strong base titration curve:
- Example: HCl vs. NaOH
HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H₂O
Titration curves show the pH change as titrant is added to the solution, indicating equivalence points where the amount of acid equals the base.
Biological Relevance
- Enzyme activity: Many enzymes require specific pH levels to function effectively.
- For example, pepsin works best in the acidic environment of the stomach.
- Blood pH: Maintained around 7.4 using buffers like bicarbonate (HCO₃⁻) and carbonic acid (H₂CO₃).
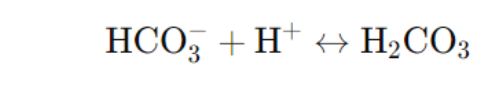
VI. Bridge/Overlap
The principles of acid and base dissociation connect to various topics in chemistry and related fields.
Connection to Organic Chemistry
Understanding acid/base strength is crucial for predicting reaction outcomes in organic synthesis. For example, carboxylic acids (R-COOH) are stronger than phenols (Ar-OH) because they dissociate more completely in water. In organic reactions, carboxylic acids can protonate bases more effectively than phenols.
Environmental Chemistry
Acid rain: Formed when sulfur dioxide (SO₂) and nitrogen oxides (NOₓ) dissolve in water, creating sulfuric (H₂SO₄) and nitric acids (HNO₃).
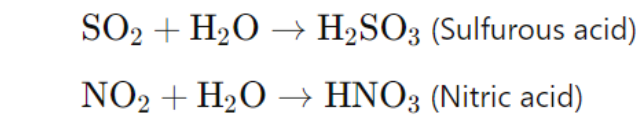
Acid rain lowers the pH of rainwater, leading to environmental damage such as soil acidification and harm to aquatic life.
VII. Wrap-Up and Key Terms
Understanding acid and base dissociation is key to many areas of chemistry. These concepts are foundational for predicting the strength of acids and bases and for their practical applications in buffers and biological systems. Recognizing the factors that affect dissociation and knowing how to measure pH and pOH will help you in various chemical contexts.
Key Terms
- Dissociation: Splitting of a compound into ions.
- Strong Acid/Base: Completely dissociates in water.
- Weak Acid/Base: Partially dissociates in water.
- pH: Measures hydrogen ion concentration.
- pOH: Measures hydroxide ion concentration.
- Ka: Acid dissociation constant.
Kb: Base dissociation constant.
VIII. Practice Questions
Sample Practice Question 1
What is the pH of a 0.01 M HCl solution?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
Ans. B
HCl is a strong acid, so, pH=−log(0.01)=−(−2)=2
Sample Practice Question 2
Which of the following is a weak base?
A. NaOH
B. NH₃
C. KOH
D. Ca(OH)₂
Ans. B
NH₃ (ammonia) partially dissociates in water, making it a weak base.







 To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these
To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these 
