Buffers and the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation are fundamental concepts in general chemistry. They are crucial for understanding acid-base balance in solutions.
Buffers help maintain a stable pH, and the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation describes the relationship between pH, pKa, and the concentrations of acid and conjugate base. This guide will explain these concepts in detail.
I. Introduction to Buffers
Buffers are solutions that resist changes in pH when small amounts of acid or base are added. They are essential in many biological and chemical processes to maintain a stable environment.
What is a Buffer?
A buffer is a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid. This means that in the buffer solution, there are molecules of the weak acid and ions of its conjugate base (or molecules of the weak base and ions of its conjugate acid). The weak acid or base doesn't completely ionize, which helps neutralize added acids or bases.
Example of a Buffer System
One common buffer system is the acetic acid (CH₃COOH) and sodium acetate (CH₃COONa) buffer. In this system:
Acetic acid (CH₃COOH) is a weak acid.
Sodium acetate (CH₃COONa) is the salt of its conjugate base (CH₃COO⁻).
II. How Buffers Work
Buffers work through neutralization, where they neutralize added acids or bases. Understanding this process is key to comprehending how buffers maintain a stable pH.
Neutralization of Added Acid
When a small amount of acid (H⁺) is added to the buffer, the acetate ion (CH₃COO⁻) reacts with the hydrogen ions (H⁺) to form more acetic acid (CH₃COOH):
CH3COO- + H+ → CH3COOH
Neutralization of Added Base
When a small amount of base (OH⁻) is added, the acetic acid (CH₃COOH) donates a hydrogen ion (H⁺) to the hydroxide ions (OH⁻), forming water and acetate ions:
CH3COOH + OH- → CH3COO- + H2O
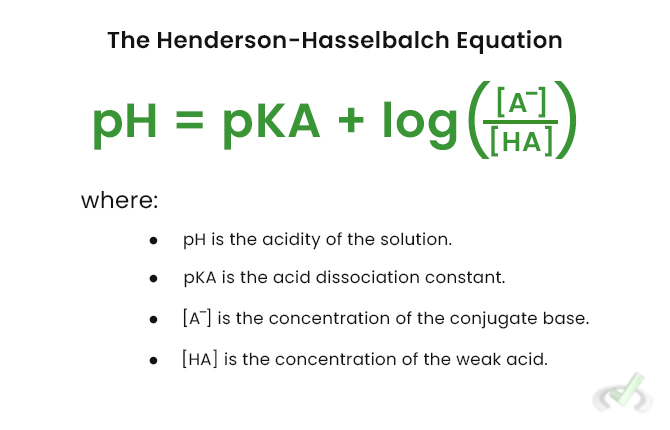
III. Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation is a crucial tool for calculating the pH of buffer solutions. It helps understand the relationship between pH, pKa, and the acid concentrations and its conjugate base.
IV. Practical Examples
Applying the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation is essential for solving real-world chemistry problems. Let’s explore a practical example.
Example Calculation
Suppose we have a buffer solution containing 0.1 M acetic acid (CH₃COOH) and 0.1 M acetate (CH₃COO⁻). The pKa of acetic acid is 4.76. What is the pH of the buffer solution?
Using the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation:

This shows that the buffer effectively maintains a pH close to the pKa value of the weak acid when the concentrations of the acid and its conjugate base are equal.
V. Importance of Buffers in Biological Systems
Buffers are crucial in biological systems where maintaining a stable pH is vital for enzyme function and metabolic processes. This section explores one of the most important buffer systems in the human body.
Blood Buffer System
One of the most important buffers in the human body is the bicarbonate buffer system, which maintains the pH of blood. The main components are carbonic acid (H₂CO₃) and bicarbonate (HCO₃⁻):
H2CO3 ↔ H+ + HCO3-
VI. Bridge/Overlap
Understanding buffers and the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation helps in grasping other chemistry topics. Here are some connections relevant to the MCAT:
Acid-Base Titration
In acid-base titration, buffers keep the pH stable near the endpoint, allowing for more accurate measurements. This is crucial for precisely determining unknown concentrations in laboratory settings, a skill tested in MCAT chemistry sections.
Environmental Chemistry
Buffers help maintain the pH of natural waters, which is essential for aquatic life. For instance, the carbonate buffer system helps maintain the pH of oceans and freshwater bodies. This is relevant for MCAT questions related to environmental science and the impact of human activities on natural systems.
Biochemistry
Many biochemical processes, such as enzyme function and metabolic pathways, rely on stable pH levels maintained by buffers. Understanding this helps in MCAT sections on biochemistry, where enzyme kinetics and metabolic pathways are key topics.
Physiology
Buffers are crucial in maintaining the pH of blood and other bodily fluids. The bicarbonate buffer system, for example, is vital for respiratory and renal physiology. MCAT physiology questions often involve understanding how the body maintains homeostasis, including pH balance.
VII. Wrap-Up and Key Terms
Understanding buffers and the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation is essential for mastering acid-base chemistry and its applications in various scientific fields. These concepts are crucial for maintaining stable environments in both biological and chemical systems.
Key Terms
- Buffer: A solution that resists changes in pH.
- Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation: A formula to calculate the pH of a buffer solution.
- Weak Acid: An acid that partially dissociates in solution.
- Conjugate Base: The species that remains after the acid has donated a proton.
- Neutralization: The process by which a buffer neutralizes added acids or bases.
VIII. Practice Questions
Sample Practice Question 1
What is the pH of a buffer solution containing 0.2 M ammonia (NH₃) and 0.2 M ammonium chloride (NH₄Cl)?
The pKa of ammonium ion (NH₄⁺) is 9.25.
A. 9.25
B. 7.00
C. 4.75
D. 10.75
Ans. A
Using the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation, with equal concentrations of NH₃ and NH₄⁺, the pH equals the pKa, which is 9.25.
Sample Practice Question 2
Using the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation, with equal concentrations of NH₃ and NH₄⁺, the pH equals the pKa, which is 9.25.
A. Sodium acetate
B. Potassium hydroxide
C. Carbonic acid
D. Hydrochloric acid
Ans. C
The blood buffer system involves carbonic acid (H₂CO₃) and bicarbonate (HCO₃⁻).







 To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these
To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these 
