Attention is a key concept in psychology. It helps us focus on what's important and ignore what's not. In this guide, we'll explore the different types of attention and how they work.
I. Understanding Attention
Attention is the mental process of concentrating on specific information while ignoring other things. It helps us manage and process the vast amount of information we encounter daily.
A. What Is Attention?
Attention involves focusing our mental energy on certain tasks or information. It allows us to filter out distractions and concentrate on what's important. This process can be considered a spotlight, highlighting what we must focus on while keeping other things in the background.
B. The Importance of Attention
Attention is essential for learning, decision-making, and everyday activities. It helps us pay attention to details, understand complex information, and remember important things. Without attention, completing tasks or learning new skills would be hard.
II. Types of Attention
There are several types of attention, each with a unique role in interacting with the world. Let's look at the main types: sustained, selective, divided, and alternating attention.
A. Sustained Attention

Sustained attention is a person’s ability to focus on one task for a long period. It's like staying focused while reading a book or playing a video game for hours. This type of attention is important for tasks that require long periods of concentration.
B. Selective Attention

Selective attention is when we focus on one thing while ignoring others. For example, when you listen to your friend in a crowded room, you filter out all the background noise. This type of attention helps us prioritize information and stay focused despite distractions.
C. Divided Attention

Divided attention, also known as multitasking, is the capability to focus on multiple tasks at the same time. For example, talking on the phone while cooking dinner. However, our brains can't fully focus on more than one task at a time, so divided attention often involves switching between tasks quickly.
D. Alternating Attention

Alternating attention refers to the ability to switch focus between different tasks. For instance, teachers might shift their attention between grading papers and answering students' questions. This type of attention requires flexibility and quick adjustments.
III. How Attention Works in the Brain
Several parts of the brain work together to manage attention. These areas control how we focus, ignore distractions, and shift our attention.
A. Prefrontal Cortex
The prefrontal cortex, found at the front of the brain, helps us plan and make decisions. It plays a key role in focusing our attention and organizing our thoughts. It's like the brain's control center, helping us decide what's important.
B. Parietal Lobe
The parietal lobe processes sensory information, like touch, sight, and sound. It helps us understand where things are in space and is involved in focusing on specific parts of our environment.
C. Anterior Cingulate Cortex
This part of the brain helps manage emotions and impulses. It also helps us focus on important tasks and manage distractions.
IV. Factors Affecting Attention
Several factors can influence our ability to pay attention, including age, fatigue, and environment.
A. Age and Attention
As we age, our attention skills can change. Older adults might struggle to concentrate for long periods or switch between tasks quickly. This is a normal part of aging.
B. Fatigue
Being tired can make it hard to focus. When we're sleepy, our brain struggles to pay attention, and we may make more mistakes.
C. Environment
The environment plays a big role in our ability to focus. A quiet, organized space can help us concentrate, while a noisy or cluttered environment can be distracting.
V. Improving Attention
There are ways to improve attention, such as practicing mindfulness, getting enough sleep, and staying organized.
A. Mindfulness
Mindfulness demands being fully present and engaged at the moment. Being mindful can help improve focus and reduce stress.
B. Good Sleep
Getting enough sleep is crucial for good attention. Sleep helps our brains rest and recover, making focusing easier during the day.
C. Organization
Keeping your space tidy and organized helps reduce distractions and makes it easier to focus on important tasks.
VI. Bridge: Attention and Other Psychological Areas
Attention is connected to many other topics in psychology, such as learning, memory, and mental health. Understanding these connections helps us see the bigger picture of how the brain works.
A. Attention and Neurobiology
Attention is closely related to the brain's chemistry. Neurotransmitters like dopamine and norepinephrine help regulate attention. For example, low levels of dopamine are linked to ADHD, a condition where people have trouble focusing.
B. Cognitive and Behavioral Neuroscience
Researchers use fMRI and EEG to study how the brain processes attention. These studies help us learn about the neural mechanisms behind different types of attention and how the brain reacts to stimuli.
C. Psychological Disorders
Attention problems can be a part of many psychological disorders. For instance, people with anxiety may find it hard to focus because they're distracted by worries. ADHD is another example where individuals struggle with sustained and selective attention.
D. Developmental Psychology
Attention skills develop throughout our lives. These skills are still developing in children, so young kids often have shorter attention spans. Understanding this development helps in educational settings and parenting.
VII. Wrap-Up and Key Terms
Attention helps us focus on important things while ignoring distractions. Understanding its types and how the brain controls them is key to improving our daily lives and learning.
Key Terms
- Sustained Attention: Focusing on one task for a long time.
- Selective Attention: Focusing on one thing and ignoring others.
- Divided Attention: Doing multiple tasks at once.
- Alternating Attention: Switching focus between tasks.
- Prefrontal Cortex: The brain's control center for planning and focus.
- Parietal Lobe: Processes sensory information and spatial awareness.
- Anterior Cingulate Cortex: Manages emotions, impulses, and focus.
VIII. Practice
Sample Practice Question 1
Scenario: You are doing your homework and listening to music at the same time. Suddenly, your friend calls, and you start talking to them while continuing your homework.
Question: What type of attention do you use when you switch between talking to your friend and doing homework?A. Sustained Attention
B. Selective Attention
C. Divided Attention
D. Alternating Attention
Ans. D
Alternating attention involves switching focus between tasks, like talking and doing homework. It requires quickly shifting your attention from one activity to another.
Sample Practice Question 2
Scenario: You find focusing hard during a lecture because your classmates are talking.
Question: Which part of your brain helps you ignore distractions and focus on the lecture?A. Prefrontal Cortex
B. Parietal Lobe
C. Anterior Cingulate Cortex
D. Occipital Lobe
Ans. A
The prefrontal cortex is involved in decision-making and focus. It helps you filter out distractions and concentrate on important tasks, like listening to a lecture.







 To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these
To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these 









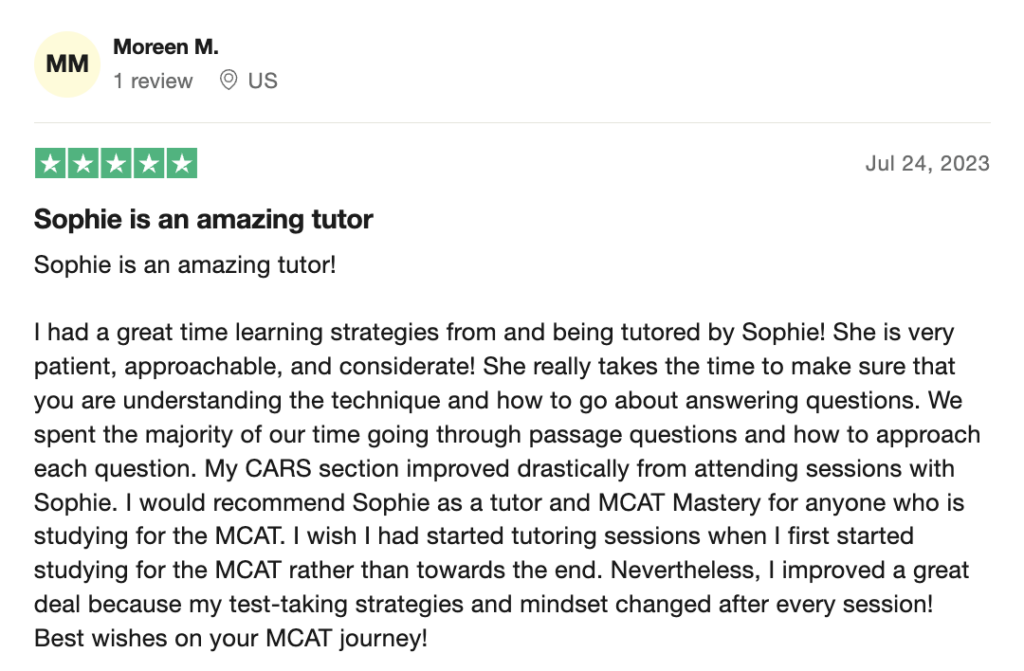

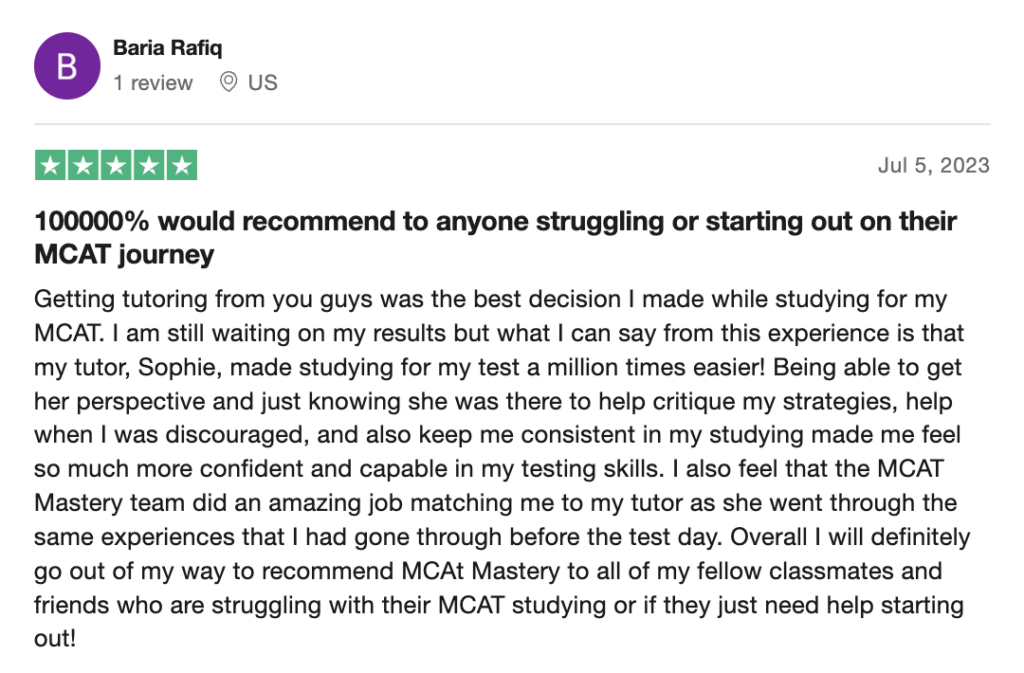
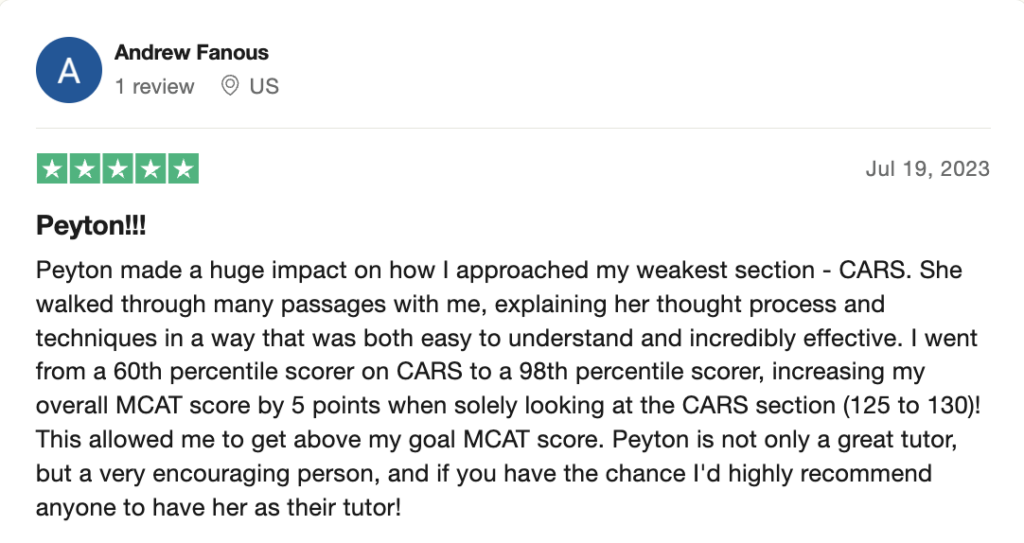
 reviews on TrustPilot
reviews on TrustPilot