Imagine trying to isolate a specific compound from a complex mixture. How do scientists achieve this seemingly daunting task?
The key is the fundamental principles of separation techniques. These techniques have been used for centuries.
Early chemists used simple methods like filtration and distillation. Over time, separation techniques have evolved into more sophisticated methods.
It allows chemists to separate complex mixtures more precisely. Let’s explore these techniques in detail.
I. Introduction to Separation Techniques
Separation techniques divide mixtures into their individual components. They are vital in organic chemistry.
It helps chemists identify, isolate, and purify substances. Several common separation techniques exist, each with its own rationale and applications.
II. Types of Separation Techniques
Organic chemistry employs various separation techniques. Each method combines the physical and chemical characteristics of mixture components for separation.
Filtration
Filtration separates solids from liquids. It is one of the simplest and oldest methods.
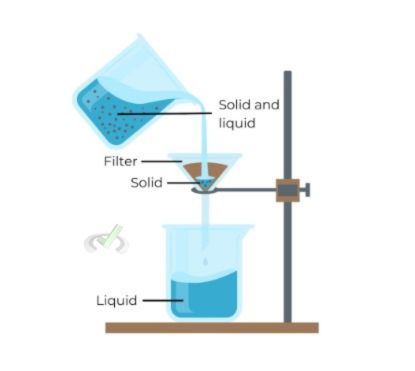
A filter allows the liquid to pass through while retaining the solid particles. Filtration can use various filters, such as paper, cloth, or specialized membranes.
Example: When making coffee, the filter separates the coffee grounds from the liquid coffee.
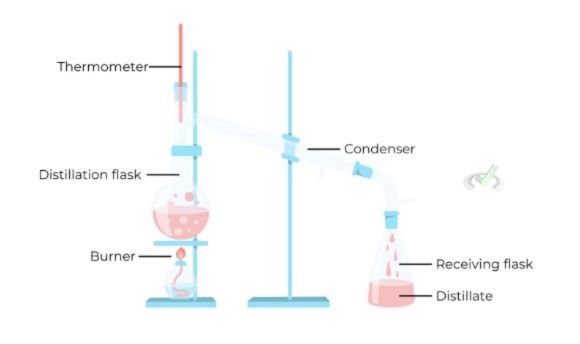
Distillation
Distillation separates liquids based on their boiling points. The mixture is heated until one component boils and turns into vapor.
The vapor condenses back into a liquid and is collected separately. Different types of distillation are used, including simple, fractional, and steam distillation. Each technique is suited for various kinds of mixtures.
Example: Distillation is used to purify drinking water by removing impurities.
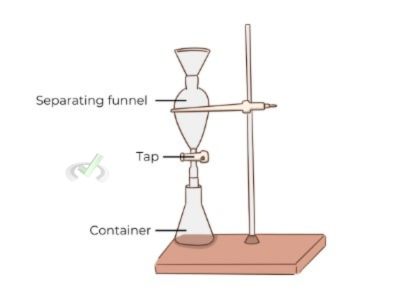
Extraction
Extraction separates compounds based on their solubility in different solvents. The mixture is mixed with a solvent in which one of the components is more soluble. The soluble component dissolves in the solvent and can be separated. There are two phases in extraction: the aqueous phase and the organic phase.
Example: Extraction separates caffeine from coffee beans using a solvent like dichloromethane.
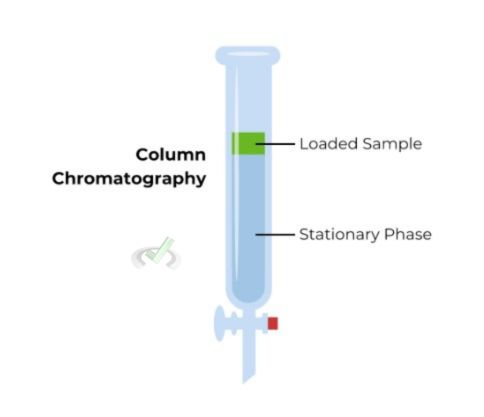
Chromatography
Chromatography separates components based on their movement through a stationary phase. Different types of chromatography include paper, thin-layer, column, and gas chromatography. Each type uses a different stationary phase and method for moving the mixture through it.
Example: Paper chromatography can be used to separate different pigments in ink.
Recrystallization
Recrystallization purifies solid compounds. The impure solid is dissolved in a hot solvent and then cooled.
The pure compound crystallizes out, leaving impurities in the solution. This process may be repeated several times to increase purity.
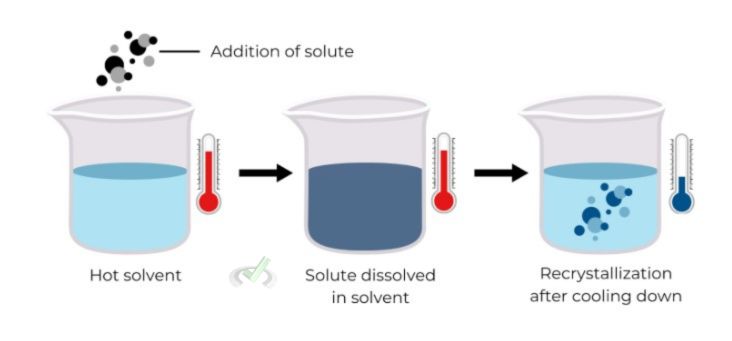
Example: Recrystallization is used to purify aspirin.
III. Rationale Behind Separation Techniques
Each separation technique has a specific rationale based on both the physical and chemical properties of the components in a mixture.
Filtration
Filtration works because solids and liquids have different particle sizes. The filter allows only the liquid to pass through while trapping the solid particles.
Distillation
The principle of distillation is based on the variation in boiling points. Each liquid component of a mixture has a unique boiling point, allowing it to be separated by controlled heating and cooling.
Extraction
Extraction takes advantage of differences in solubility. Different compounds dissolve to different extents in various solvents. This property allows for selective separation.
Chromatography
Chromatography depends on differences in how compounds interact with the stationary and mobile phases. When components strongly interact with the stationary phase, they tend to move at a slower pace, aiding in their segregation.
Recrystallization
Recrystallization is based on the principle that pure compounds form crystals more readily than impure ones. As the solution cools, the pure compound crystallizes out, leaving impurities in the solution.
IV. Applications of Separation Techniques
Separation techniques are widely used in both laboratory and industrial settings. They are essential for research, quality control, and production.
Laboratory Research
Separation techniques are used to isolate and identify compounds in research. This helps chemists study the properties and reactions of specific substances.
Example: In drug discovery, scientists use separation techniques to isolate active compounds from natural sources.
Quality Control
Separation techniques ensure product purity and quality in industries like pharmaceuticals and food. This is critical for safety and effectiveness.
Example: Quality control tests in the pharmaceutical industry use chromatography to check the purity of drugs.
Production
Separation techniques are used in industrial production to purify raw materials and products, ensuring that the final products meet the required standards.
Example: The petroleum industry uses distillation to separate crude oil into different components like gasoline and diesel.
V. Scientific Significance of Separation Techniques
Let's explore how understanding separation techniques connects to broader scientific ideas. This enriches our knowledge of chemical behavior and its applications in various fields.
Structure-Function Relationship
The efficiency of separation techniques depends on understanding the structure and properties of the components in a mixture. This helps predict how different compounds will behave during separation.
As such, the structure-function relationship is also critical in biochemistry, where the shape of biomolecules determines their function.
Chemical Reactions
Many chemical reactions require pure starting materials. Separation techniques are crucial for obtaining these pure substances.
They also help isolate products from reaction mixtures. Purifying reagents and products are essential in metabolic pathways, where enzymes catalyze reactions that produce specific molecules.
Environmental Science
Separation techniques play a vital role in environmental science. They are used to analyze pollutants and purify water and air samples. For example, chromatography is used to detect pollutants in water samples.
Medical Applications
Separation techniques are used in diagnostics and treatment in medicine. They help isolate biomolecules for study and therapy. Chromatography is also utilized in this field to separate proteins for studying diseases.
VI. Wrap-Up and Key Terms
Understanding the rationale for separation techniques involves grasping several key concepts and principles. Let's review:
Key Terms
- Filtration: Separation of solids from liquids using a filter.
- Distillation: Separation of liquids based on boiling points.
- Extraction: Separation based on solubility in different solvents.
- Chromatography: Separation based on movement through a stationary phase.
- Recrystallization: Purification of solids by crystallization from a solution.
Practice Questions
Sample Practice Question 1
What separation technique would you use to separate sand from water?
A. Distillation
B. Filtration
C. Chromatography
D. Extraction
Ans. B
Filtration separates solids from liquids, making it suitable for separating sand from water.
Sample Practice Question 2
How does distillation separate components in a mixture?
A. By size
B. By solubility
C. By boiling point
D. By movement through a stationary phase
Ans. C
Distillation separates components based on their boiling points by heating the mixture and condensing the vapor of the component that boils first.







 To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these
To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these 










 reviews on TrustPilot
reviews on TrustPilot