We previously defined phosphates as a functional group with a central phosphorus atom bonded to four oxygen atoms. Phosphorus is an essential component in biology, serving important functions in energy production, cellular function, and cell structure.
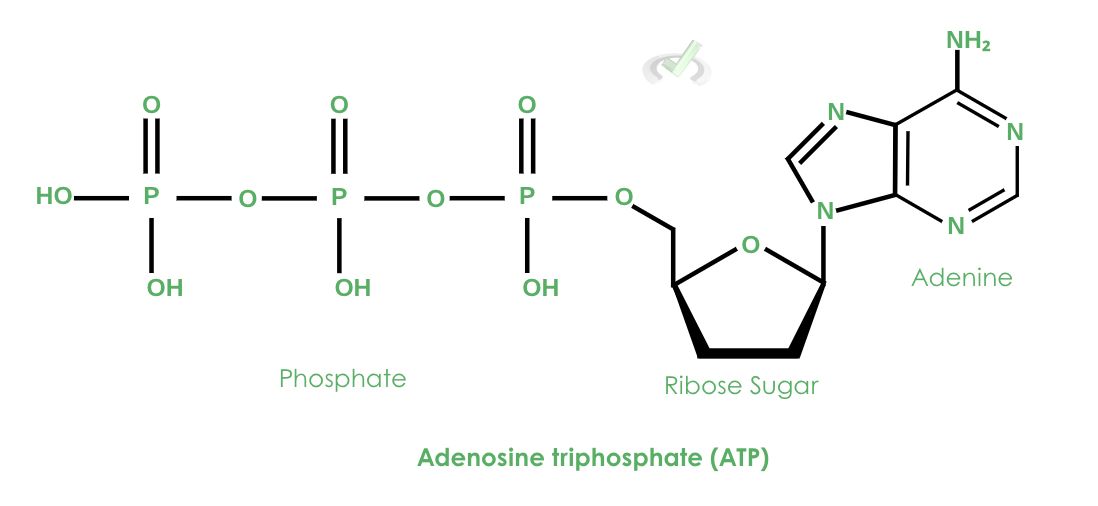
One essential role of phosphorus is its role as a component of adenosine triphosphate (ATP)–the molecule that serves as a source of energy for use and storage. This molecule is capable of releasing energy through a process known as hydrolysis.
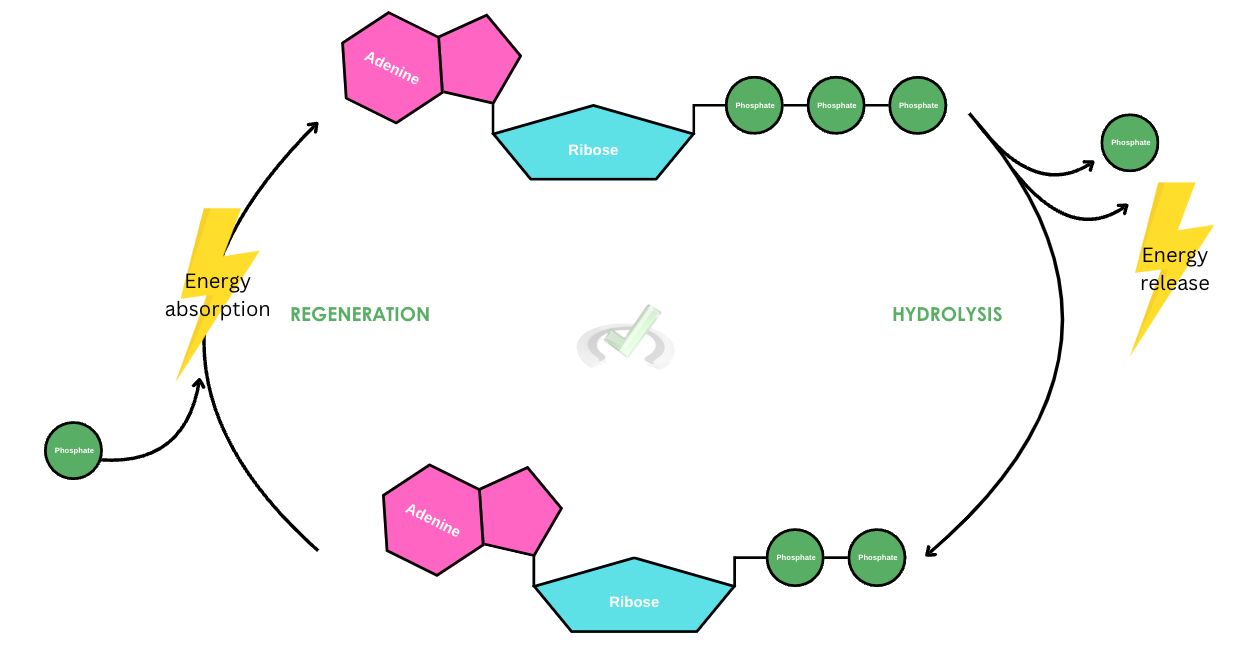
During hydrolysis, ATP breaks down into ADP and an inorganic phosphate. The release of one phosphate group is also followed by the release of energy. ATP bonds are characterized by high-energy bonds. When an ATP is hydrolyzed, it releases a significant amount of energy.
The term triphosphate refers to the three phosphate groups attached to the ribose. These phosphates have strong bonds among each other as a result of their negative charges!
I. Negative Charge
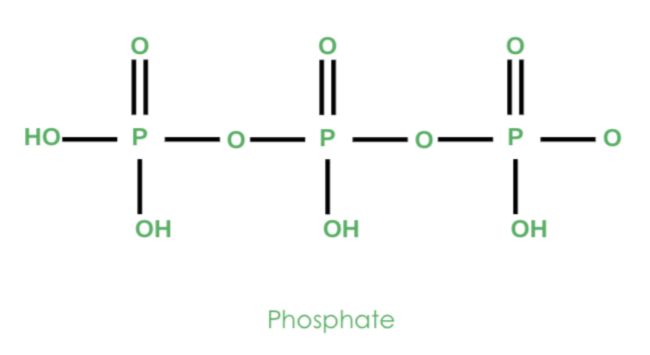
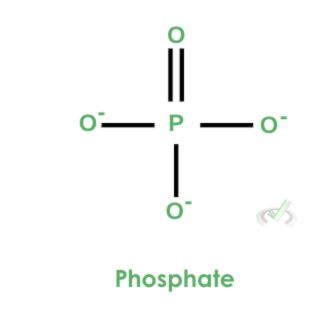
Looking at things more closely, let’s look at phosphate. Notice how phosphate is composed of a central phosphorus atom bonded to four oxygen atoms. One oxygen atom is double-bonded to phosphorus, and the remaining three oxygen atoms are bonded singly.
These oxygen atoms with a single bond to phosphorus have negative charges. As a result, the overall formal charge of phosphate is -3.
This negative charge is a crucial feature of phosphorus-containing compounds. Because phosphate groups have a negative charge, they are highly hydrophilic, meaning they are highly attractive to water molecules. This allows the formation of strong bonds with hydrogen.
II. High-Energy Bonds
High-energy bonds found in ATP are characterized by their high energy content in the form of chemical potential energy. When these bonds are hydrolyzed, they release a significant amount of energy.
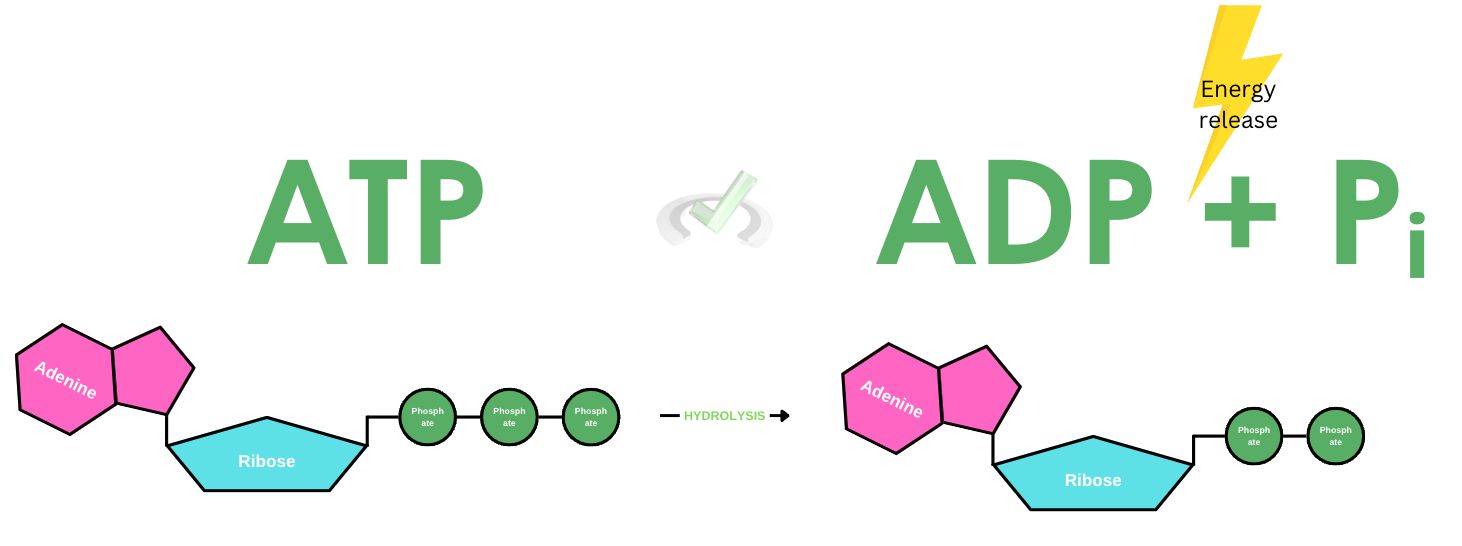
As a result of the negative charge repulsion from the phosphate group, the bonds formed between phosphates tend to have a strong repulsion between them. Think of it as a bond held by a rubber band. When these bonds are broken, this “rubber band” that keeps them together snaps and relaxes, releasing energy as the bond gets broken.
III. Conclusion
Now we know that phosphate groups have a negative charge and this repulsion between charges allows these groups to have high-energy bonds. Let’s look at how this applies to phosphorus-containing compounds in our bodies.
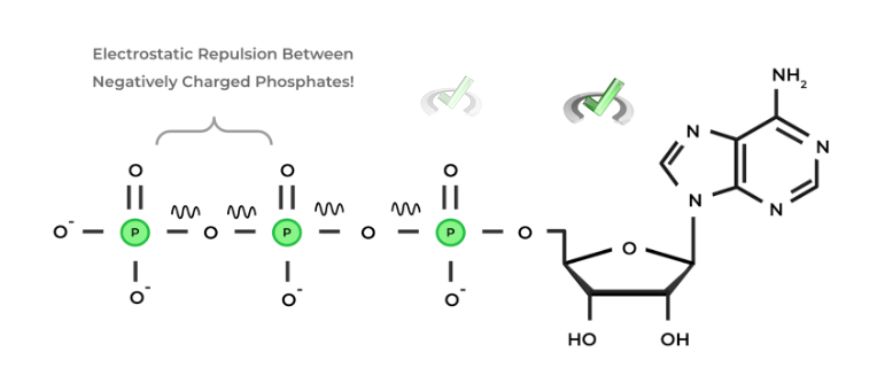
Because of the negative charges on phosphate groups, these phosphate groups are bound tightly to each other, forming a strong electrostatic repulsion between negatively charged phosphates.
The negative charges allow strong bonds to form. When these bonds form, they form high-energy bonds as a result of the strong electrostatic repulsion. This is an important concept in biology. The reason why ATP is such an ideal energy source for our cells is because of its chemical makeup!
During hydrolysis, ATP loses a phosphate group and transforms into ADP or adenosine diphosphate. Because there is one less phosphate group present, it in effect, reduces the repulsion in the molecule. This makes ADP more stable than ATP. Think of it this way: When three people hold a rubber band, stretching it equally between them, there is greater force felt between the three people. If you’re the one holding one side, you’ll feel a strong tension from the opposite pull of the two other people holding the rubber band. When one person leaves, the rubber band relaxes a bit more and you’ll feel like the pull isn’t as strong as when there were three of you holding the rubber band!
IV. Practice Questions
Sample Practice Question 1
Which of the following statements is not accurate?
A. All phosphorus-containing compounds are phosphates.
B. All phosphates are phosphorus-containing compounds.
C. Phosphates have a negative charge that forms high-energy bonds.
D. ATP releases energy through breaking a bond.
Ans. A
Sample Practice Question 2
How does the negative charge of phosphate groups influence its interaction with other molecules?
A. It forms a strong metallic bond with other molecules.
B. It prevents the phosphate from interacting with other molecules.
C. It allows the formation of ionic bonds and interactions with positively charged molecules.
D. It makes a strong bond.
Ans. C







 To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these
To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these 








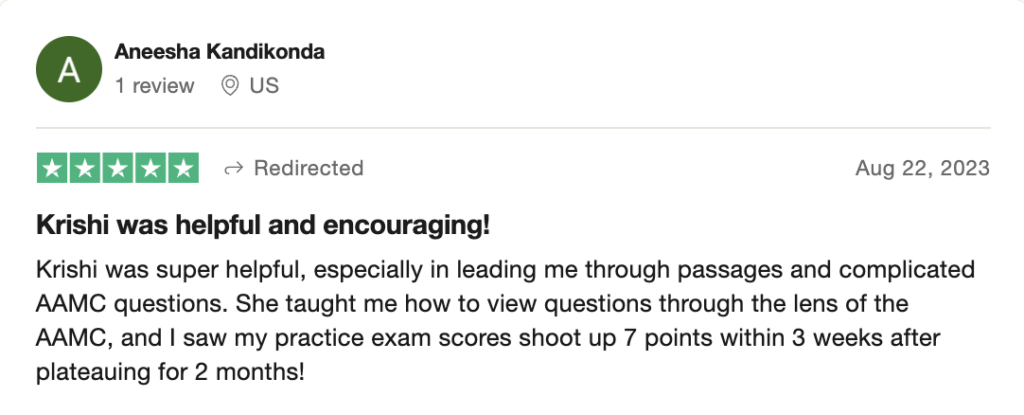
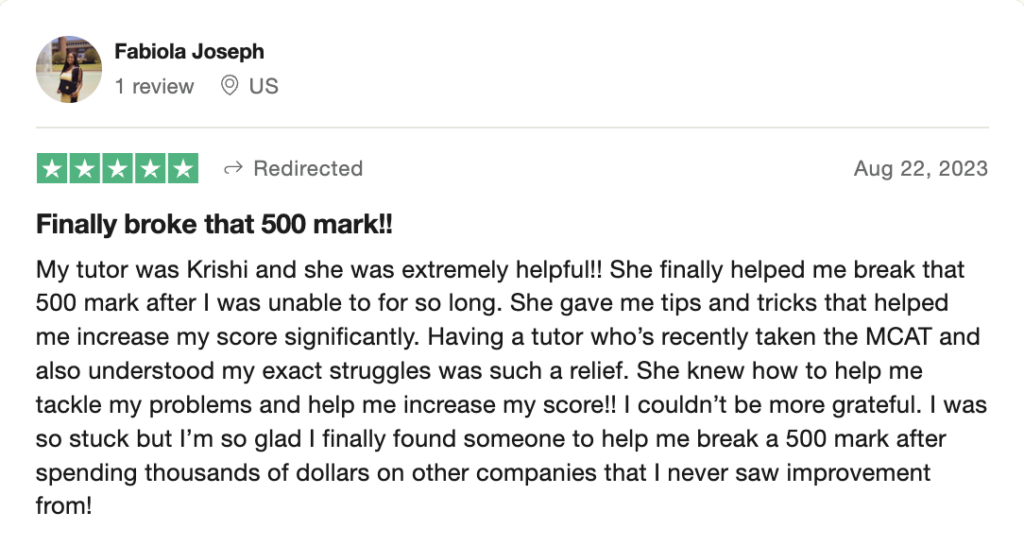
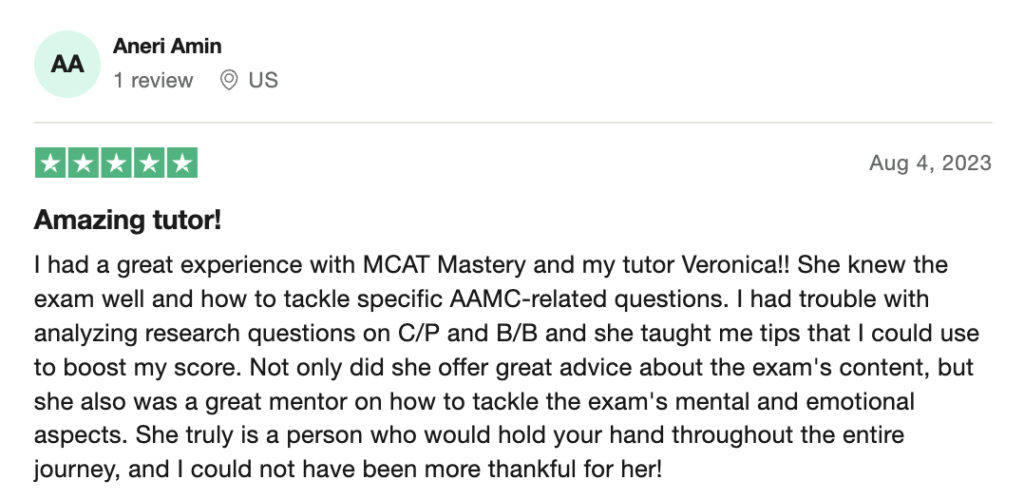

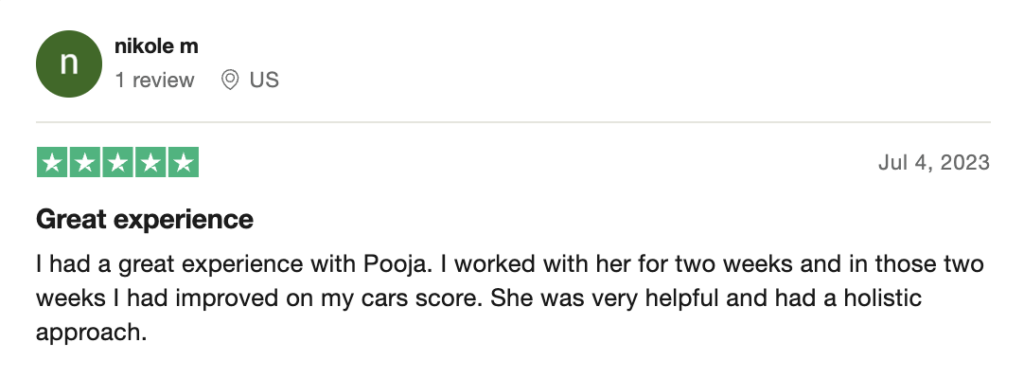
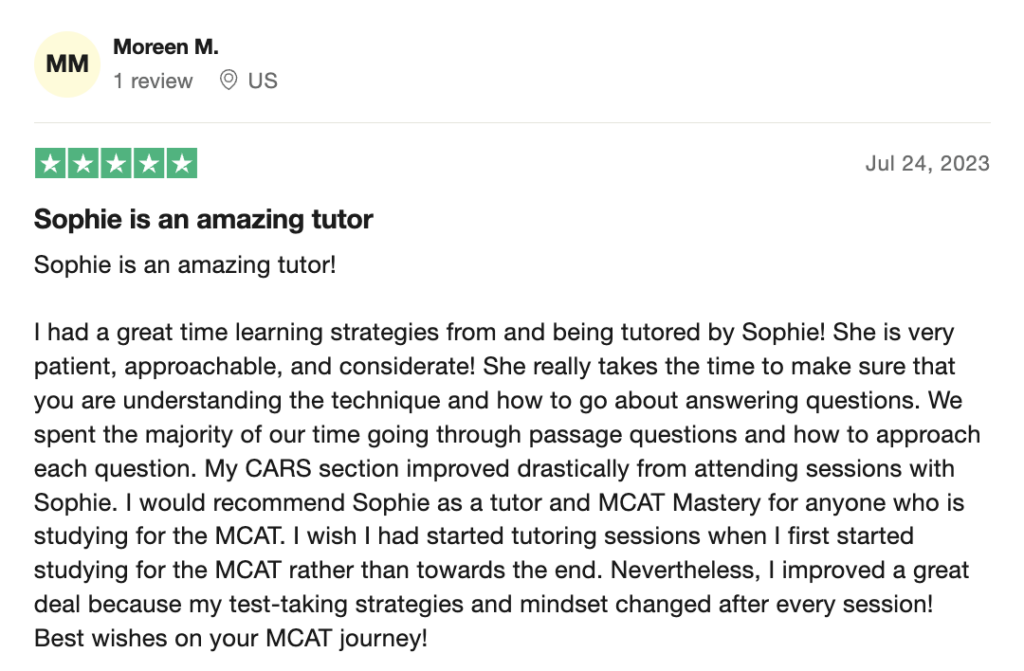

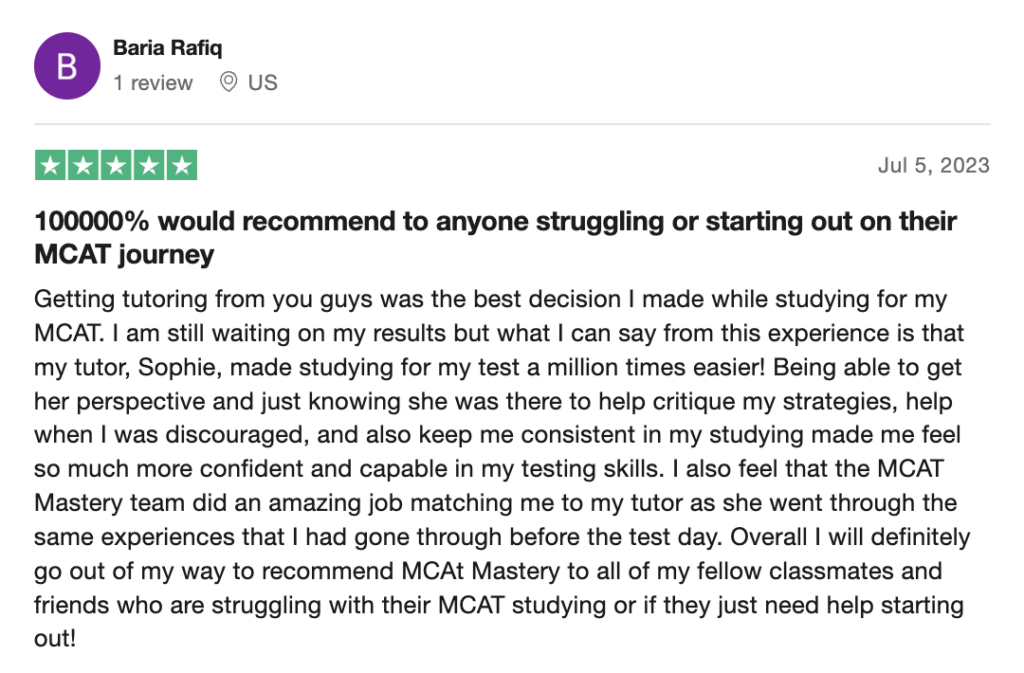
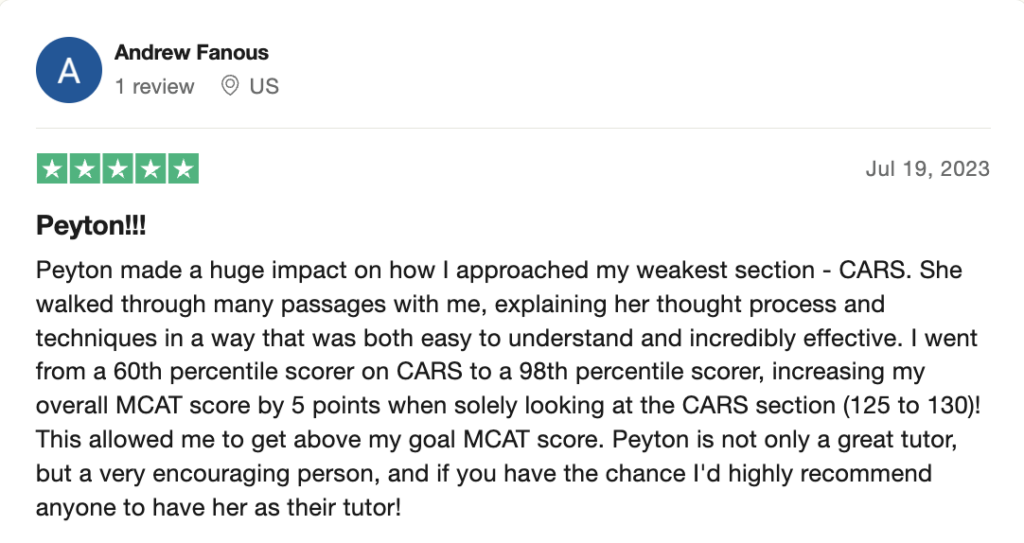
 reviews on TrustPilot
reviews on TrustPilot