The thermodynamics of phase changes involves studying how energy changes when substances change from one state of matter to another. This guide will explain the key concepts, formulas, and examples related to phase changes. We'll cover how energy is involved in melting, freezing, boiling, and condensing processes.
I. Introduction to Phase Changes
Phase changes occur when a substance changes from one state of matter to another. These states include solid, liquid, and gas. Phase changes involve energy changes without altering the chemical structure of the substance.
A. Key Concepts
- Heat (q): Energy transferred due to temperature difference. It is measured in joules (J) or calories (cal).
- Temperature (T): Measure of thermal energy. It is measured in degrees Celsius (°C) or Kelvin (K).
- Enthalpy (ΔH): Heat content of a system at constant pressure. It represents energy changes during phase changes.
II. Types of Phase Changes
Different types of phase changes involve either absorbing or releasing energy.
A. Melting and Freezing
- Melting (Fusion): Solid to liquid. Absorbs heat.
- Freezing (Solidification): Liquid to solid. Releases heat.

Example: Calculate the heat required to melt 10 grams of ice at 0°C. The enthalpy of fusion (ΔHf) for water is 334 J/g.
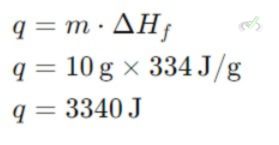
B. Boiling and Condensing
- Boiling (Vaporization): Liquid to gas. Absorbs heat.
- Condensing (Condensation): Gas to liquid. Releases heat.
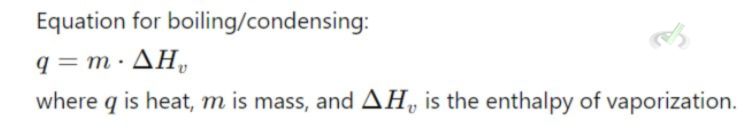
Example: Calculate the heat required to vaporize 20 grams of water at 100°C. The enthalpy of vaporization (ΔHv) for water is 2260 J/g.

C. Sublimation and Deposition
- Sublimation: Solid to gas. Absorbs heat.
- Deposition: Gas to solid. Releases heat.
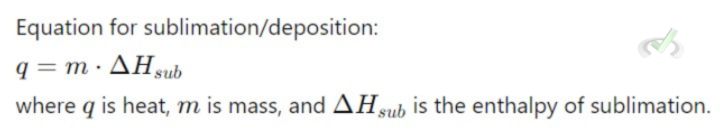
Example: Calculate the heat required to sublimate 5 grams of dry ice (solid CO₂). The enthalpy of sublimation (ΔHsub) for CO₂ is 571 J/g.
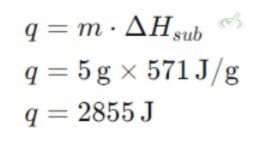
III. Calculating Heat for Phase Changes
To calculate the heat involved in a phase change, use the specific enthalpy values and mass.
A. Example Problem
Calculate the heat required to melt 10 grams of ice at 0°C. The enthalpy of fusion (ΔHf) for water is 334 J/g.
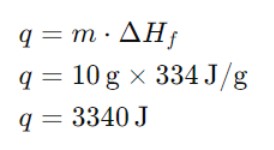
B. Heating Curves
A heating curve shows temperature changes as heat is added to a substance. It includes flat regions where phase changes occur. These regions represent where heat is used to change the phase without changing temperature.
IV. Energy and Phase Changes
Understanding how energy changes during phase changes is crucial in chemistry and everyday life.
A. Latent Heat
Latent heat is the energy absorbed or released during a phase change. It does not change the temperature. Examples include the heat of fusion (melting/freezing) and heat of vaporization (boiling/condensing).
B. Endothermic and Exothermic Processes
- Endothermic: Absorbs energy (e.g., melting, vaporization).
- Exothermic: Releases energy (e.g., freezing, condensation).
V. Chemical Equations in Phase Changes
Chemical equations can represent phase changes. These equations show the states of the reactants and products.

VI. Applications and Examples
Understanding phase changes is important in many areas, from cooking to industrial processes.
A. Everyday Life
- Cooking: Boiling water for cooking.
- Freezing: Making ice cubes in a freezer.
B. Industrial Applications
- Refrigeration: Uses phase changes of refrigerants to cool spaces.
- Distillation: Separates mixtures based on different boiling points.
VII. Bridge: Connecting Thermodynamics to Broader Chemistry Concepts
Thermodynamics of phase changes connects to many other topics in chemistry.
A. Energy Changes in Reactions
Phase changes are related to energy changes in chemical reactions. Both involve the transfer of heat and work.
B. Chemical Kinetics
The study of reaction rates also considers how temperature and energy influence the speed of reactions.
C. Environmental Chemistry
Understanding phase changes helps explain natural phenomena, like the water cycle, which involves melting, freezing, and evaporation.
VIII. Wrap-Up and Key Terms
Understanding the thermodynamics of phase changes involves several key concepts and terms. Let's review:
Key Terms
- Heat (q): Energy transfer due to temperature difference.
- Temperature (T): Measure of thermal energy.
- Enthalpy (ΔH): Heat content at constant pressure.
- Latent Heat: Energy absorbed or released during phase changes.
- Endothermic: Absorbs energy.
- Exothermic: Releases energy.
IX. Practice Questions
Sample Practice Question 1
Calculate the heat required to vaporize 20 grams of water at 100°C. The enthalpy of vaporization (ΔHv) for water is 2260 J/g.
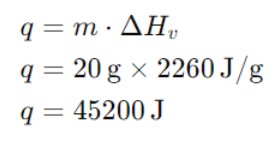
Explanation:
Multiply the mass (20 grams) by the enthalpy of vaporization (2260 J/g) to find the total heat.
Sample Practice Question 2
What happens to the temperature of a substance during a phase change?
A. It increases.
B. It decreases.
C. It stays the same.
D. It fluctuates.
Ans. C
During a phase change, the temperature remains constant while the substance absorbs or releases energy.







 To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these
To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these 








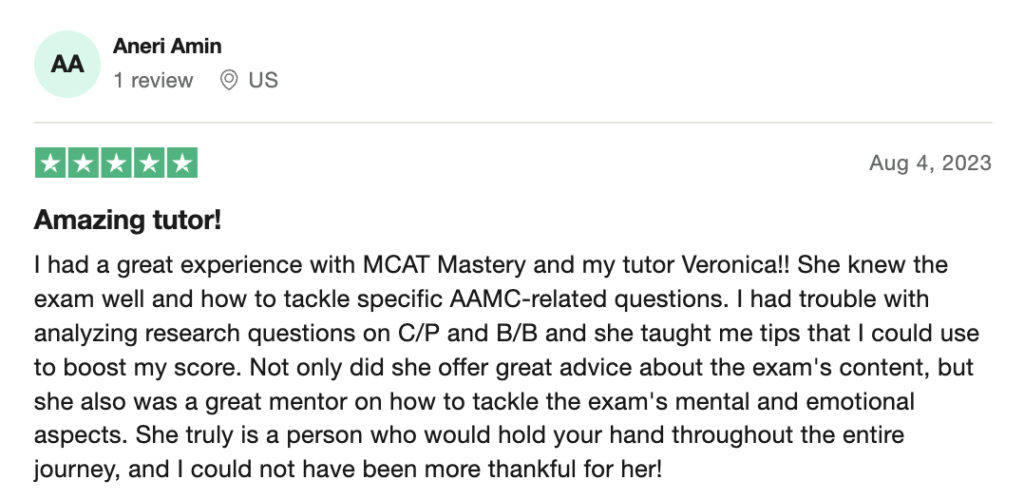

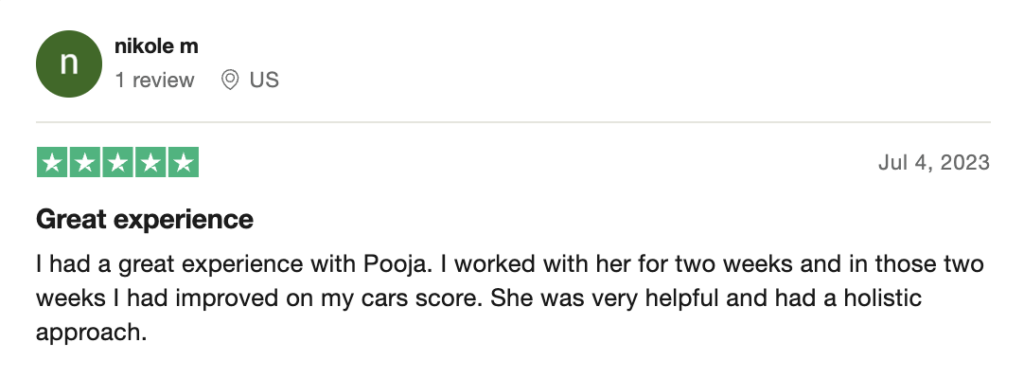
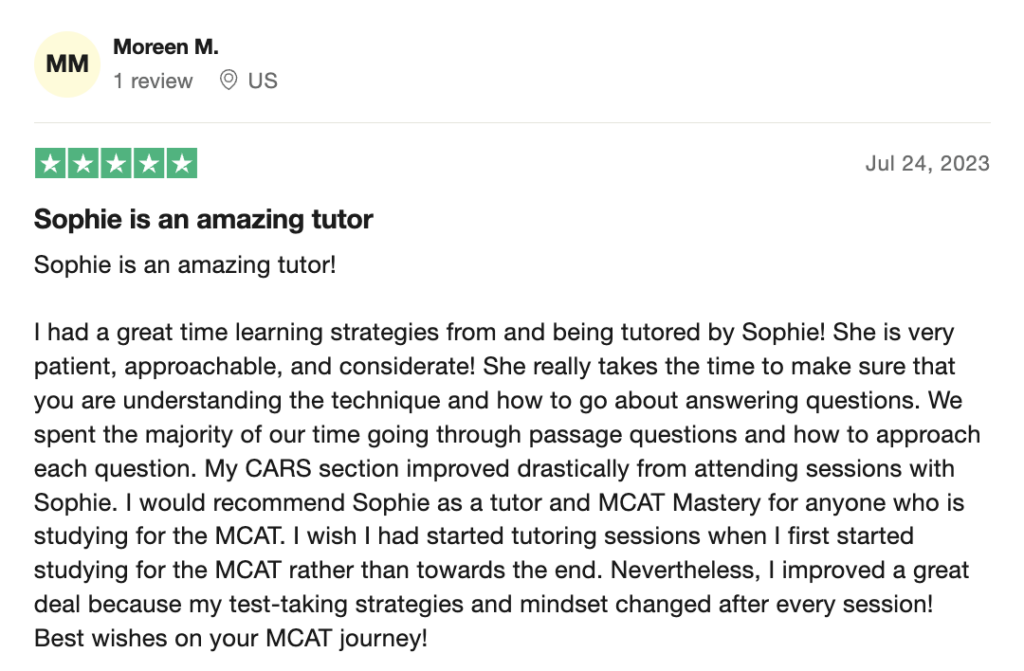

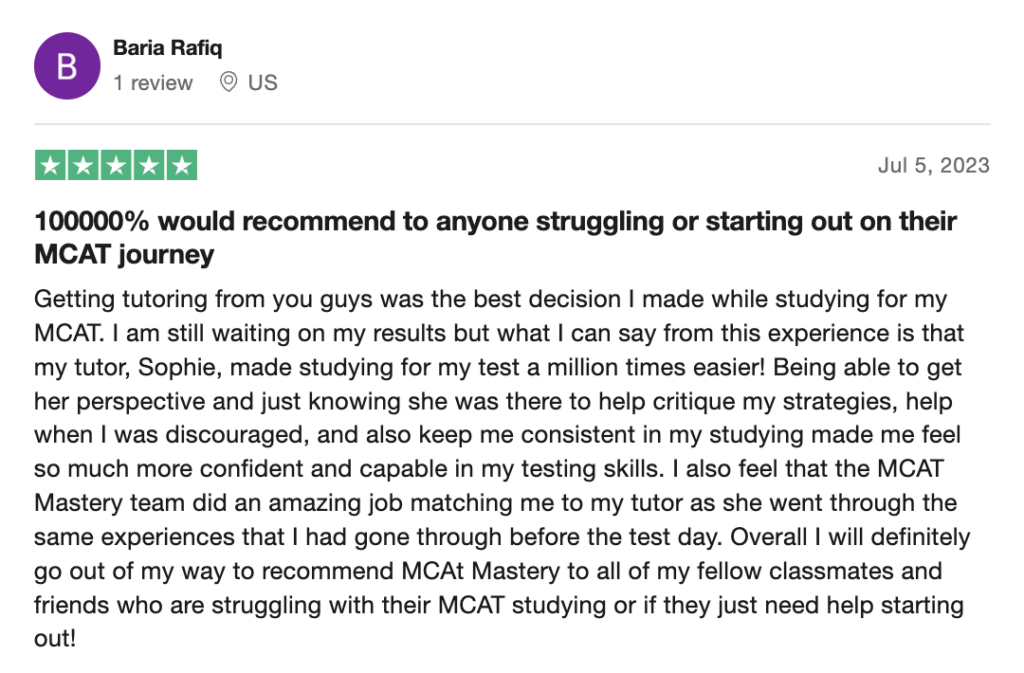
 reviews on TrustPilot
reviews on TrustPilot