I. What are the Functions and Metabolic Reactions of Ketone Bodies?
Should I do the keto diet, like what’s that all about? While we’re not professional dieticians or nutritionists here at MCAT Mastery, we can say with confidence that the mechanism behind the diet is fascinating as we’ll cover some of the basics right here!
Whether you’ve heard about them on the news or other social media platforms, ketone bodies still do have a crucial role in providing energy to the body in order to power the daily physiological functions that keep us going!
Similarly to the other fatty acid and protein metabolism articles, this process is relatively low yield so we’ll make sure to cover the pathways on a surface level! Just try to get a general overview of this content and their importance to physiological function.
II. Important Ketones and their Metabolism
A great way to think of ketones is as a transporting intermediate molecule for acetyl-CoA when needed as an energy source. Let’s first get into some of the main ketones!
A. Key Ketones
As mentioned before, ketones can be utilized as an energy source, being synthesized utilizing acetyl-CoA as a precursor which comes from the breakdown of fatty acids as discussed later.
2 prominent ketones in the body are acetoacetate & beta-hydroxybutyrate. Acetone is also a ketone but is found in such low levels where its effect is not significant.
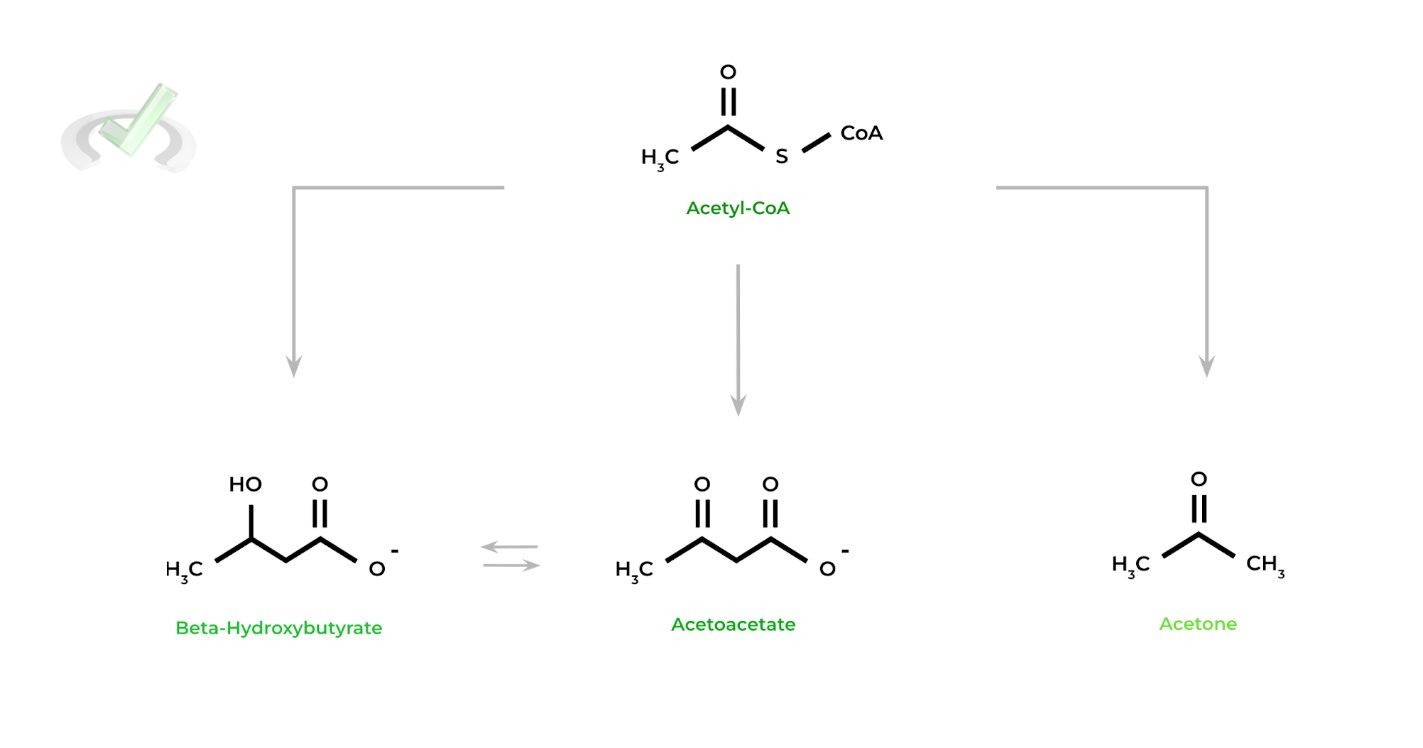
As you’ll see shortly, acetoacetate is really the main ketone as beta-hydroxybutyrate and acetone will ultimately need to be converted into acetoacetate before being utilized as an energy source.
B. Ketogenesis and Ketolysis
The primary site for ketogenesis is the liver, specifically in the hepatocytes’ mitochondria. As stated above, the acetyl-CoA produced from fatty acid 𝜷-oxidation is the precursor for the ketones.
The generated ketones can then enter the bloodstream and be uptaken by major organs that’ll use ketolysis to harness the energy from the ketones.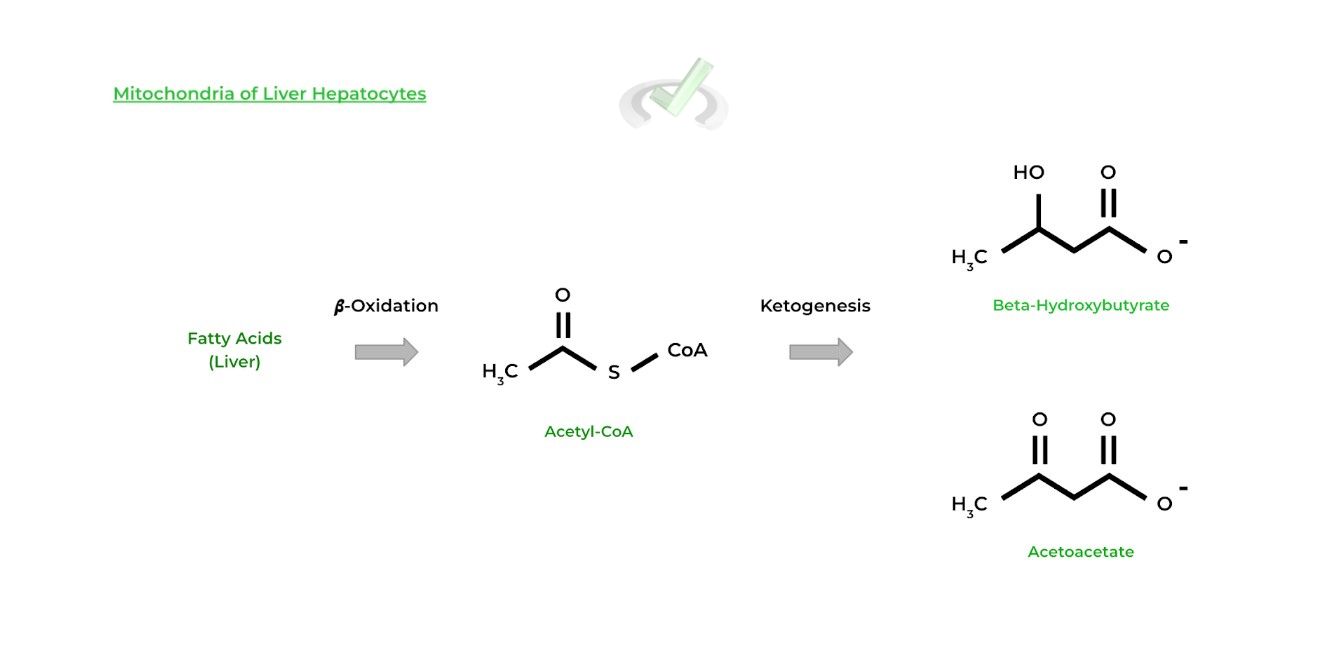
After uptake, beta-hydroxybutyrate will convert back to acetoacetate, which is then converted back to acetyl-CoA and can enter the citric acid cycle to be utilized as energy!
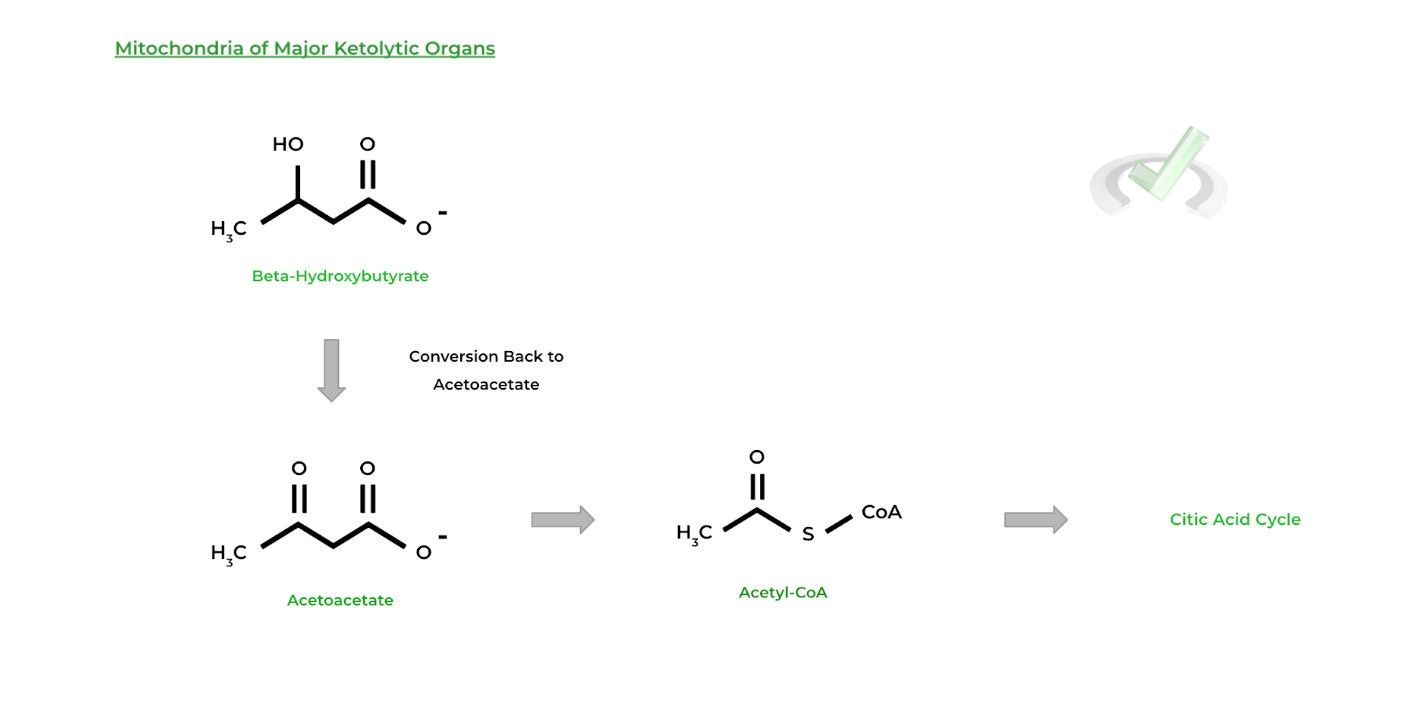
The major organs that can utilize ketones for energy are the brain, heart, and skeletal muscles. An important note is that the liver CANNOT use ketone bodies for energy even though it’s the primary source of ketogenesis.
This is because the liver lacks an important enzyme involved in ketolysis, which makes it in able to use ketones for energy!III. Bridge/Overlap
The importance of ketone bodies is highly evident in periods of extreme starvation, as they’ll become one of the main reserves for energy in periods of carbohydrate deficiency. Let’s take a look at how this works!
I. Ketone Bodies during Starvation Periods
During periods of starvation, the body, primarily at the liver and muscle, first undergoes glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis, in order to generate glucose which can be utilized by other vital organs as sources of energy.
However, the glycogen storage depletes, the body now needs another source of energy which can be provided in the form of ketones.
𝜷-oxidation breaks down fatty acids to acetyl-CoA which can be converted into ketones and go on to provide another source of energy during carbohydrate deficiency.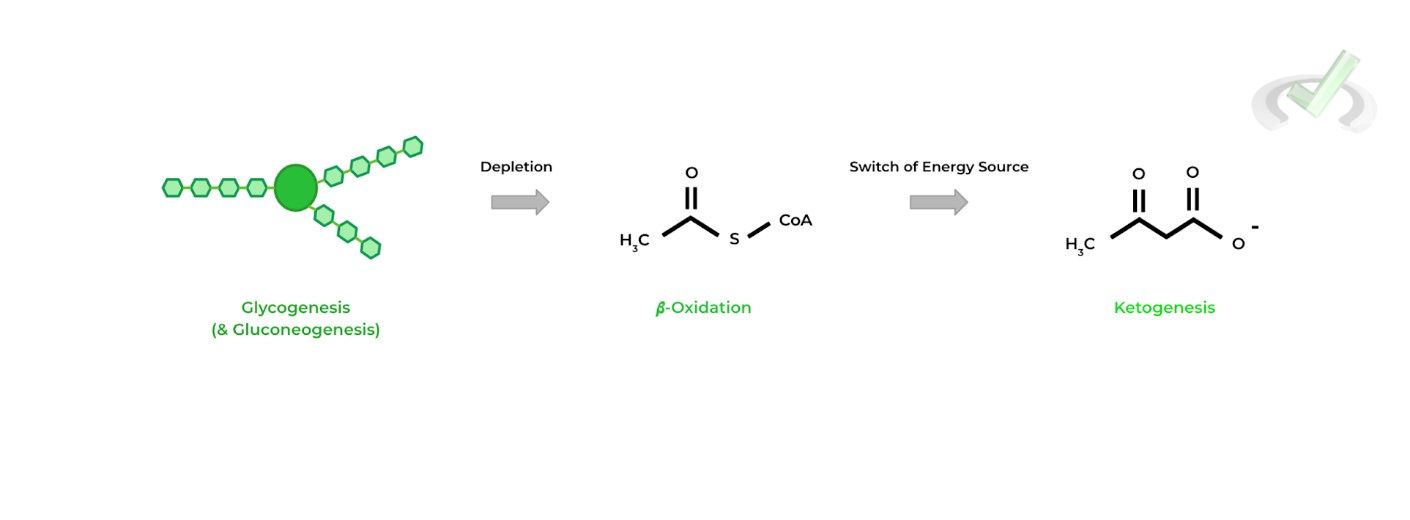
IV. Wrap Up/Key Terms
Let’s take this time to wrap up & concisely summarize what we covered above in the article!
A. Key Ketones
The 2 primary ketones utilized by the body are acetoacetate and beta-hydroxybutyrate. Acetone is also a ketone, but is found in such low concentrations where it’s insignificant.
All the ketones are synthesized utilizing acetyl-CoA as a precursor, which is derived from the 𝜷-oxidation of fatty acids. One great way to think of ketones is a transporting intermediate molecule for acetyl-CoA.B. Ketogenesis and Ketolysis
The liver is the primary site for ketogenesis, specifically in the hepatocytes’ mitochondria. The acetyl-CoA from fatty acid 𝜷-oxidation is then converted into ketones.
These can then enter the bloodstream and be uptaken by major ketolytic organs such as the brain, heart, and skeletal muscle.
Beta-hydroxybutyrate must first be converted back to acetoacetate before acetoacetate is converted into acetyl-CoA, which can then enter the citric acid cycle to produce more energy!V. Practice
Take a look at these practice questions to see and solidify your understanding!
Sample Practice Question 1
List the steps of ketogenesis and ketolysis in order. Note that some of the steps may not be used based on the validity of their statements.
I. Ketone Uptake from Bloodstream via Brain, Liver, and Heart
II. 𝜷-Oxidation of Fatty Acids in Liver Producing Acetyl-CoA
III. Conversion of Beta-Hydroxybutyrate to Acetoacetate
IV. Acetyl-CoA goes to Citric Acid Cycle
A. III, II, IV
B. II, III, IV
C. II, I, III, IV
D. I, II, III, IV
Ans. B
As we mentioned in the question stem, pay attention to the validity of the statements! Step I is false because ketones cannot be utilized by the liver as they lack a crucial ketolytic enzyme.
Disregarding statement I, all the other statements are true and follow the order as given by answer B.
Sample Practice Question 2
The keto diet is a recently popular diet which is known to promote fat loss quickly. Which of the following would have the most restricted portion in the keto diet?
A. Carbohydrates
B. Fats
C. Protein
D. Vitamins
Ans. A
Try and think back to what stimulates ketogenesis! Ketogenesis takes form when in a carbohydrate deficiency because there is a lack of sugar that can be utilized as a source of energy.
This forces the body to undergo ketogenesis to produce the ketones through the breakdown of fatty acids, which is why fat loss is relatively quick during the keto diet as fat is being burned off in order to produce ketones.







 To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these
To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these 
