I. What are the Functions of the Musculoskeletal System?
Maybe after reading these sets of articles, we’ll all be motivated to get up, hit the gym or the great outdoors, and start moving our bodies and exercising! While this is definitely much easier said than done, our ability for us to get up and get moving comes straight from the coordinated function of the musculoskeletal system.
Though often thought of as the organ system of athletes and gym bros, we definitely can overlook the importance of the musculoskeletal system in our daily lives. Let’s go ahead and delve into the main functions of the musculoskeletal system and how it helps us get our body moving!
II. Main Roles of the Musculoskeletal System
As the name implies, this system actually comprises two main tissues: muscle tissue and bone tissue which work together synergistically to allow for the movement and protection of the body and so much more. Let’s go ahead and break them down a little bit more!
A. Functions of Muscle Tissue
The main role of muscle tissue is to allow for movement of the body through their constant contraction and relaxation — when regarding the movement of the body, this primarily involves the contraction of the skeletal muscles.
Skeletal muscles attach to bones via connective tissue called tendons and via their contraction can allow for the movement of those bones along axes defined by points where the bones meet called joints. Take a look at the example below where the biceps muscles allows for movement of the forearm:
The biceps muscle has an origin point at the humerus and an insertion at the radial bone. The biceps muscle then contracts to allow for flexion along the elbow joint! To allow for extension, relaxation of the biceps muscle occurs which essentially reverses the process.
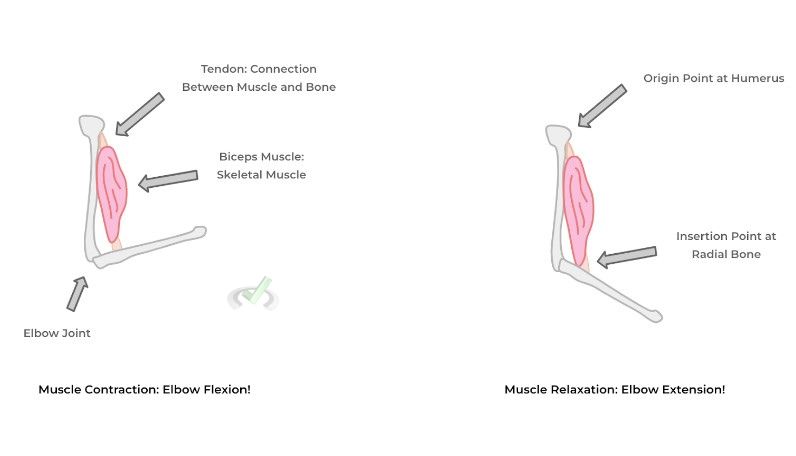
As shown, these various contractions and relaxation of skeletal muscles, which get their name due to their attachment to the skeletal bones, occurs in miniscule time and allows for all our wide range bodily movement from walking outside to the fine, pinpoint movements needed to type this article!
Additionally, there are various other types of muscle which also contract to serve other physiological functions: these include cardiac muscle whose contractions work to pump blood and smooth muscle which has a wide range of physiological function from peristalsis to vasoconstriction/dilation!
B. Functions of the Skeletal Tissue
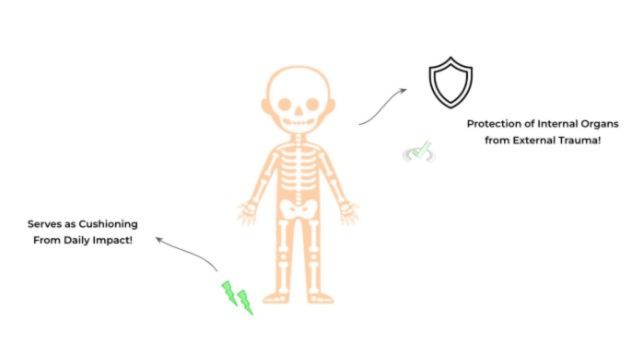
When compared to the muscle tissue, the roles of the skeletal tissue is much more widespread and extends all the way from body support to endocrine processes. The main role of the skeletal system is to act as a framework for the body for support and protection from the external world.
The strong mineral density of bone allows it to accommodate the daily impact we experience, even in actions as simple as walking! In addition to the skin, it provides an enclosure and cushioning for the internal organs from the external environment.
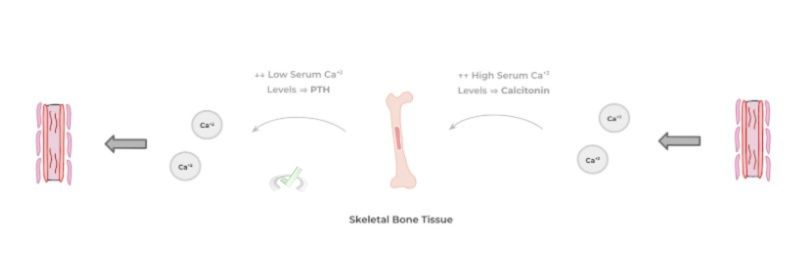
In addition, skeletal tissues also have endocrine function particularly in the storage of calcium! Based on the levels of serum calcium in the body, calcium can either be stored in or released from bone tissue to maintain physiological homeostasis!
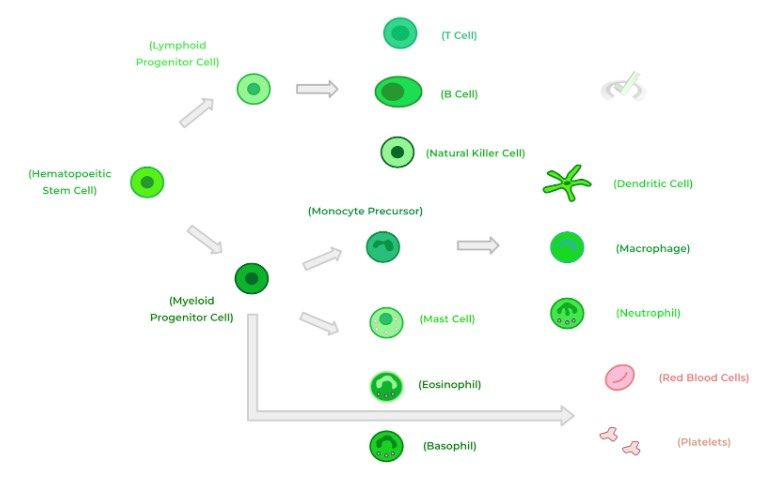
Additionally, as we covered in our immune system articles, the red bone marrow of skeletal tissue is actually the site of both red and white blood cell development as they contain the hematopoietic stem cells which differentiate into the various cells found within the blood
III. Bridge/Overlap
While, at least personally for me, highschool and college physics is something we may want to forget and put in the back of our minds, it is still important to note that a lot of basic physics principles and concepts can be applied to the movement of our body! Let’s see an application by revisiting the bicep curl example!
I. Torque Force and Biceps Curl
Recall that torque is the force required to cause rotation around an axis — an textbook example of this would be the force you apply in order to rotate a wrench. In this case, the same principle can be applied to arm flexion!
In this case, the torque force is generated by the contraction of the biceps muscle! As such, it causes the rotation of the forearm along the elbow joint! Take a look below at the actual formula as well as the diagram for how each term correlates to a certain part of bicep contraction!
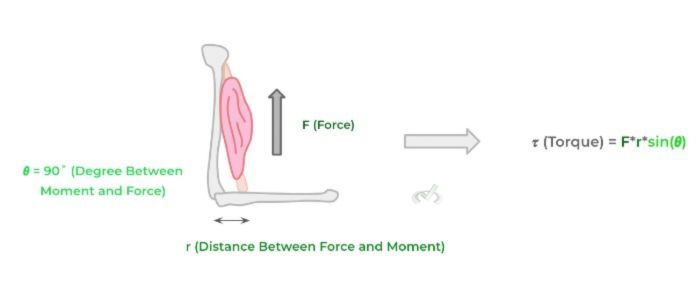
IV. Wrap Up/Key Terms
Let’s take this time to wrap up & concisely summarize what we covered above in the article!
A. Functions of Muscle Tissue
The main function of the muscles is for movement of the body via the constant contraction and relaxation. Through attachments via the bones, skeletal muscles can allow for the movement of the bones which is responsible for our bodily movement!
In addition to skeletal muscle, there are various other types of muscle tissue such as cardiac muscle found in the heart in order to pump blood throughout the body and smooth muscle which has abundant physiological function such as peristalsis and vasodilation/constriction.
B. Functions of the Skeletal Tissue
The main function of the skeletal system is to act as a solid support framework for the body and to act as a cushion and protect the internal organs from external trauma!
In addition, the skeletal tissue also serves as a big reservoir for calcium storage and various endocrine organs can promote the storage or release of calcium from the bone matrix in order to maintain physiological homeostasis.
The red bone marrow of skeletal tissue also contains the hematopoietic stem cells which are the precursor cells for all red and white blood cells!
V. Practice
Take a look at these practice questions to see and solidify your understanding!
Sample Practice Question 1
A pathologist has a sample of a muscle tissue biopsy that is suspected to be cancerous. In addition, the possible muscle tissue cancer specimen also looks to have some component of bone tissue associated with it. What type of muscle tissue is likely to be present in the biopsy specimen?
A. Skeletal Muscle Tissue
B. Cardiac Muscle TIssue
C. Smooth Muscle Tissue
Ans. A
Because the muscle tissue biopsy contains some aspects of bone tissue, the specimen is most likely a skeletal muscle tissue because this type of muscle tissue attaches to bone to allow for bodily movement.
Sample Practice Question 2
Erythropoietin is a type of hormone released from the kidney and allows for increased production of red blood cells. Which of the following tissue sites would erythropoietin bind to and stimulate erythrocyte production?
A. Compact Bone
B. Skeletal Muscle TIssue
C. Smooth Muscle Tissue
D. Red Bone Marrow
Ans. D
Recall that the red bone marrow is the main site for red and white blood cell production because they contain the hematopoietic stem cells which are precursor cells for the blood cells!







 To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these
To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these 
