Understanding reproductive processes is crucial for comprehending how life begins and develops. Let's explore the key steps in human reproduction, including gamete production, fertilization, pregnancy, and childbirth. By examining these processes, we can better appreciate the intricate details that contribute to creating new life.
I. Introduction to Reproductive Processes
Reproductive processes are a complex journey that begins with the formation of special cells and ends with the birth of a new human being. Imagine planting a seed in the ground and watching it grow into a tree.
Similarly, human reproduction starts with tiny cells that, through a series of steps, develop into a baby. These steps include producing sperm and eggs, meeting these cells, and the growth of the resulting zygote into an embryo and then a fetus.
II. Gamete Production
Gametes are the reproductive cells necessary for fertilization. In humans, these cells are sperm in males and eggs (ova) in females.
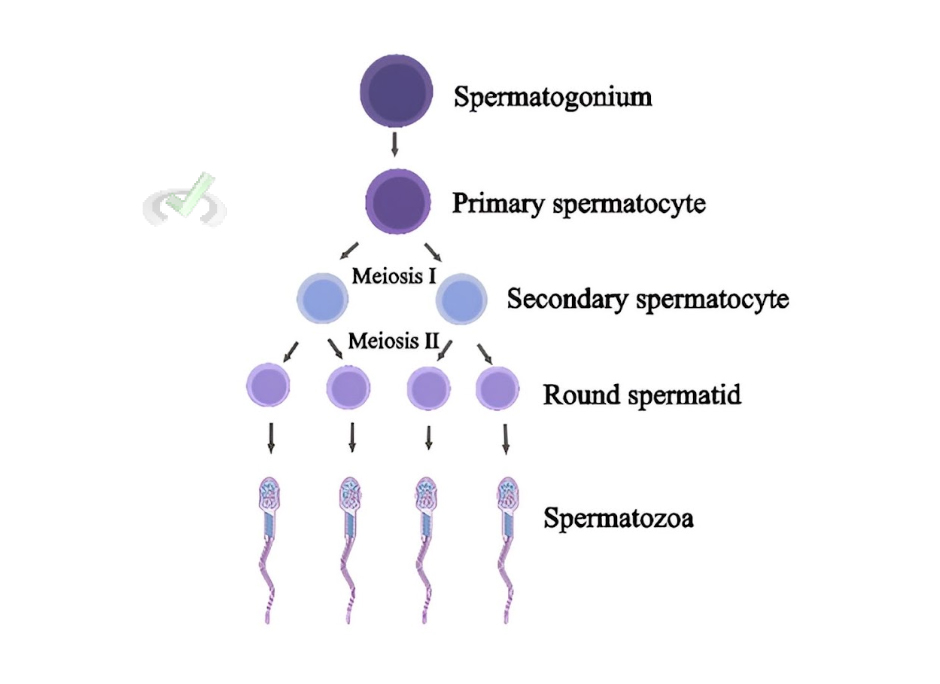
Sperm Production (Spermatogenesis)
Spermatogenesis: This is the process by which sperm is produced in the testes. It begins at puberty and continues throughout a man's life. The process occurs in the seminiferous tubules within the testes.
Stages of Spermatogenesis:
- Spermatogonia: These are the stem cells that divide to form sperm cells.
- Primary Spermatocytes: These cells undergo the first division of meiosis, a type of cell division that reduces the number of chromosomes by half.
- Secondary Spermatocytes: These cells undergo the second division of meiosis.
- Spermatids: These are immature sperm cells that mature into spermatozoa, or sperm cells.
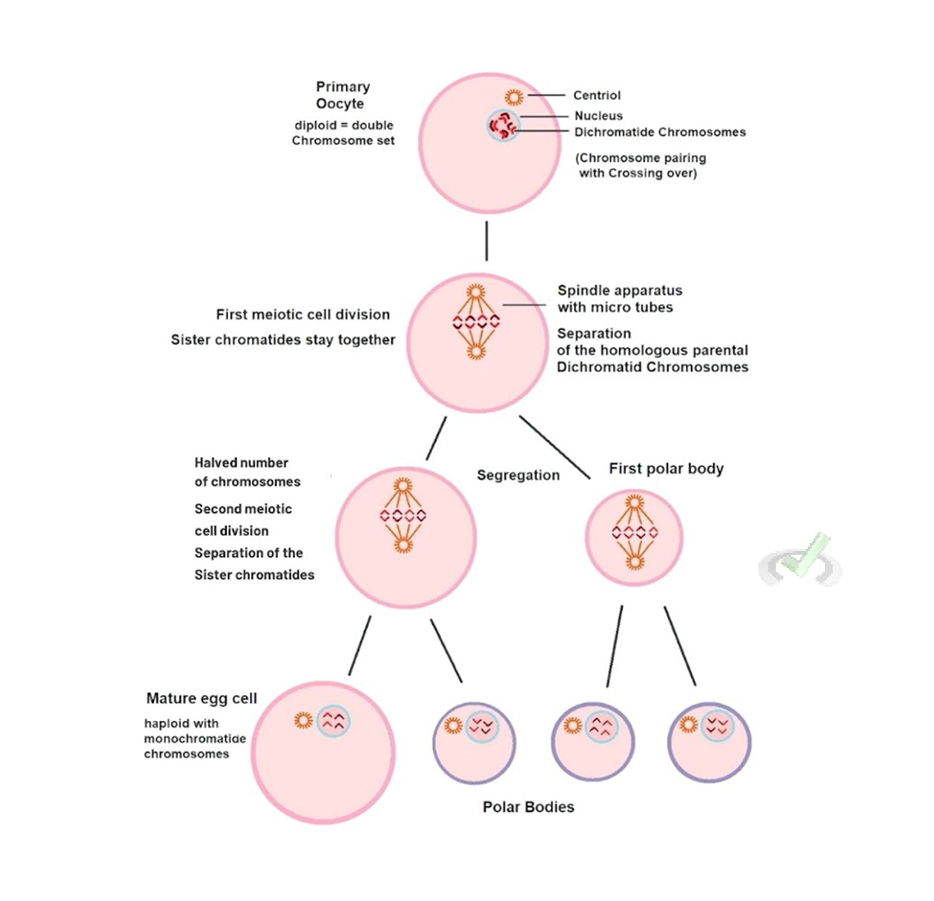
Egg Production (Oogenesis)
Oogenesis: This is the process by which eggs are produced in the ovaries. It begins before a female is born, pauses at birth, and resumes at puberty.
Stages of Oogenesis:
- Oogonia: These are the stem cells that divide to form egg cells.
- Primary Oocytes: These cells begin meiosis but pause until puberty.
- Secondary Oocytes: During each menstrual cycle, one primary oocyte resumes meiosis and becomes a secondary oocyte.
- Ovum: If fertilization occurs, the secondary oocyte completes meiosis to form a mature egg.
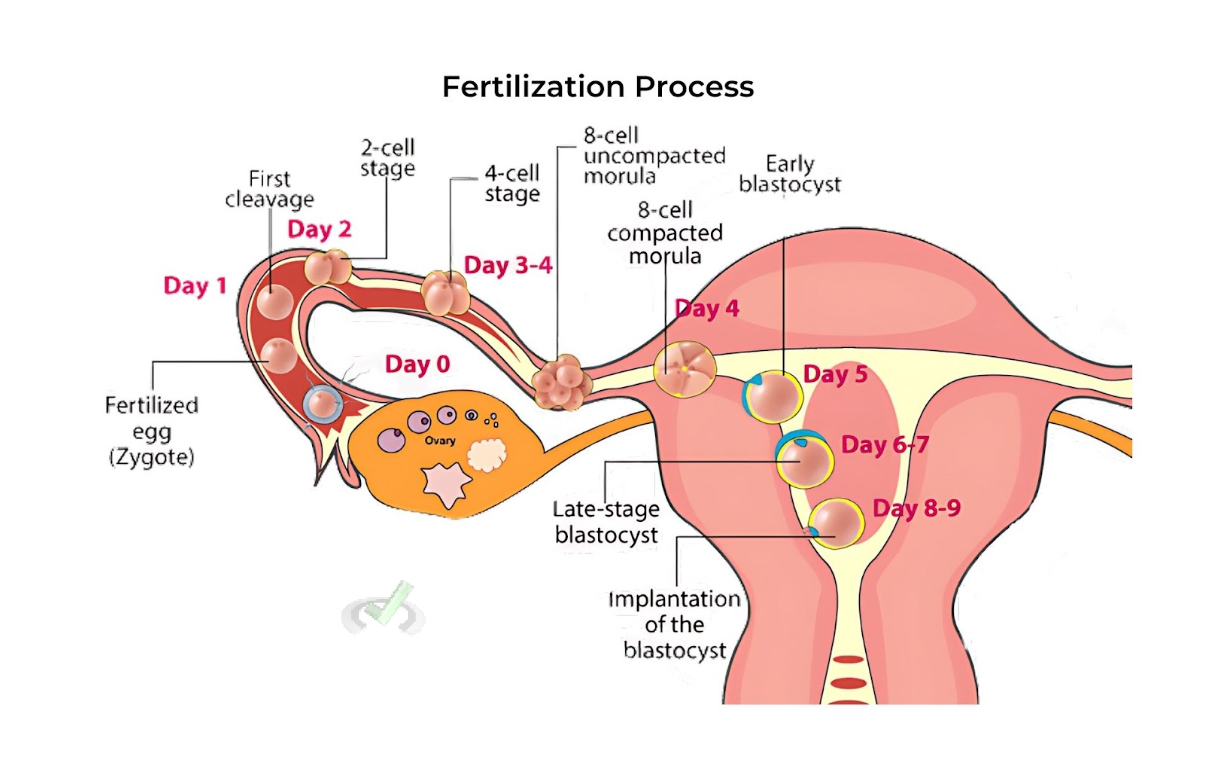
III. Fertilization
Fertilization is when a sperm cell and an egg cell unite to form a zygote.
The Process of Fertilization
- Sperm Journey: Sperm travels through the female reproductive tract to reach the egg in the fallopian tube.
- Acrosome Reaction: Enzymes are released from the sperm to penetrate the egg's outer layer.
- Sperm Penetration: The sperm penetrates the egg's outer layer.
- Fusion: The sperm and egg nuclei merge, combining their genetic material to form a zygote.
Importance of Fertilization
Fertilization is crucial because it combines genetic material from both parents, resulting in a unique individual. It also triggers the egg to complete its final stage of meiosis.
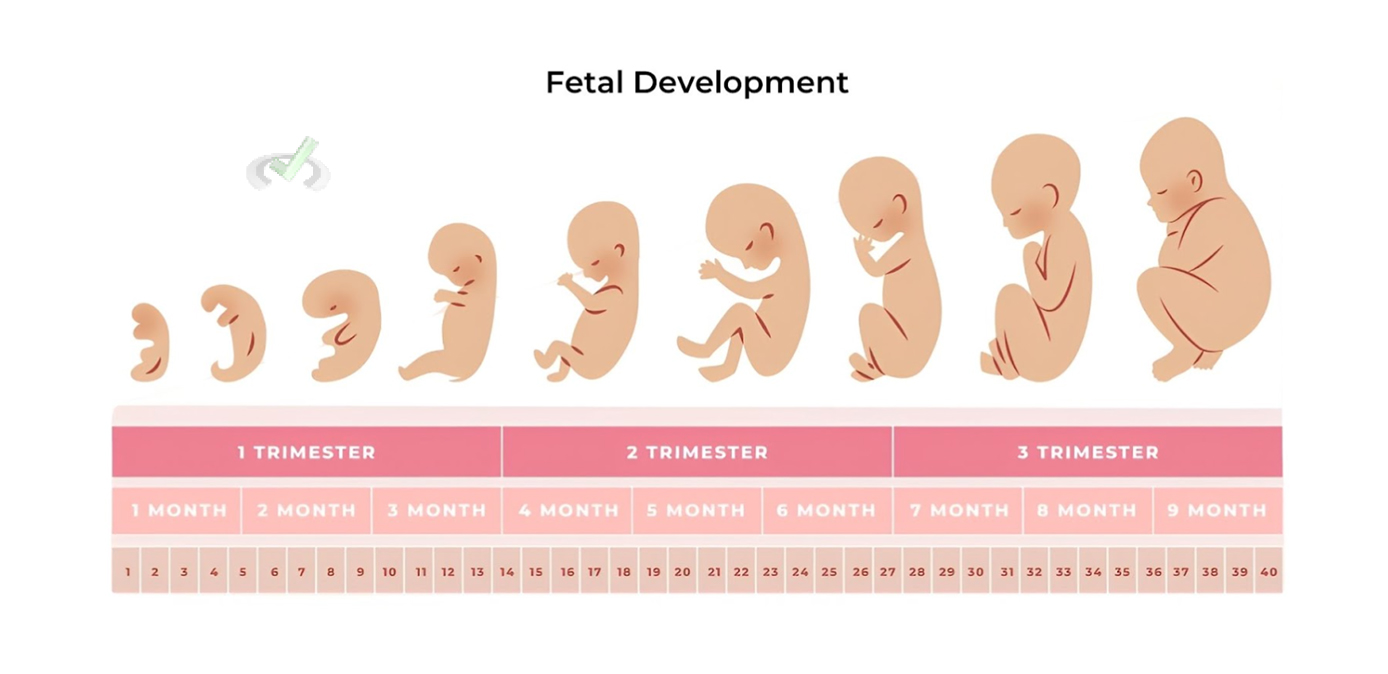
IV. Pregnancy
Pregnancy is when a fertilized egg develops into a baby inside the mother's uterus. It typically lasts about 40 weeks.
Stages of Pregnancy
- First Trimester: The zygote implants in the uterine wall and develops into an embryo. Major organs begin to form. Early prenatal care is crucial during this stage.
- Second Trimester: The fetus grows larger, and the organs continue to develop. The mother may start to feel the baby move. The sex of the baby can usually be determined during this trimester.
- Third Trimester: The fetus continues to grow and mature. The body prepares for birth. The baby positions itself for birth and gains most of its weight during this time.
Development During Pregnancy
The developing baby goes through various stages:
- Zygote: The single cell formed after fertilization.
- Embryo: The developing organism from implantation to about 8 weeks.
- Fetus: From 8 weeks to birth, the developing baby is called a fetus.
Prenatal Care
- Prenatal Tests: Common tests include ultrasounds, blood tests, and amniocentesis, which help monitor the health of the baby and the mother.
- Nutrition and Lifestyle: Proper nutrition, avoiding harmful substances like alcohol and drugs, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle is crucial for the health of both the mother and the baby.
V. Childbirth
Childbirth is the process of delivering the baby from the uterus to the outside world. It involves several stages.
Stages of Labor
- Early Labor: The cervix dilates and effaces (thin out).
- Active Labor: The cervix dilates more rapidly, and contractions become stronger and more frequent. The transition phase occurs when the cervix is fully dilated at the end of active labor.
- Delivery of the Baby: The baby moves through the birth canal and is born.
- Delivery of the Placenta: The placenta, which nourishes the baby during pregnancy, is expelled from the uterus.
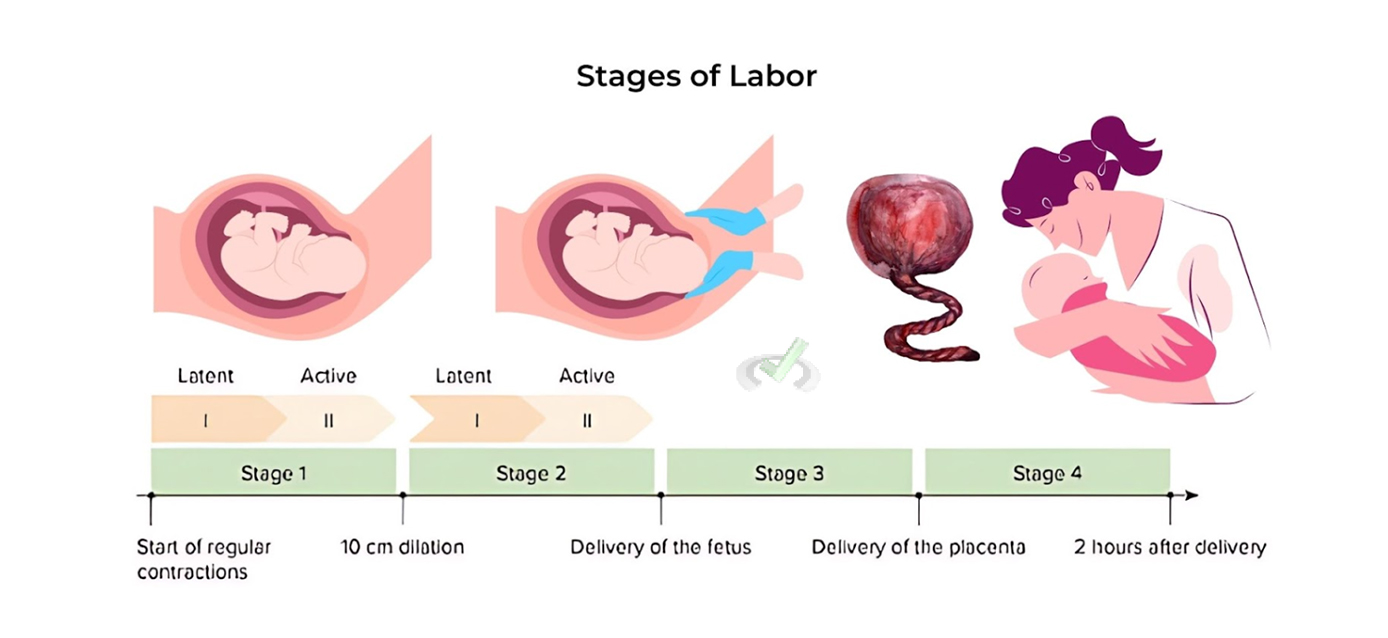
Methods of Childbirth
- Vaginal Birth: The baby is born through the birth canal.
- Cesarean Section (C-Section): The baby is delivered through a surgical incision in the mother's abdomen and uterus.
VI. Reproductive Health and Well-being
Understanding reproductive processes is not just about creating new life. It also involves maintaining reproductive health and well-being.
Reproductive Health
Preventing STIs: Safe sex practices and regular check-ups help prevent sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
Fertility Awareness: Knowing how the reproductive system works can help plan or prevent pregnancy.
Health Screenings: Regular health screenings, such as Pap smears and prostate exams, are crucial for early detection of reproductive health issues.
Emotional and Physical Well-being
Mental Health: Emotional support and counseling can be vital during pregnancy and after childbirth. Hormonal changes during and after pregnancy can affect a mother's mental health.
Physical Health: A healthy lifestyle, including proper nutrition and exercise, supports reproductive health.VII. Wrap-Up and Key Terms
Let's review the key points we covered about reproductive processes!
Key Processes
- Gamete Production: Spermatogenesis in males and oogenesis in females.
- Fertilization: The union of sperm and egg to form a zygote.
- Pregnancy: The development of the baby from a zygote to birth.
- Childbirth: The delivery of the baby through labor and delivery.
- Spermatogenesis: Process of sperm production.
- Oogenesis: Process of egg production.
- Zygote: The fertilized egg cell.
- Embryo: Early stage of development after implantation.
- Fetus: Later stage of development until birth.
VIII. Practice Questions
Sample Practice Question 1
Complete the following statement: The process by which sperm are produced is called __________.
A. Oogenesis
B. Fertilization
C. Spermatogenesis
D. Pregnancy
Ans. C
Spermatogenesis is the process of sperm production in the testes.
Sample Practice Question 2
What is the term for the developing baby from implantation to about 8 weeks?
A. Zygote
B. Fetus
C. Embryo
D. Ovum
Ans. C
An embryo is the term for the developing baby from implantation to about 8 weeks.







 To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these
To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these 
