We defined ionic bonds as bonds formed through the transfer of electrons. It’s also a bond that happens between metals and nonmetals.
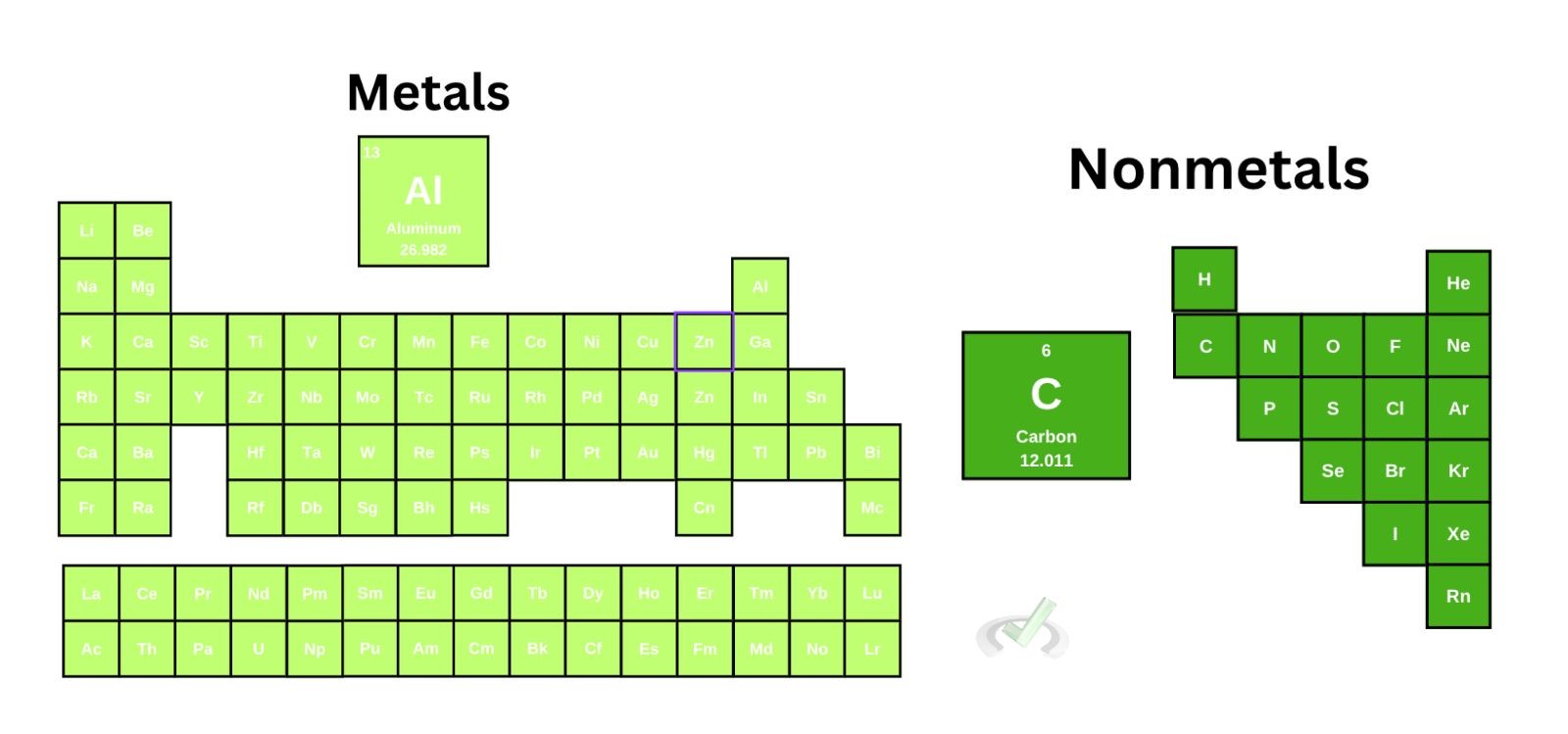
In an ionic bond, a metal donates an electron to a nonmetal. Once a metal donates an electron, it becomes a cation. Once the nonmetal accepts an electron, it becomes an anion. This shift into ions happens since the metal loses a negatively charged electron; it loses a negative charge and becomes positive. In the same way, a nonmetal gains an electron and a negative charge, which turns it into an anion.
One of the many reasons why ionic bonds are known as the strongest bonds is due to their nature of bonding. Ionic bonds form through electrostatic attraction between a cation and an anion. Covalent bonds form by sharing electrons to gain stability. On the other hand, Ionic bonds involve an actual transfer of electrons; once bonding is through, the attraction between the positively charged ion and the negatively charged ion keeps the bond intact. Covalent bonds rely on the overlap of orbitals where they share an electron pair. In contrast, ionic bonds remain strong due to their opposite charges.I. Ionic Bonding
We previously introduced the formula for ionic bonding. Here, we have a metal C with a charge of positive x and a nonmetal A with a charge of negative y. Once these two bond, they form an ionic compound combining metal and nonmetal.

The subscript for the cation is just the absolute value of the charge of the anion, and the subscript for the anion has the same value as the charge of the cation! These subscripts indicate how many atoms of an element are present to form a stable ionic compound.
II. Other Examples
Let’s dig deeper by exploring a few examples.
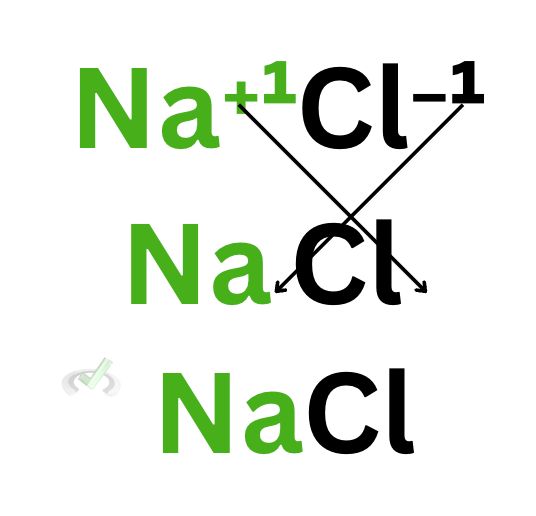
A. Sodium Chloride (NaCl)
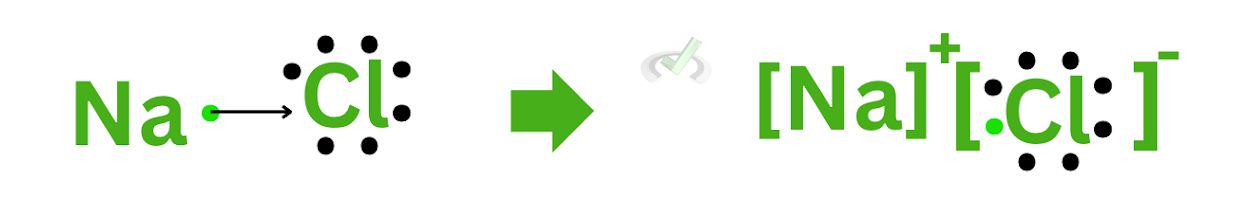
Here, sodium has a plus 1 charge, and chloride has a minus 1 charge. Once it forms an ionic bond, its subscripts will change to their respective charges. Since both subscripts would only be 1, there is no need to write down 1 as a subscript of each element.
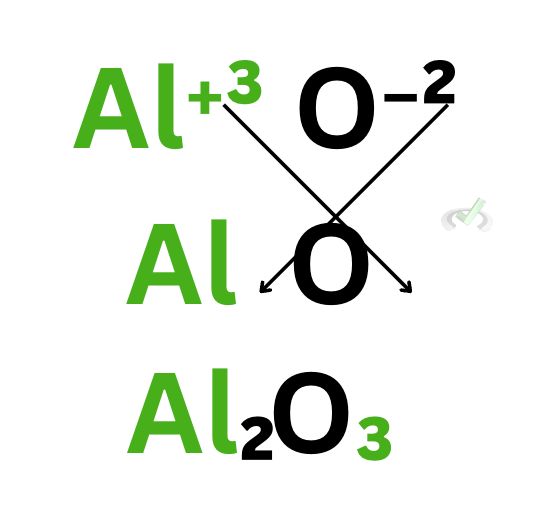
B. Aluminum Oxide (Al₂O₃)

For aluminum oxide, we see that aluminum has a charge of plus 3 and oxide has a charge of -2. Note that for ions, we normally change their names from their elemental names to indicate that the element is now an ion. Thus, we call oxygen “oxide” and chlorine “chloride.”
Now, we’ll do the same thing we did for sodium chloride. The charge of the nonmetal (O) goes as a subscript of the metal, and the charge of the metal (Al) becomes the subscript of the nonmetal. We see that aluminum has a subscript of 2 and oxygen has a subscript of 3.
C. Barium Chloride (BaCl₂)
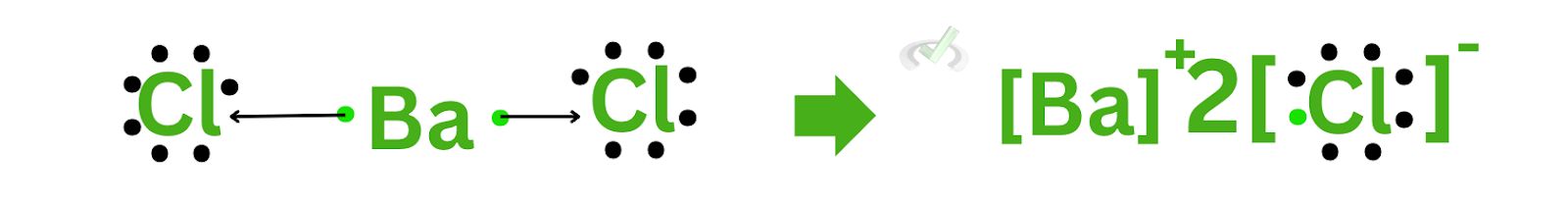
Barium has a plus 2 charge, and chloride has a minus 1 charge. Doing the same thing we did, barium will now have a subscript of 1, and chloride will have a subscript of 2. Since it’s already implied that barium is already 1 element, we no longer have to include 1 as a subscript. This leaves us with the ionic compound barium chloride (BaCl₂).
III. Conclusion
Ionic bonds are the strongest types of bonds due to the electrostatic attraction between a cation and an anion. These bonds form between cations and anions through the transfer of electrons. We use the charge of the metal as the subscript of the nonmetal and the charge of the nonmetal as the subscript of the metal. Once these two form an ionic bond. These subscripts indicate the number of atoms involved in the ionic compound formed.
IV. Key Terms
- Anion - A negatively charged ion.
- Cation - A positively charged ion.
- Covalent bond - A bond between nonmetals through electron sharing.
- Electrostatic attraction - The force of attraction between opposite charges.
- Ionic bond - A bond formed between a metal and a nonmetal through the transfer of electrons.
V. Practice Questions
Sample Practice Question 1
Which of the following statements is not true?
A. An ionic bond will form between carbon and oxygen.
B. A metal will transfer its electrons to a nonmetal in an ionic bond.
C. An ionic bond forms between potassium and chlorine.
D. A nonmetal accepts electrons from a metal in an ionic bond.
Ans. A
Sample Practice Question 2
Calcium ions have a plus 2 charge whereas a sulfate ion has a minus 2 charge. These ions form an ionic bond. Which of the following does not show the product of ionic bonding through these two ions?
A.
B.
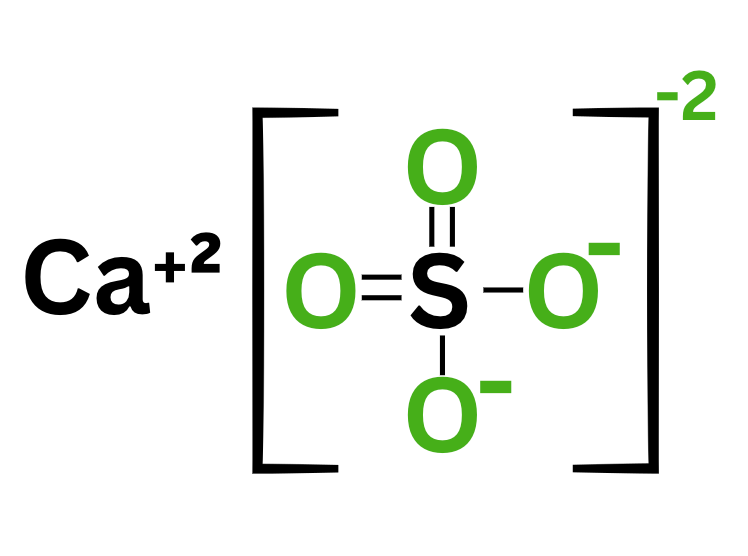
C.
D.
Calcium Sulfate
Ans. A








 To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these
To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these 
