When we think of chemistry, the ball and stick figure of molecules must be the first thing that pops up in our minds. While there is a lot more to this structure than being a symbol of chemistry, this representation of molecules is actually a helpful way to visualize how molecules look.
These models are theorized to effectively visualize the arrangement of atoms in a molecule. There are many important aspects to it but one of the key things we notice in these structures is that molecular geometry is affected by electron repulsion. This is why when we want to discuss how molecules look, we consider all of the valence electrons involved in a molecule–bonded or not.
I. Electron Repulsion
The concept of electron repulsion is simple: electrons repel each other.
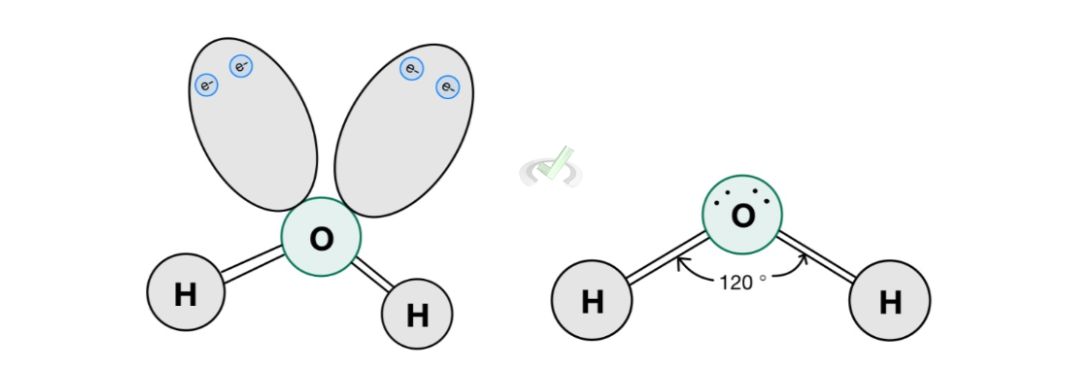
Atoms are surrounded by a cloud of electrons. When these atoms are involved in a molecule, they tend to be as far away from other electrons as possible. A good example of this is a water molecule.
Water has two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. Oxygen has six valence electrons and when it bonds with two hydrogen atoms, it completes its octet with two lone pairs. Its molecular geometry will be bent because the two lone pairs will repel each other and the hydrogen atoms.
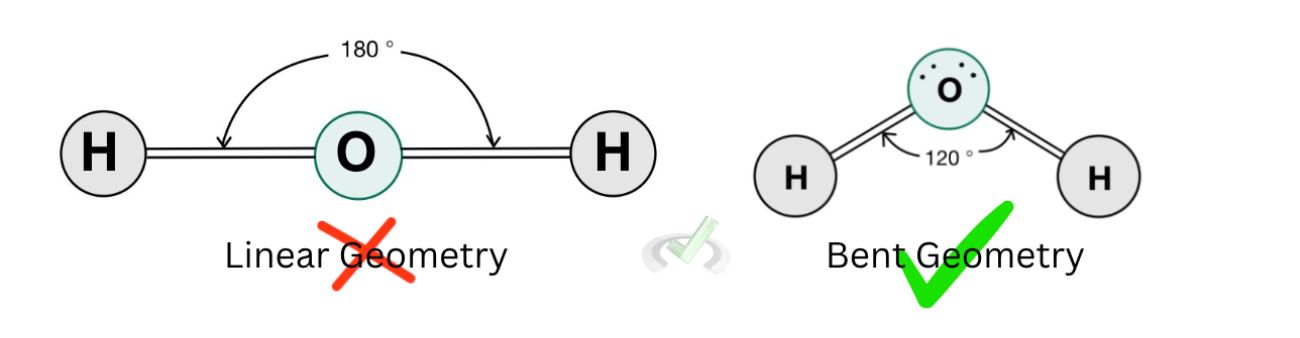
This bending of the molecular geometry is due to the electron repulsion between the lone pairs and the hydrogen atoms. It cannot simply assume a linear geometry because the lone pairs of electrons act as if they were bonding atoms as well.
II. Electronic Geometry and Molecular Geometry
In the example above, we saw two structures of the water molecule: one where lone electron pairs were present and the other where lone pairs weren't present.
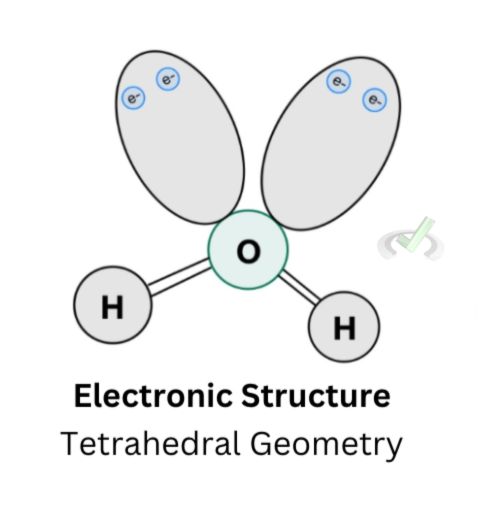
The structure showing lone pairs is known as electronic geometry. In drawing the electronic geometry, we acknowledge the spaces that lone pair(s) take in the molecular structure. We do this by including the lone pairs to draw the electron structure.
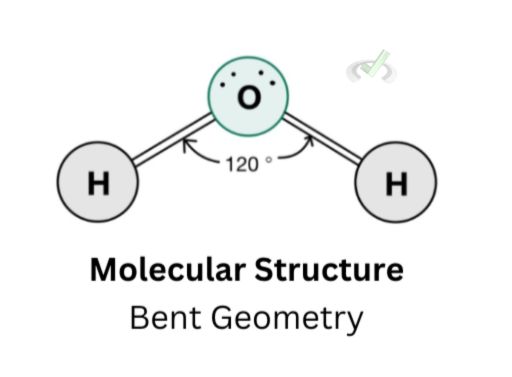
Molecular structure, on the other hand, shows the formal structure of a molecule without the lone pairs. This way, we see how the molecule looks while still considering the electron repulsion caused by the lone pairs. Notice how the hydrogen molecules and the oxygen still assume the same shape in their electronic geometry. The only difference in this case is not having any lone pair.
III. Other Examples
Let’s use the table below to better understand how we can think of electronic and molecular geometry when we look at molecules.
Steric Number | No Lone Pair | One Lone Pair | Two Lone Pairs |
|---|---|---|---|
2 | 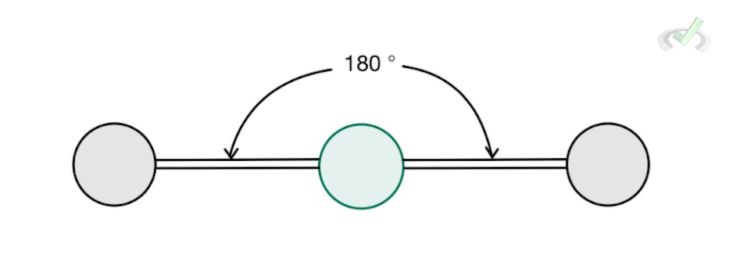 Linear AX₂ | Enter your text here... | Cell |
3 | 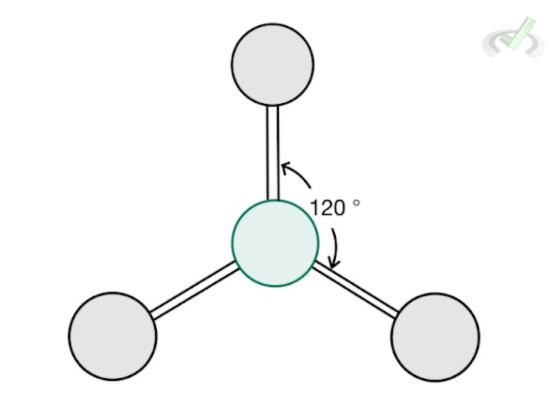 Trigonal Planar AX₃ | 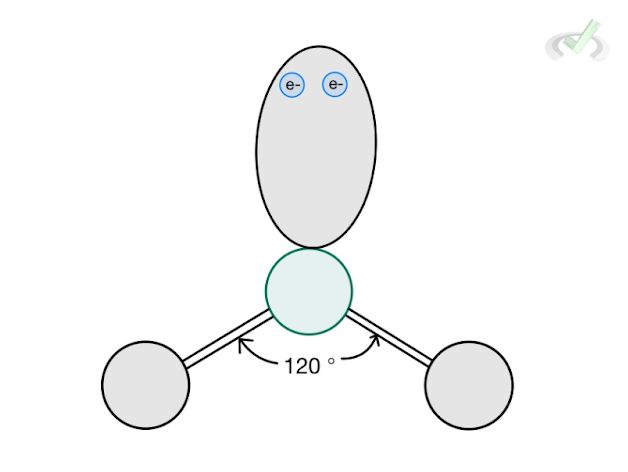 Bent AX₂ | Cell |
4 | 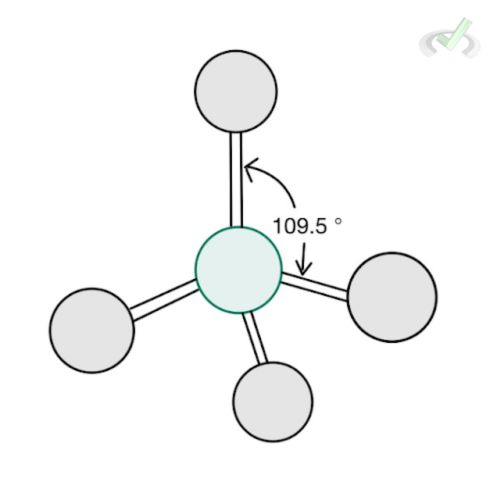 Tetrahedral AX₄ | 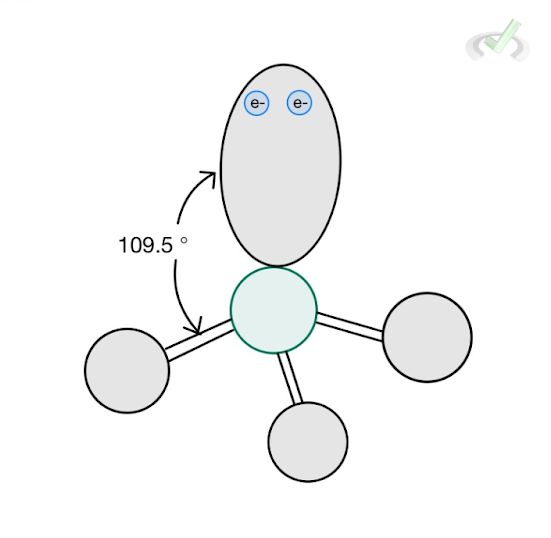 Trigonal Pyramidal AX₃ | 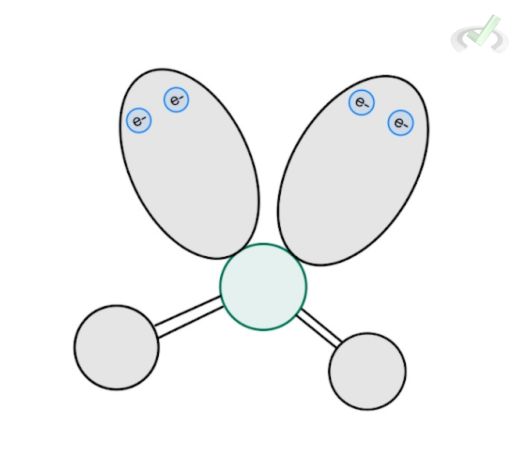 Bent AX₂ |
The Steric Number is the total number of atoms bonded to a central atom and the lone pairs attached. We use the steric number to predict the molecular structure of a molecule
A. Linear Geometry
Let’s use beryllium hydride as an example. This molecule is one that does not obey the octet rule. It only has 2 valence electrons to share and is stable enough in the form of BeH2.
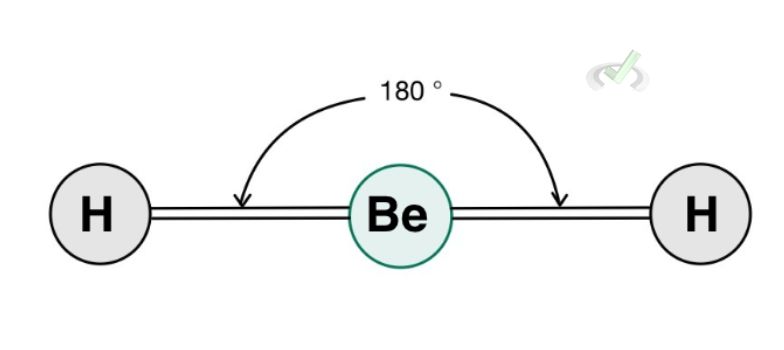
This molecule assumes a linear geometry since hydrogen atoms repel each other. Since there are no lone pairs around the central atom and two bonding atoms, it has a steric number of 2, and it assumes a linear structure. This also means that its electronic geometry is the same as its electronic geometry due to the lack of lone pairs–only the hydrogen atoms in this case would repel each other and the best shape it can take up being as far away from each other as possible, is a linear geometry.
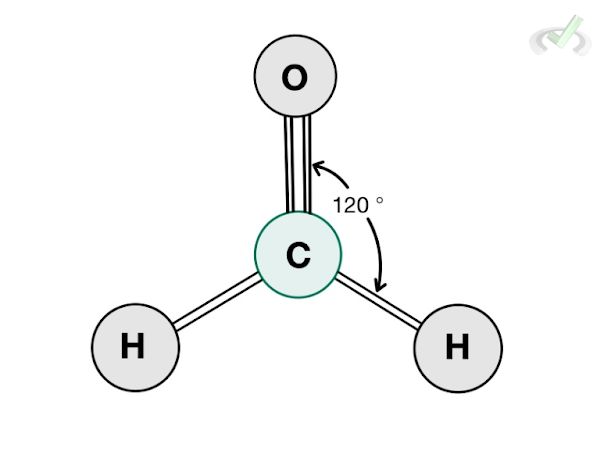
B. Trigonal Planar
Formaldehyde (CH2O) is a molecule that has three bonding atoms and no lone pair. Since there are three bonding atoms and no lone pairs, it has a steric number of 3. Its structure follows a trigonal planar structure where each bonding atom forms an angle of 120 degrees from each other.
C. Tetrahedral
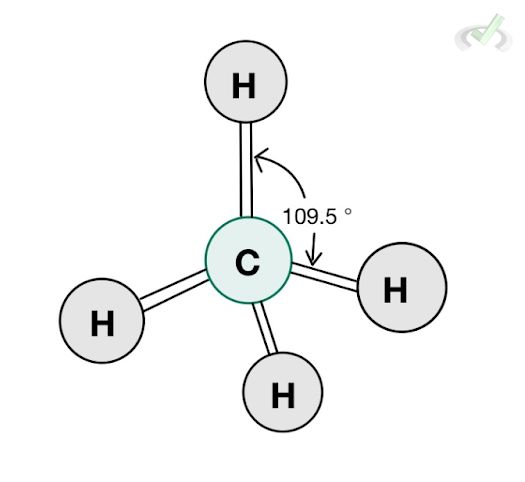
Methane (CH4) is a molecule with a tetrahedral structure. Its steric number is four since it has four bonding atoms and no lone pair. Each bonding atom forms an angle of 109.54 degrees from each other.
D. Trigonal Pyramidal
Ammonia (NH3) has three bonding atoms and one lone pair. Therefore, it has a steric number of four (3 hydrogen + 1 lone pair). It then assumes a tetrahedral electronic structure where all valence electrons form an angle of 109.5 degrees.
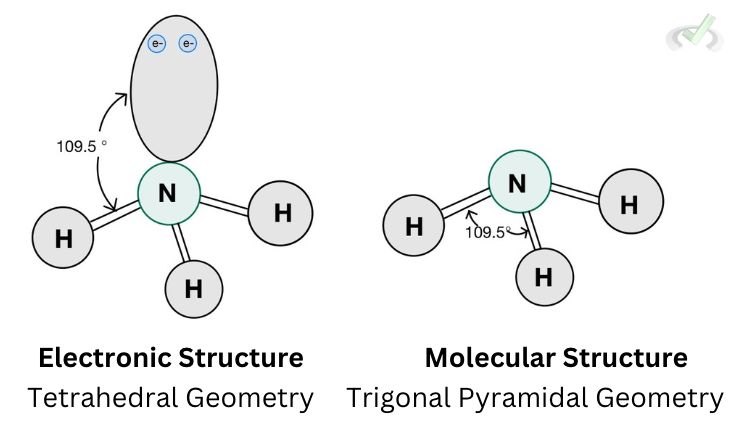
The structure, however, is different when we look at the molecular structure of ammonia, here, we consider the electronic repulsion effect of the lone pair but we no longer include the lone pair in drawing the structure.
E. Bent Structure
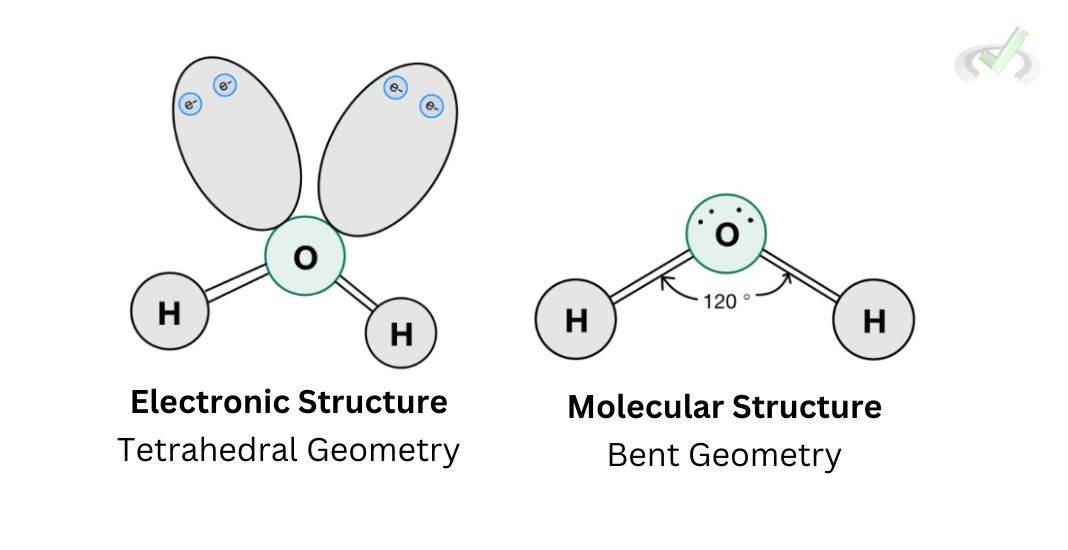
Water is a molecule with a tetrahedral electronic structure since it has a steric number of 4 (2 hydrogen + 2 lone pairs). Its molecular structure follows a bent structure since we no longer include the lone pairs in the structure itself. We only consider its electronic repulsion. The overall molecular structure of water would be bent.
IV. Conclusion
Atoms in a molecule assume positions according to electron repulsion. Since electrons repel each other, the tendency of atoms and lone pairs surrounding a central atom in a molecule is to be as far away from each other as possible. This leads to a molecular geometry that allows stability in response to electron repulsion. When we consider the arrangement of a molecule showing the lone pairs and the bonding atoms, we’re taking note of the electronic geometry of a molecule. When we remove these electron pairs from a structure and only look at how the molecule would look with its bonding atoms involved, we then consider its molecular geometry.
V. Key Terms
- Electron Repulsion - The repulsive force between electron pairs in a molecule which affects the arrangement of atoms in a molecule.
- Electronic Geometry - The arrangement of atoms in a molecule that considers all electron pairs–bonding and lone pairs.
- Molecular Geometry - The arrangement of atoms in a molecule excluding the lone pairs.
VI. Practice Questions
Sample Practice Question 1
Which of the following does not have a tetrahedral structure?
A. Electronic geometry of ammonia (NH3)
B. Molecular geometry of methane (CH4)
C. Electronic geometry of water (H2O)
D. Molecular geometry of boron trifluoride (BF3)
Ans. D
Sample Practice Question 2
Which of the following statements is not true?
A. The electronic geometry of carbon dioxide is the same as its molecular geometry.
B. Sulfur dioxide (SO2; one lone pair) has a bent molecular geometry.
C. Boron trichloride (BCl3) has a tetrahedral electronic geometry.
D. Water has a bent molecular geometry and a tetrahedral electronic geometry.
Ans. C







 To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these
To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these 
