Electrochemical cells involve redox reactions, where chemical energy is converted into electrical energy or vice versa. Understanding the redox chemistry in these cells is essential because it explains how they generate or use electrical energy. This is fundamental in the operation of batteries, fuel cells, and other devices.
I. Introduction to Electrochemical Cells
Electrochemical cells generate electrical energy from chemical reactions or use electrical energy to cause chemical changes. There are two main types: galvanic (or voltaic) cells and electrolytic cells.
Galvanic Cells
Definition: These cells generate electrical energy from spontaneous redox reactions.
Example: A common example is the zinc-copper cell, which powers small devices.
Electrolytic Cells
Definition: These cells use electrical energy to drive non-spontaneous chemical reactions.
Example: Electrolysis of water to produce hydrogen and oxygen gases, which can be used as clean fuel sources.
II. Basic Components of Electrochemical Cells
Each electrochemical cell consists of several key components:
- Anode: The electrode where oxidation occurs.
- Cathode: The electrode where reduction occurs.
- Electrolyte: The medium that allows ion movement between the electrodes, completing the electrical circuit.
III. Redox Reactions in Electrochemical Cells
In an electrochemical cell, redox reactions occur at the electrodes. Here’s how they work:
Oxidation at the Anode
- Process: A substance loses electrons.
- Example: In a zinc-copper cell, zinc is oxidized:
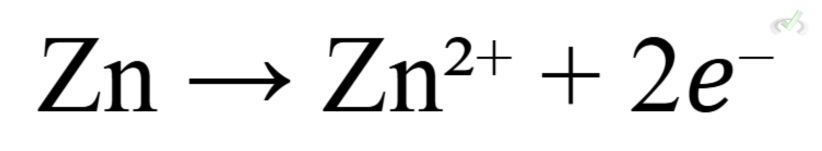
Reduction at the Cathode
- Process: A substance gains electrons.
- Example: In a zinc-copper cell, copper is reduced:
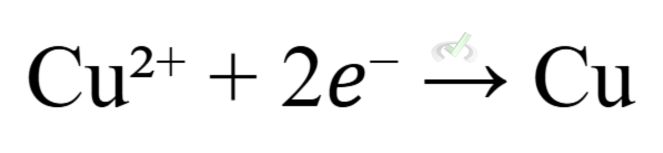
IV. Common Types of Electrochemical Cells
A. Galvanic Cells (Voltaic Cells)
These cells convert chemical energy into electrical energy through spontaneous redox reactions. Here's a detailed look at a zinc-copper galvanic cell:
- Setup: Zinc electrode (anode), copper electrode (cathode), and an electrolyte solution.
- Reaction:
- At the Anode (Oxidation):
- At the Cathode (Reduction):
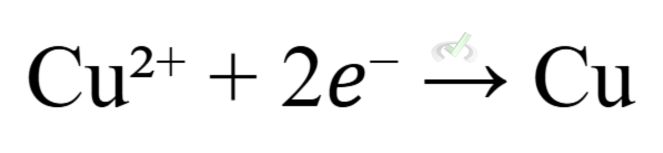
- Overall Cell Reaction:
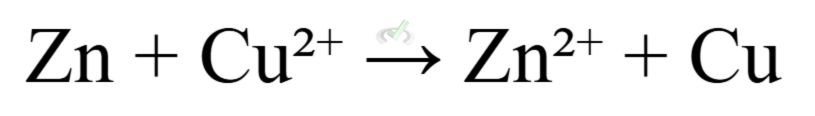
B. Electrolytic Cells
These cells use electrical energy to drive non-spontaneous reactions. An example is the electrolysis of water:
- Setup: Two electrodes in water connected to a power source.
- Reaction:
- At the Anode (Oxidation):
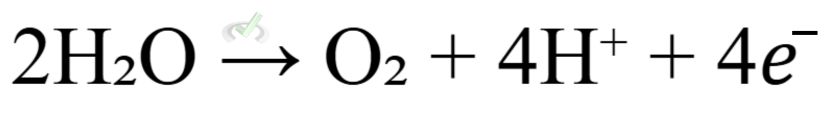
- At the Cathode (Reduction):
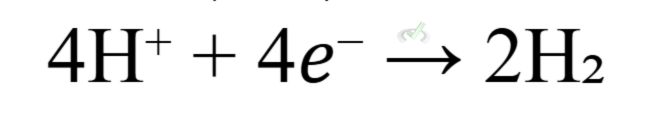
- Overall Cell Reaction:
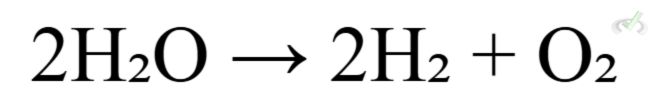
V. Applications of Electrochemical Cells
Electrochemical cells have various applications:
Batteries: Devices that store chemical energy and convert it to electrical energy.
- Example: Lithium-ion batteries used in smartphones and electric cars.
Fuel Cells: Devices that generate electricity by combining hydrogen and oxygen.
- Example: Hydrogen fuel cells are used in some vehicles and backup power systems.
Electrolysis: A process that uses electrical energy to drive a chemical reaction.
- Example: Electrolysis of water to produce hydrogen and oxygen gases.
VI. Important Concepts in Electrochemical Cells
A. Electrode Potentials
The voltage difference between an electrode and its surroundings.
Standard Electrode Potential (E°): Measured under standard conditions (1M concentration, 1 atm pressure, 25°C).B. Nernst Equation
Purpose: Calculates the cell potential under non-standard conditions.
Equation:
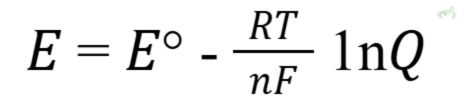
Where:
- E = cell potential
- E° = standard cell potential
- R = gas constant (8.314 J/(mol·K))
- T = temperature in Kelvin
- n = number of moles of electrons
- F = Faraday's constant (96485 C/mol)
- Q = reaction quotient
VII. Bridge/Overlap
Electrochemical cells play a central role in chemistry and bridge into many other fields that impact our daily lives and the environment. Understanding how these cells work helps us appreciate their broader implications and applications. Here’s how electrochemical cells connect to various areas:
A. Energy Conversion
Electrochemical cells show how chemical energy can be converted to electrical energy. This is important in many technological applications.
B. Environmental Impact
Fuel cells produce clean energy, reducing dependence on fossil fuels and lowering emissions. This is crucial for environmental sustainability.
VIII. Wrap-Up and Key Terms
Understanding redox reactions in electrochemical cells is crucial for academic study and practical applications. These reactions power many of the devices we use every day, and they also play a significant role in efforts to create more sustainable energy sources.
Key Terms:
- Anode: Electrode where oxidation occurs.
- Cathode: Electrode where reduction occurs.
- Electrolyte: Substance that allows ion movement between electrodes.
- Galvanic Cell: Generates electricity from spontaneous redox reactions.
- Electrolytic Cell: Uses electricity to drive non-spontaneous reactions.
IX. Practice Questions
Sample Practice Question 1
What happens at the anode of a galvanic cell?
A. Reduction
B. Oxidation
C. Ion Exchange
D. Electron Flow
Ans. B
In a galvanic cell, the anode is where oxidation (loss of electrons) occurs.
Sample Practice Question 2
Which component in an electrochemical cell allows ions to move between electrodes?
A. Anode
B. Cathode
C. Electrolyte
D. Salt Bridge
Ans. C
The electrolyte facilitates the movement of ions within the cell.







 To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these
To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these 
