Gas laws are fundamental in understanding how gases behave under different pressure, volume, and temperature conditions. This knowledge is crucial in fields ranging from meteorology to engineering.
I. Introduction to Gas Laws
Gas laws describe how gases interact with pressure, volume, and temperature changes. Let's explore these fundamental laws.
A. Boyle's Law
Boyle's Law states that the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume, provided the temperature is constant. This means if you increase the pressure, the volume decreases, and if you decrease the pressure, the volume increases. This is because gas particles are forced closer together when pressure is applied.
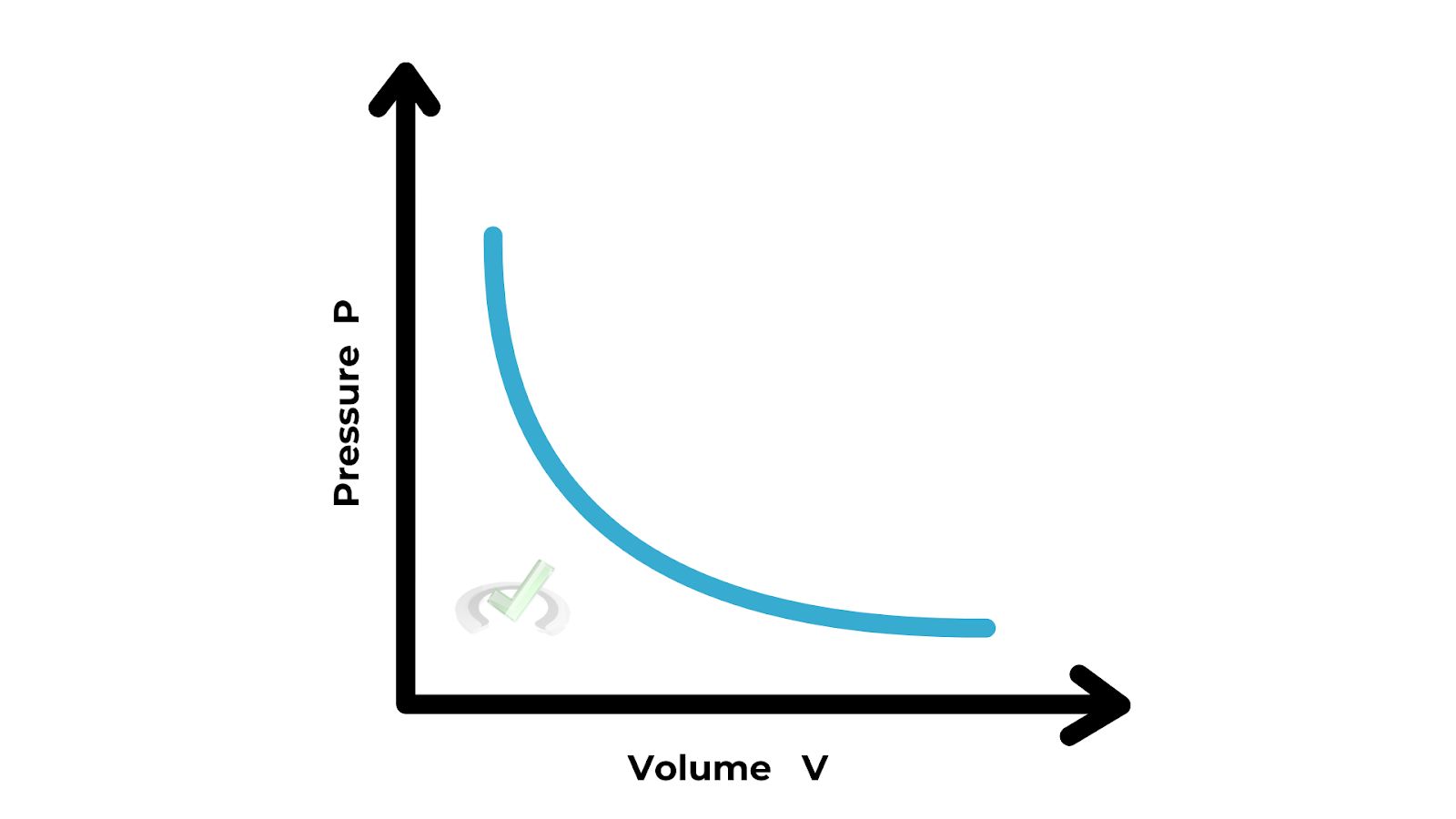
Formula:
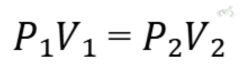
Example:
If gas occupies 3 liters at 2 atmospheres (atm) of pressure, what volume will it occupy at 3 atm?
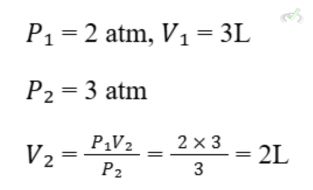
B. Charles's Law
Charles's Law states that the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature (in Kelvin), provided the pressure is constant. This means if you increase the temperature, the volume increases; if you decrease the temperature, the volume decreases. This is because gas particles move faster at higher temperatures, causing the gas to expand.
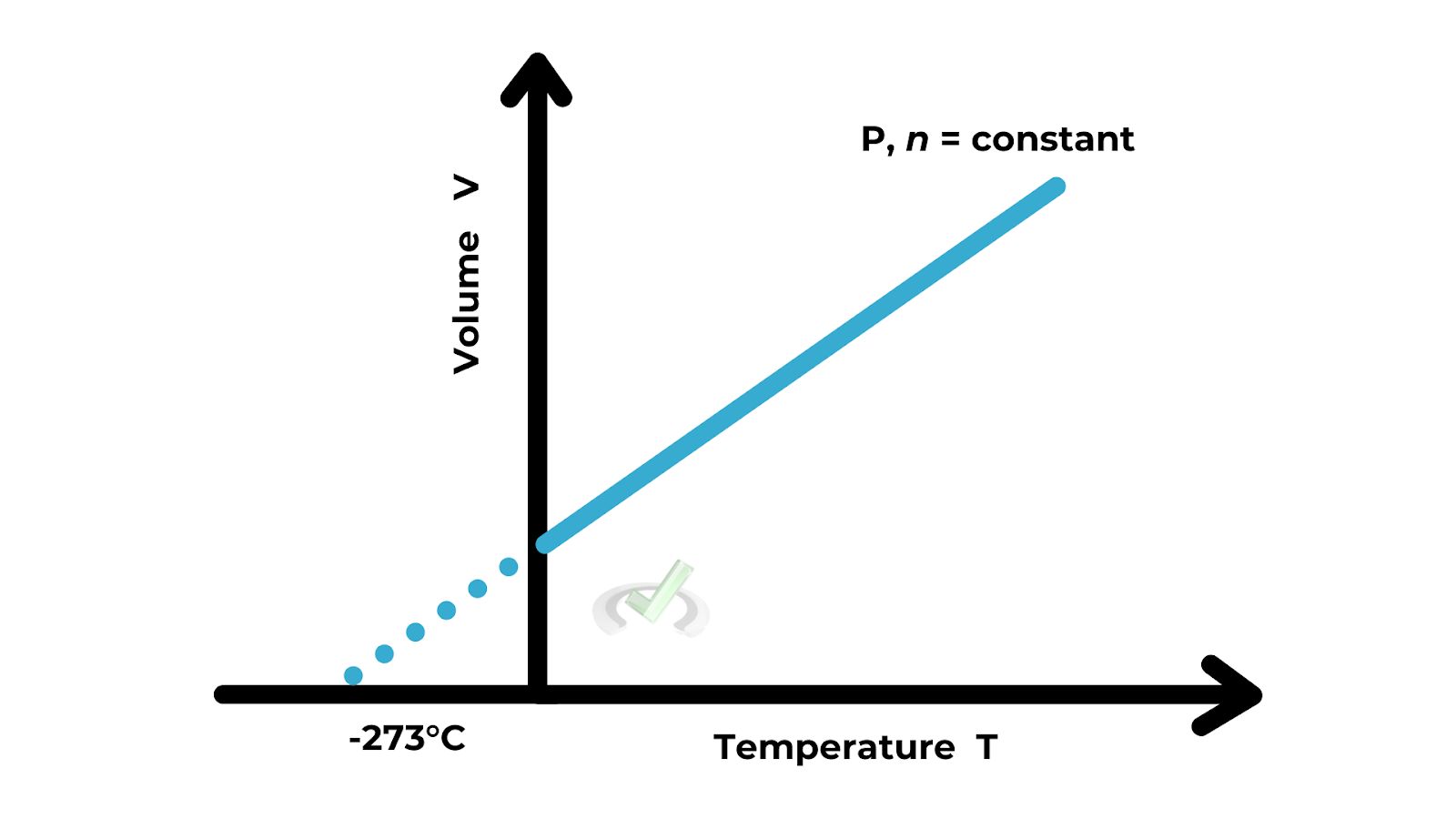
Formula:
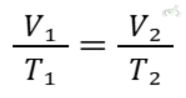
Example:
If gas occupies 1 liter at 300 K, what volume will it occupy at 600 K?
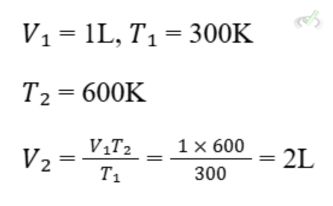
C. Avogadro's Law
Avogadro's Law states that the volume of a gas is directly proportional to the number of moles of gas, provided the temperature and pressure are constant. This means if you increase the number of moles, the volume increases. This is because more gas particles take up more space.
Formula:
Example:
If 1 mole of gas occupies 22.4 liters at standard temperature and pressure (STP), what volume will 2 moles occupy?
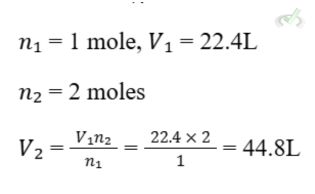
II. Combined Gas Law
The Combined Gas Law combines Boyle's, Charles's, and Avogadro's laws into one equation that shows the relationship between pressure, volume, and temperature for a fixed amount of gas.
Formula:
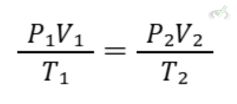
Derivation:
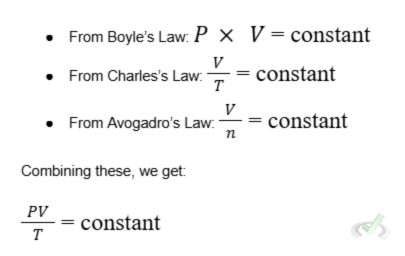
Example:
If a gas occupies 2 liters at 1 atm and 300 K, what will be its volume at 2atm and 400 K?
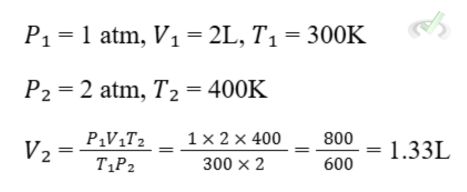
III. Ideal Gas Law
The Ideal Gas Law is a fundamental equation describing ideal gas behavior. It incorporates the relationships between pressure, volume, temperature, and number of moles.
Formula:
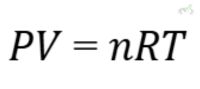
Where:
- P = Pressure
- V = Volume
- n = Number of moles
- R = Universal gas constant (0.0821 L·atm/K·mol)
- T = Temperature in Kelvin
Example:
What is the volume of 1 mole of gas at 1 atm and 273 K?
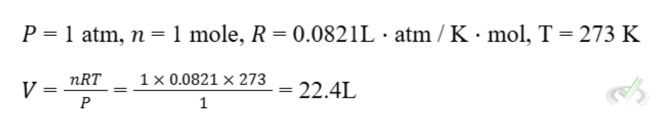
IV. Real Gases and Deviations from Ideal Behavior
Real gases do not always follow the ideal gas law, especially at high pressures and low temperatures. The Van der Waals equation accounts for these deviations by introducing two constants, aaa, and bbb, which correct for intermolecular forces and molecular volume.
Formula:
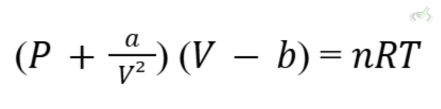
A. Deviations at High Pressure
At high pressure, gas molecules are closer together, and intermolecular forces become significant, causing deviations from ideal behavior. Due to these attractions, real gases have smaller volumes than predicted by the ideal gas law.
B. Deviations at Low Temperature
At low temperatures, gas molecules move slower, and attractions between them become more noticeable, leading to deviations from the ideal gas law. Real gases condense to liquids at low temperatures, which the ideal gas law does not predict.
Example: Carbon dioxide deviates significantly from ideal behavior at high pressures and low temperatures, leading to the formation of dry ice.V. Applications and Examples
Understanding gas laws is crucial for many practical applications.
A. Breathing
The mechanics of breathing involve Boyle's law. When you inhale, your diaphragm expands, reducing pressure in the lungs and allowing air flow. When you exhale, the diaphragm contracts, increasing pressure and forcing air out.
B. Weather Balloons
Weather balloons expand as they rise due to decreasing external pressure. This demonstrates Boyle's law as the volume increases with decreasing pressure. The pressure is lower at higher altitudes, so the balloon's volume increases until it bursts.
C. Internal Combustion Engines
Engines operate on principles of gas laws, where fuel combustion increases pressure, driving the pistons. This involves both Boyle's and Charles's laws. The combustion process increases temperature, increasing pressure and volume, pushing the piston.
VI. Bridge/Overlap
Gas laws are foundational for understanding more complex chemical reactions and behaviors.
A. Kinetic Molecular Theory
This theory explains gas behavior in terms of particle motion. It states that gas particles are in constant, random motion and that temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of these particles. This theory helps explain why gas laws work as they do.
B. Stoichiometry
Gas laws help stoichiometric calculations involving gases, such as predicting the volume of gas produced in a reaction. For example, in a chemical reaction, knowing the amount of reactants and using the ideal gas law can help calculate the volume of gas produced.
C. Thermodynamics
Gas laws are integral to thermodynamic principles, including studying heat, work, and energy in chemical processes. Understanding gas laws is essential for grasping concepts such as enthalpy, entropy, and Gibbs free energy, which are key topics in thermodynamics.
D. Phase Changes
The role of gas laws in understanding phase changes is crucial. For example, knowing how pressure and temperature affect the state of matter can explain why water boils at lower temperatures at higher altitudes (lower pressure).
VII. Wrap-Up and Key Terms
Understanding gas laws is essential for grasping the more complex applications in various scientific and medical fields. Below are the key terms and their definitions that encapsulate the high-yield information needed for mastering the topic of gas laws.
Key Terms
- Boyle's Law: Pressure and volume relationship at constant temperature.
- Charles's Law: Volume and temperature relationship at constant pressure.
- Avogadro's Law: Volume and moles relationship at constant temperature and pressure.
- Ideal Gas Law: Relationship between pressure, volume, temperature, and moles for ideal gases.
- Van der Waals Equation: Adjusted ideal gas law for real gases considering intermolecular forces and molecular volume.
- Kinetic Molecular Theory: Explains gas behavior based on particle motion.
VIII. Practice Questions
Sample Practice Question 1
What happens to the volume of a gas if the pressure increases while the temperature remains constant?
A. It increases
B. It decreases
C. It remains the same
D. It doubles
Ans. B
According to Boyle's Law, when the pressure on a gas increases and the temperature stays the same, the volume of the gas decreases. This is because pressure and volume are inversely related—when one goes up, the other goes down.
Sample Practice Question 2
If a gas occupies 5 liters at 1 atm and 298 K, what will be its volume at 2 atm and 298 K?
A. 10 L
B. 2.5 L
C. 1 L
D. 5 L
Ans. B
Using Boyle's Law, if the pressure doubles from 1 atm to 2 atm, the volume of the gas will halve, as long as the temperature remains the same. So, if the original volume was 5 liters, the new volume would be 2.5 liters.


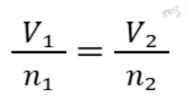





 To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these
To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these 
