Imagine you’re in a kitchen, mixing ingredients for a recipe. Sometimes, the mixture bubbles up and changes on its own, like baking soda reacting with vinegar. Other times, it just sits there, needing heat or stirring to come together.
This is like chemistry’s recipe for spontaneity—Gibbs Free Energy. The rulebook tells us when a reaction will take off naturally or need help. Let’s dive into how this concept drives reactions around us.
I. Introduction to Gibbs Free Energy
Gibbs free energy is a concept in thermodynamics that helps predict if a chemical reaction will happen on its own. It combines a system's enthalpy (heat content) and entropy (disorder) into one value that indicates if a reaction is favorable.
Gibbs Free Energy (G): A thermodynamic quantity defined as:
ΔG=ΔH−TΔS
Where:
- H is enthalpy, which is the total heat content of a system. It includes both the internal energy and the energy needed to make room for the system by displacing its environment.
- T is the temperature in Kelvin.
S is entropy, which measures the disorder or randomness in a system. Higher entropy means higher disorder.
II. Understanding Spontaneity in Reactions
A chemical reaction is spontaneous if it occurs without any external help. The Gibbs free energy change (ΔG) helps determine whether a reaction is spontaneous.
- ΔG<0: The reaction is spontaneous. It will proceed on its own.
- ΔG>0: The reaction is non-spontaneous. It will not proceed without external energy.
ΔG=0: The reaction is at equilibrium. The forward and reverse reactions occur at the same rate.
III. Calculation of Gibbs Free Energy
The change in Gibbs free energy (ΔG) can be calculated using the equation: ΔG=ΔH−TΔS where:
- ΔH is the change in enthalpy, indicating if the reaction absorbs or releases heat.
ΔS is the change in entropy, indicating the change in disorder.

IV. Gibbs Free Energy and Equilibrium
At equilibrium, ΔG=0, the reaction reaches a state where the forward and reverse reactions occur simultaneously.

V. Factors Affecting Gibbs Free Energy
Several factors can influence Gibbs free energy and, consequently, the spontaneity of a reaction.
- Temperature: Increasing temperature can change the sign of ΔG, affecting spontaneity. For example, an endothermic reaction (positive ΔH) may become spontaneous at higher temperatures if the entropy (ΔS) increase is significant.
- Pressure: Affects ΔG for reactions involving gases. Higher pressure generally favors the side of the reaction with fewer gas molecules.
Concentration: Changes in reactant or product concentrations shift ΔG. According to Le Chatelier's principle, increasing reactant concentration or decreasing product concentration will shift the equilibrium position, affecting ΔG.
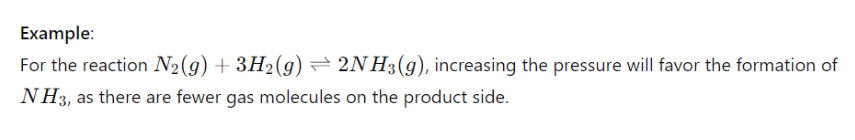
VI. Common Types of Spontaneous Reactions
Spontaneous reactions can be broadly categorized based on their ΔG\Delta GΔG values.
A. Kinetic Product: Speed Matters
ΔG<0
Release free energy.
Example: Cellular respiration, where glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) is converted into CO₂ and H₂O, releasing energy.
B. Endergonic Reactions
ΔG>0
Absorb free energy.
Example: Photosynthesis, where CO₂ and H₂O are converted into glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) using sunlight.
VII. Bridge/Overlap
Grasping Gibbs free energy provides a foundation for more complex topics in chemistry, such as:
A. Thermodynamic Stability
Gibbs Free Energy helps us determine the stability of different substances and the likelihood of their reactions. For example, diamond and graphite are both carbon forms but have different stabilities. Gibbs Free Energy explains why graphite is more stable at room temperature, even though diamond is more valuable and doesn’t easily turn into graphite.
B. Kinetics
Kinetics is about how fast a reaction happens. While Gibbs Free Energy tells us whether a reaction is spontaneous (whether it can happen independently), kinetics tells us how quickly it will happen. For example, a catalyst can speed up a reaction by lowering the energy needed to start it. However, Gibbs Free Energy still determines if the reaction will happen naturally.
C. Electrochemistry
Gibbs Free Energy connects to how batteries work and their efficiency in electrochemistry. For instance, in a battery like a galvanic cell, the Nernst equation uses Gibbs Free Energy to predict the voltage (or electrical energy) the battery can produce. This helps us understand how long a battery might last or how powerful it is.
VIII. Wrap-Up and Key Terms
Understanding Gibbs free energy and spontaneity involves mastering several key concepts:
- Gibbs Free Energy (G): Indicates reaction spontaneity.
- Spontaneous Reaction: Occurs without external input (ΔG<0).
- Equilibrium: State where ΔG=0.
- Exergonic Reaction: Releases free energy.
Endergonic Reaction: Absorbs free energy.
IX. Practice Questions
Sample Practice Question 1
What is the Gibbs free energy change (ΔG) for a reaction with ΔH=−50 kJ/mol and ΔS=0.1 kJ/(mol\cdotpK) at 300 K?
A. -80 kJ/mol
B. -20 kJ/mol
C. 0 kJ/mol
D. 30 kJ/mol
Ans. B
The Gibbs free energy change is −20 kJ/mol−20kJ/mol, calculated by subtracting the product of temperature and entropy change from the enthalpy change. This negative value indicates the reaction is spontaneous.
Sample Practice Question 2
Which of the following describes a non-spontaneous reaction?
A. ΔG<0
B. ΔG>0
C. ΔG=0
D. None of the above
Ans. B
Non-spontaneous reactions have a positive Gibbs free energy change (ΔG>0).







 To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these
To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these 
