In the previous article on Keto-Enol Tautomerization, we discussed enolates. Now, we’ll dive into the Aldol Addition and Condensation reactions. These reactions are important in organic chemistry, especially when it comes to carbon-carbon bond formation.
Before getting into the reactions, it’s important to revisit some basic concepts:
- Alpha, Beta, Gamma Carbons: The carbons adjacent to the carbonyl group (C=O) are numbered starting from the carbonyl. The carbon next to the carbonyl is the alpha carbon, the one after that is beta, and so on. This numbering system helps us discuss the positions of atoms relative to the carbonyl group.
- Alpha Hydrogens: The hydrogens bonded to the alpha carbons are called alpha hydrogens. These hydrogens are acidic because of the electronegativity of the carbonyl group, which makes them easy to remove with a base.
I. Aldol Addition
In the Aldol Addition, an enolate reacts with another carbonyl group (like an aldehyde or ketone) to form a new product. Let’s break down the steps involved:
Step 1: Enolate Formation
A strong base removes an alpha hydrogen, leaving behind an enolate ion (a resonance-stabilized intermediate). This enolate has a negative charge on the oxygen, making it nucleophilic.
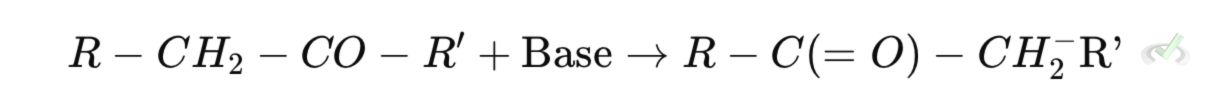
Here, R-CH₂-CO-R' is a ketone or aldehyde, and Base removes the alpha hydrogen.
Step 2: Enolate Addition
The enolate acts as a nucleophile and attacks another carbonyl carbon, forming an alkoxide intermediate. This step results in the formation of a beta-hydroxy aldehyde or ketone.
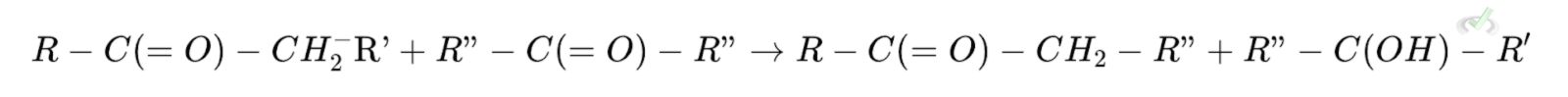
Where R" is the attacking carbonyl group.
Step 3: Alkoxide Protonation
To neutralize the negative charge on oxygen in the alkoxide, it will take a proton from water (or another source), forming a hydroxyl group (-OH).
This step results in the formation of a beta-hydroxy aldehyde or beta-hydroxy ketone.Final Aldol Addition Product
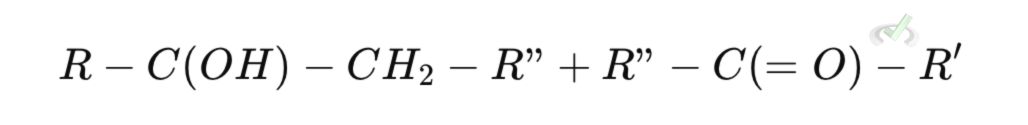
II. Aldol Condensation
After aldol addition, the product can undergo dehydration to form a conjugated enone or enal (alkene aldehyde or alkene ketone).
Dehydration Process
When heat is applied, the product undergoes a loss of water. This results in the formation of a C=C double bond and the conversion of the product into a more stable structure. The final product is called an enone (for ketones) or enal (for aldehydes).
Dehydration Reaction
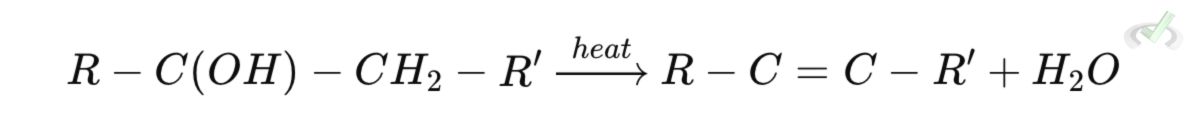
The elimination of water leads to the formation of an unsaturated aldehyde or unsaturated ketone (enol or enone).
III. Summary:
- Aldol Addition: Involves the formation of a beta-hydroxy aldehyde/ketone by nucleophilic addition of an enolate to a carbonyl.
- Aldol Condensation: Occurs when the aldol addition product undergoes dehydration, resulting in a conjugated enone (for ketones) or enal (for aldehydes).
IV. Key Terms
- Aldol - An organic compound containing an aldehyde or ketone and an alcohol.
- Aldol Addition - A chemical reaction that involves the bonding of an enolate and a carbonyl compound resulting in a β-hydroxy aldehyde or ketone.
- Enolate ion - An ion formed from the deprotonation of an -hydrogen. This is also an intermediate form for many chemical reactions in organic chemistry.
V. Practice Questions
Sample Practice Question 1
What is the main difference between aldol addition and aldol condensation?
A. Aldol addition does not require a strong base, while aldol condensation does.
B. Aldol addition forms a beta-hydroxy aldehyde/ketone, while aldol condensation results in an enone or enal.
C. Aldol addition requires dehydration, while aldol condensation does not.
D. Aldol addition is irreversible, while aldol condensation is reversible.
Ans. B
Aldol addition stops at the formation of a β-hydroxy aldehyde or ketone, while aldol condensation proceeds further with dehydration, producing an α,β-unsaturated aldehyde (enal) or α,β-unsaturated ketone (enone).
Sample Practice Question 2
Which among these is the most likely product in the aldol condensation of a ketone?
A. Enal
B. α, β-unsaturated aldehyde
C. Enone
D. β-hydroxy ketone
Ans. C
In aldol condensation, ketones undergo dehydration after aldol addition, forming an α,β-unsaturated ketone (enone) as the final product. Aldehydes, on the other hand, typically form α,β-unsaturated aldehydes (enals).







 To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these
To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these 
