Carboxylic acids have a carbonyl and a hydroxyl group attached to the carbonyl carbon at the end of a chain. These compounds are widely occurring compounds in chemistry. They are characterized by an R-COOH structure due to the carbonyl and hydroxyl groups having the same carbon. They are also a parent group for other compounds known as carboxylic acid derivatives or acyl compounds.
I. Structure of Carboxylic Acids
The structure of carboxylic acids is pretty straightforward. They are functional groups with a carbonyl at the end and an -OH group attached to the carbonyl. This is much more simplified by its general formula R-COOH, where R is the remainder of the whole molecule.
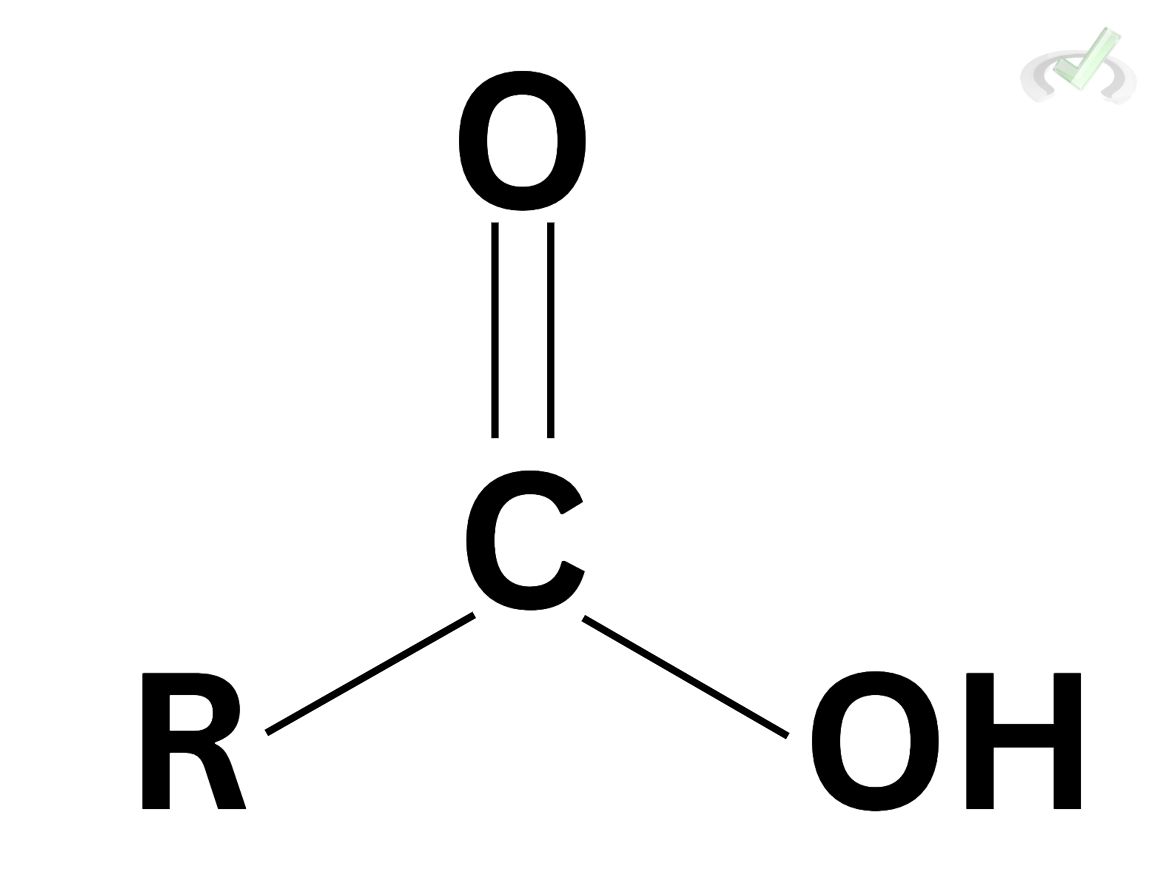
One way to synthesize carboxylic acids is by oxidizing primary alcohols and aldehydes. In this process, primary alcohols will oxidize into aldehydes. Further oxidation of aldehydes will produce carboxylic acids. The synthesis of these compounds can come from the hydrolysis of nitriles, esters, and amides.
These are important in a lot of biological systems. You might encounter these in the MCAT, so you must learn how to name these compounds.
II. Naming rules
Carboxylic acids are named by adding the suffix “oic” to the number of carbons and an acid at the end. You’re essentially adding “-oic acid” at the end of the carbon chain.
Let’s take this compound for example:
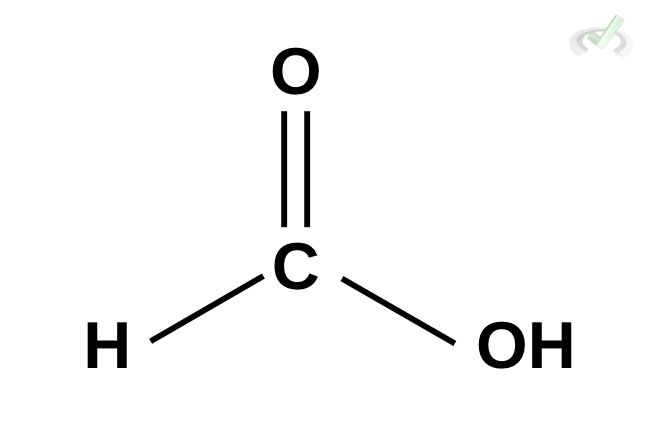
This is known as methanoic acid. It uses the prefix “meth” since it only has one carbon and is followed by the suffix “-oic” + acid.
Try this one:
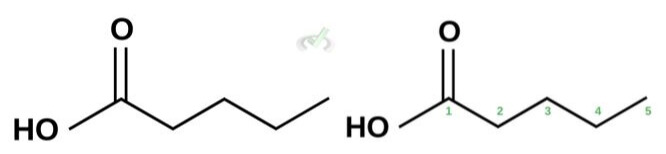
Note that we count our first carbon from the carbon carbonyl. In this case, we have 5 carbon atoms. We can name this compound pentanoic acid.
Examples:
Methanoic Acid (Formic Acid)
Structure: HCOOH
- A single carbon attached to a carboxyl group (-COOH).
- Naming: "Meth-" for one carbon, "-oic acid" for the carboxyl group, resulting in Methanoic Acid.
Pentanoic Acid (Valeric Acid)
Structure: CH₃CH₂CH₂COOH
- A 5-carbon chain with a carboxyl group (-COOH) at the end.
- Naming: "Pent-" refers to five carbon atoms, and the "-oic acid" suffix gives Methanoic Acid.
3-Chlorobutanoic Acid
Structure: CH₃CHClCOOH
- A 4-carbon chain, with a chlorine atom attached to the 3rd carbon.
- Naming: "3-Chloro" indicates chlorine at the 3rd position, followed by "-butanoic acid", resulting in 3-Chlorobutanoic Acid.
4-Methylhexanoic Acid
Structure: CH₃CH₂CH(CH₃)COOH
- A 6-carbon chain with a methyl group attached to the 4th carbon.
- Naming: "Hex-" for six carbons, "4-methyl" for the methyl group at position 4, leading to 4-Methylhexanoic Acid.
Benzoic Acid
Structure: C₆H₆COOH
- A benzene ring (C₆H₆) with a carboxyl group (-COOH) attached.
- Naming: Since the carboxyl group is directly attached to the benzene ring, it's simply called Benzoic Acid.
5-Cyclohexane Octanoic Acid
Structure: C₆H₁₀CH₂COOH
- An 8-carbon chain with a cyclohexane group at the 5th carbon.
- Naming: "Octanoic acid" for an 8-carbon chain, "5-cyclohexane" for the cyclohexane group attached to the 5th carbon, giving 5-Cyclohexane Octanoic Acid.
III. Conclusion
Carboxylic acids are functional groups with a general formula of R-COOH. Its structure is composed of a hydroxyl group attached to a carbonyl carbon. This carbon is found at the end of a functional group. We name these compounds by adding the suffix “-oic” and denoting this as an acid. Counting the number of carbon atoms begins at the carbonyl carbon. For carboxylic acids with other functional groups attached, we prioritize carboxylic acids by adding the suffix at the end and putting the locant of the functional groups in front.
V. Key Terms
- Carboxylic acid - A functional group with a general formula RCOOH
VI. Practice Questions
Sample Practice Question 1
Which of the following is the correct name for a carboxylic acid with a 4-carbon chain and a chlorine atom attached to the second carbon?
A. 2-Chlorobutanoic Acid
B. 3-Chlorobutanoic Acid
C. 2-Chloroethanoic Acid
D. 1-Chloropropanoic Acid
Ans. A
The compound has a 4-carbon chain (butanoic acid), with the chlorine attached to the second carbon. The position of chlorine is indicated as "2-chloro," resulting in the name 2-Chlorobutanoic Acid.
Sample Practice Question 2
Which of the following is the correct name for a carboxylic acid with a 4-carbon chain and a chlorine atom attached to the second carbon?
A. 2-Chlorobutanoic Acid
B. 3-Chlorobutanoic Acid
C. 2-Chloroethanoic Acid
D. 1-Chloropropanoic Acid
Ans. A
The compound has a 7-carbon chain (heptanoic acid), with a hydroxyl group (-OH) at the 3rd carbon. The name reflects the position of the hydroxyl group, resulting in 3-Hydroxyheptanoic Acid.







 To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these
To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these 
