When NBA scouts and general managers are scouting for promising NBA prospects, they often have a variety of approaches and methods to decide which ones might be a good fit for a specific team
Just like choosing a specific player to fill a specific role for a team, organic chemists can use different laboratory techniques in order to separate and selectively isolate specific substances of interest!
After going through this chapter overview, you’ll have the basics of the different techniques that can be used to isolate specific substances.
I. Introduction to Extraction and Filtration
Extraction and filtration are methods used to separate substances. Extraction involves transferring a solute from one solvent to another. This helps isolate specific compounds.
Filtration separates solid particles from liquids or gases, helping to purify compounds. Both techniques are used to isolate and purify compounds in organic chemistry.
II. Extraction Techniques
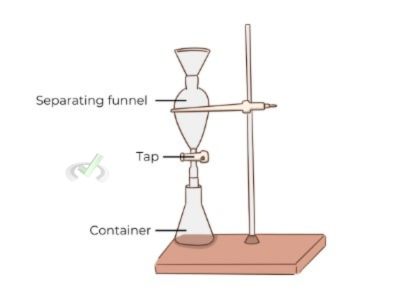
Extraction is a process where a substance is separated from a mixture using a solvent. There are different types of extraction techniques.
A. Liquid-Liquid Extraction
Liquid-liquid extraction involves two immiscible liquids. One liquid contains the compound to be extracted.
The other liquid, the solvent, dissolves the compound. When the two liquids are mixed, the compound transfers to the solvent.
For example, caffeine extraction from coffee. Water is the first solvent, and dichloromethane (DCM) is the second solvent. Caffeine moves from the water to the DCM.
B. Solid-Liquid Extraction
Solid-liquid extraction involves a solid and a liquid. The liquid solvent dissolves the compound from the solid.
For example, making tea. The hot water (solvent) extracts flavor compounds from the tea leaves (solid).
C. Factors Affecting Extraction
Several factors affect extraction efficiency:
- Solvent Choice: The solvent should dissolve the target compound well. Choosing the right solvent is crucial for effective extraction.
- Temperature: Higher temperatures often increase extraction rates. This can help dissolve the compound more quickly.
- Mixing: Proper mixing ensures better contact between phases. This improves the efficiency of the extraction process.
III. Filtration Techniques
Filtration is a process that separates solids from liquids or gases. Depending on the nature of the mixture, different filtration methods are used.
A. Gravity Filtration
Gravity filtration uses gravity to pull liquid through a filter. This method removes solid impurities from liquids.
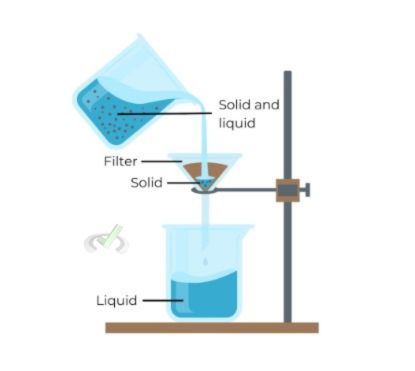
An example of gravity filtration is filtering sand from water. The water passes through the filter, leaving the sand behind.
B. Vacuum Filtration
Vacuum filtration uses a vacuum to pull the liquid through the filter. This method is faster than gravity filtration and collects solid products from a liquid.
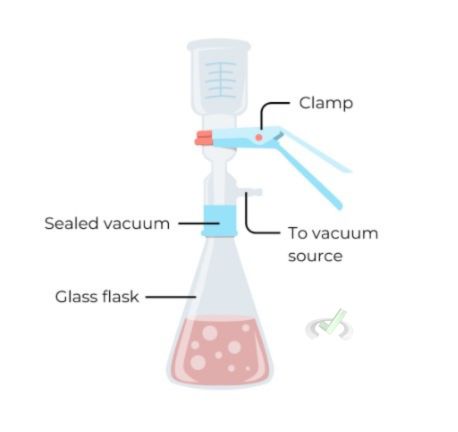
Collecting a precipitate from a reaction mixture is an example of vacuum filtration. The vacuum speeds up the filtration process.
C. Factors Affecting Filtration
Several factors affect filtration efficiency:
- Filter Paper Pore Size: The size of the pores in the filter paper should be small enough to trap the solid particles. Choosing the right pore size is important to avoid losing any solids.
- Vacuum Strength: A stronger vacuum speeds up the filtration process. This can be useful when filtering large volumes of liquid.
- Solid Particle Size: Smaller particles may pass through the filter so that a finer filter may be needed. Adjusting the filter type can help retain all solid particles.
IV. Extraction and Filtration in Connection to Broader Scientific Concepts
Understanding extraction and filtration connects to broader topics in chemistry and other sciences.
A. Solubility and Solvent Selection
Solubility plays a crucial role in extraction. Choosing the right solvent based on the solubility of compounds is essential. For example, nonpolar solvents like hexane are used to extract nonpolar compounds.
B. Phase Separation
Phase separation is essential in both extraction and filtration. Knowing how to separate different phases is crucial. One example is using a separatory funnel to separate two immiscible liquids in liquid-liquid extraction.
C. Laboratory Techniques
Extraction and filtration are fundamental laboratory techniques. They are used in various scientific experiments and industrial processes. For instance, filtration is used to produce beverages to remove unwanted solids.
V. Wrap-Up and Key Terms
Understanding extraction and filtration involves several key concepts. Let's review:
- Extraction: A process of separating a substance from a mixture using a solvent.
- Filtration: A process of separating solids from liquids or gases using a filter.
- Liquid-Liquid Extraction: Using two immiscible liquids to separate a compound.
- Solid-Liquid Extraction: Using a liquid solvent to dissolve compounds from a solid.
- Gravity Filtration: Using gravity to pull liquid through a filter.
- Vacuum Filtration: Using a vacuum to pull liquid through a filter.
- Solvent: A liquid that dissolves a solute.
- Phase Separation: Separating different phases in a mixture, such as liquids or solids.
VI. Practice Questions
Sample Practice Question 1
What is the purpose of extraction in organic chemistry?
A. To mix compounds
B. To separate a substance from a mixture using a solvent
C. To heat compounds
D. To measure compounds
Ans. B
Extraction involves transferring a solute from one solvent to another to separate it from a mixture.
Sample Practice Question 2
Which filtration method uses a vacuum to speed up the process?
A. Gravity Filtration
B. Solid-Liquid Extraction
C. Liquid-Liquid Extraction
D. Vacuum Filtration
Ans. D
Vacuum filtration uses a vacuum to pull the liquid through the filter, making the process faster.







 To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these
To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these 
