Imagine what happens when we switch the TV on and off multiple times without breaks. In any circuit, a load will experience a rush of current going in, which can destroy the TVTV's destruction due to the power supply rushing the TV. The TV may experience fluctuations in current, which can destroy the device. While resistors can impede electron flow, in cases where there is a sudden cut in the circuit, a device must store some amount of energy the way a battery does to avoid ruining the load. Capacitors do this–they help store electrons the way batteries do so that when the circuit is suddenly cut off from the power source, temporary energy storage will help manage the load.
I. Capacitors and Capacitance
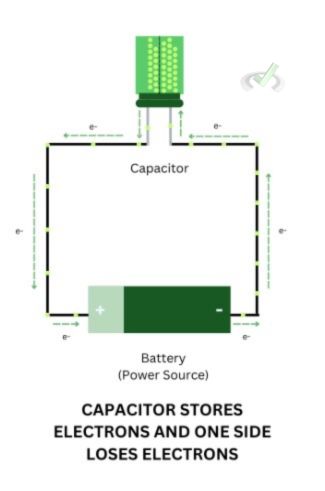
Capacitors are components that store a small amount of energy. They help store energy and compensate for power losses. Imagine what happens when fluctuations in electricity occur–any device connected to a power source can be impaired due to a sudden flux or loss of normal current flow. Capacitors act as a deterrent to these fluctuations in current by acting as a temporary source of electrons.
Mechanism
In a closed circuit connected to a capacitor, one plate of the capacitor stores some electrons from the battery, and another plate loses electrons. These electrons are stored on one plate, and once this side is filled and the other loses electrons, a potential difference exists between the two plates. This potential difference allows the capacitor to act like a battery since it also triggers the flow of electrons. Electrons in these two plates will not merge since an insulator separates them.
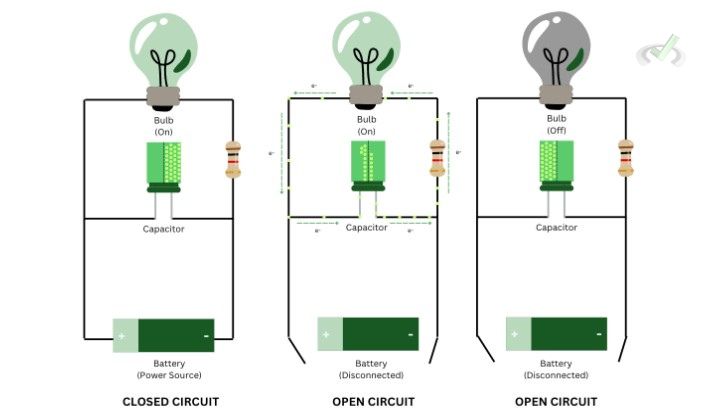
A closed circuit will continue to function and light up a bulb. Electrons from the battery will continue to flow toward the load since the capacitor is now filled with electrons. The flow of electrons stops once the circuit is opened or when the battery is disconnected. If no capacitor is present, an open circuit will normally stop functioning due to the lack of electrons flowing. However, since a capacitor is present, electrons coming from the capacitor will move toward the load due to an existing potential difference. This will temporarily allow the bulb to light up for a short time. Once the electrons fill up the other side, there is no longer a potential difference to keep the electrons moving through the bulb. In return, the bulb will turn off and only turn on once connected to a power source.
II. Capacitance
Capacitors are components of a circuit that store electrons or charges. They have a high capacitance when storing a huge amount of electric charge at a given voltage. When something has a high capacitance, it can store a lot of energy. This also means the capacitor performs well through voltage fluctuations since it can easily store and discharge charges.
Mathematically, we can describe capacitance as the ability to store a charge per voltage unit. The equation gives this:
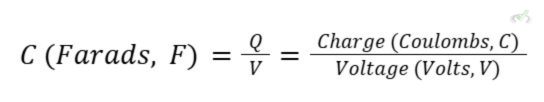
An object's capacitance is also dependent on the physical characteristics of the material used and the insulator placed between the plates.
III. Capacitance in Circuits
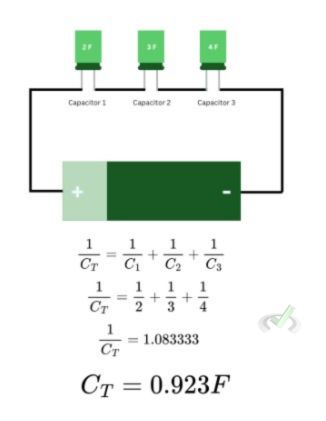
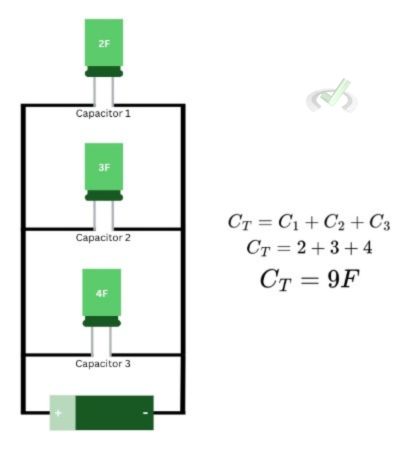
Calculating the capacitance in series and circuits works the opposite of how we calculate the resistance in series and parallel. As you will notice, the capacitance in parallel will be quite larger than a series circuit carrying the same capacitors with the same capacitance. This is because, for parallel circuits, the voltage across the capacitor is the same. This means the total charge stored in the circuit will be the sum of all charges. For series circuits, the voltage coming into each capacitor may be different.
A. Capacitance in Series Circuits
In series circuits, capacitance can be calculated similarly to how we calculate resistance in parallel. The reciprocal of the total capacitance across a circuit is equal to the sum of all of the reciprocals of the individual capacitance of the capacitors present.
We express the total capacitance in a series circuit as:
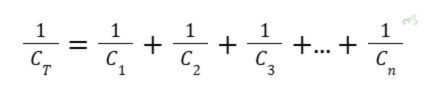
B. Capacitance in Parallel Circuits
For parallel circuits, the calculation for total capacitance is also similar to how we calculate the resistance in series circuits. The total capacitance of all capacitors in a parallel circuit equals the sum of all the individual capacitors present in the circuit. This is expressed as:
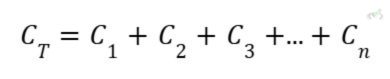
IV. Conclusion
Capacitors help maintain the flux of electrons in a circuit by acting similarly to a battery. It releases electrons on one side, which creates a positive space, and it takes in electrons, which creates a highly negative space on another. This creates a potential difference that drives electron flow, allowing a load to receive some energy when the circuit is opened. The ability of a capacitor to store charge per unit of voltage is known as the capacitance. A high capacitance indicates a higher energy storage for a significant time. Calculating the capacitance in series and parallel is the opposite of how we calculate the resistance in both circuits due to the nature of the voltages received by components across each circuit.
V. Key Terms
- Capacitor - A component that stores charges by creating an electric field between two plates.
- Capacitance - The ability to store electric charge per unit of voltage.
- Potential Difference - The difference in electric potential energy between two points.
VI. Practice Questions
Sample Practice Question 1
If a 5F capacitor is charged to 100V, what is the electric charge stored in the capacitor?
A. 500 C
B. 500 V
C. 150 V
D. 510 C
Ans. A
Sample Practice Question 2
Determine the total charge across the parallel circuit shown below.
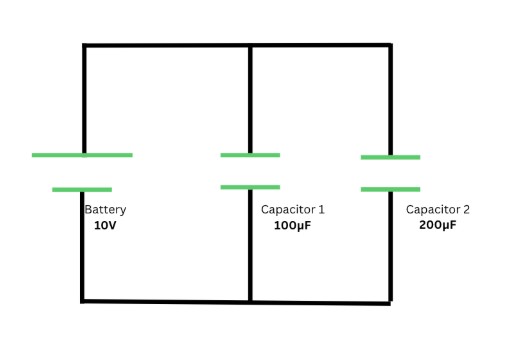
A. 3.00 C
B. 0.30 C
C. 0.003 C
D. 3.30 C
Ans. C







 To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these
To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these 
