Electricity powers many things in our daily lives, from the lights in our homes to our devices. To fully grasp how electricity works, it's essential to understand two concepts in energy.
In this study notes, let's explore electric potential energy and electric potential. These concepts are the foundational topics in physics. They explain why charges move and how much energy is involved.
I. Electric Potential Energy
Electric potential energy is the energy a charge has due to its position in an electric field. This is similar to gravitational potential energy. It is where an object’s energy depends on its position in a gravitational field.
Moreover, electric potential energy is the work done to move a charge from a reference point (usually infinity) to a specific point in an electric field. This process occurs without changing the charge's kinetic energy.
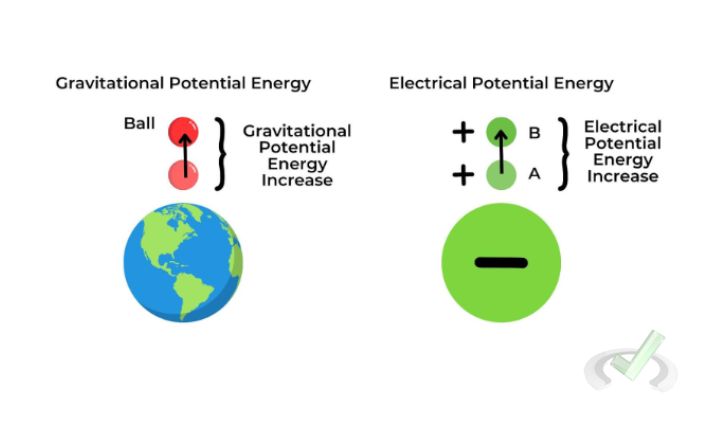
For example, a ball at the top of a hill has gravitational potential energy because of its height. Similarly, a charged particle has electric potential energy. This is due to its position relative to other charges.
The formula for electric potential energy (U) is:

II. Electric Potential
Electric potential is the potential energy per unit charge at a specific point in an electric field. It tells us how much work would be needed to move a unit charge to that point.
The formula for electric potential (V) is:
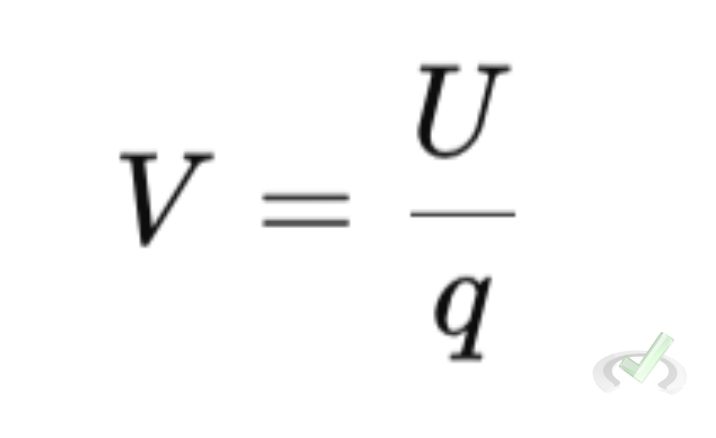
Where:
- U is the electric potential energy
- q is the charge
Example: If the electric potential energy U is 10 joules and the charge q is 2 coulombs. The electric potential V would be:
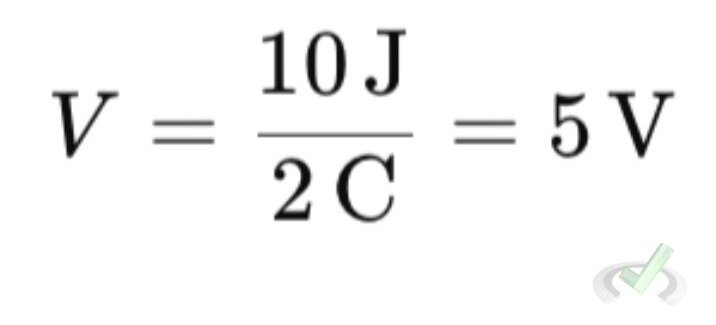
III. Relationship between Electric Potential Energy and Electric Potential
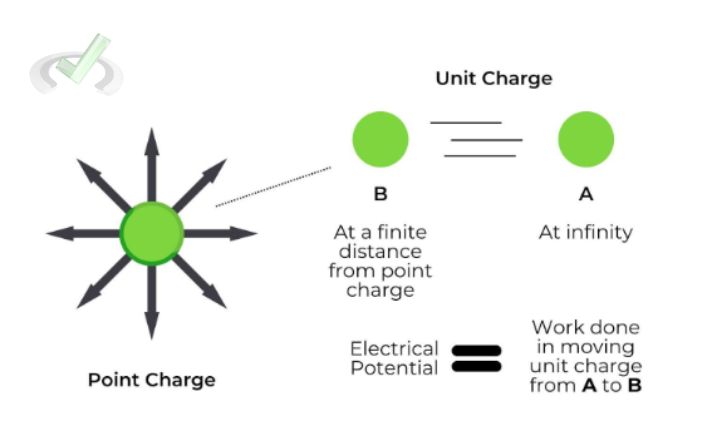
Electric potential energy and electric potential are related but different. Electric potential is the energy per charge. Meanwhile, electric potential energy is the total energy due to a charge's position in an electric field.
For example, if a charge q is placed in an electric field with a potential V, the electric potential energy U can be calculated using: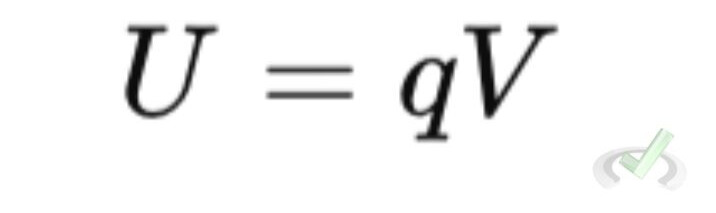
IV. Applications and Importance
Understanding the distinction between electric potential energy and electric potential is crucial in many fields.
Electronics: Capacitors store energy as electric potential energy. It can be released to power devices or smooth out electrical signals.
Medical Devices: MRI machines use electric potential concepts to create detailed images of the body's interior.
Environmental Science: Scientists study electric potential to understand phenomena like lightning. This involves the movement of charges within clouds.
V. Behavior of Charges in Electric Fields
Charges behave in specific ways in electric fields. This behavior is influenced by both electric potential energy and electric potential.
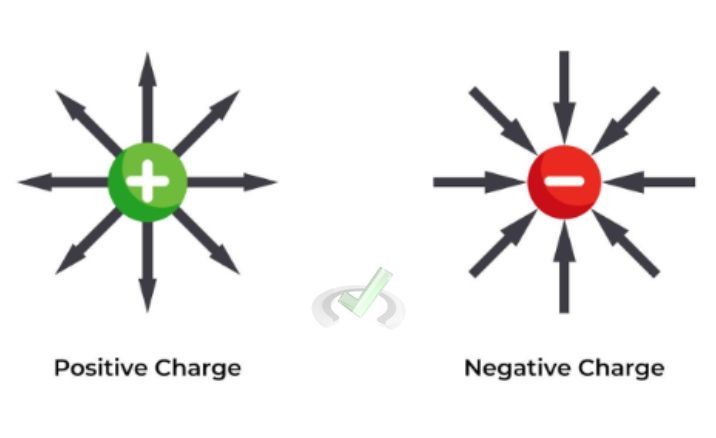
- Movement of Charges: Positive charges move from high electric potential to areas of low electric potential. Meanwhile, negative charges move in the opposite direction.
- Work Done by Electric Fields: The work done to move a charge in an electric field is related to the change in electric potential energy. The equation for work done (W) is
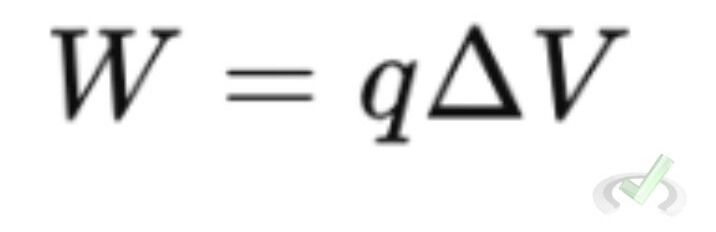
Where ΔV is the change in electric potential.
VI. Connecting Electric Potential Concepts to Broader Scientific Ideas
Electric potential energy and electric potential connect to many broader scientific ideas.
- Nervous System: The nervous system relies on electric potentials to transmit signals. When neurons fire, changes in electric potential across their membranes. This creates signals that travel along nerve cells.
- Cardiac Function: The heart's rhythm is controlled by electric potentials that coordinate the contraction of heart muscles. Electrocardiograms (ECGs) measure these potentials to monitor heart health.
- Chemistry: Electric potentials influence how molecules and ions interact in chemical reactions. Reactions in polar solvents stabilize ions through electric potentials. This can proceed more rapidly and with different outcomes.
VII. Wrap-Up and Key Terms
To solidify our understanding, let's review some key terms:
- Electric Potential Energy: Energy due to a charge's position in an electric field.
- Electric Potential: Potential energy per unit charge.
- Electric Field: A region where a charge experiences a force.
- Voltage: Another term for electric potential, often used in practical applications.
VIII. Practice Questions
Sample Practice Question 1
What energy does a charge have due to its position in an electric field?
A) Electric PotentialB) Electric Field Strength
C) Electric Potential Energy
D) Voltage
Ans. C
Electric potential energy is the energy a charge has due to its position in an electric field.
Sample Practice Question 2
Which of the following is a measure of potential energy per unit charge?
A) Electric FieldB) Voltage
C) Electric Potential Energy
D) Coulomb’s Law
Ans. B
Voltage, or electric potential, is the potential energy per unit charge.







 To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these
To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these 
