Demographic shifts are changes in the population's structure and composition over time. These shifts affect many aspects of society, including the economy, healthcare, and social services. Understanding these changes helps us grasp broader social dynamics and anticipate future needs.
I. What is Demographic Shift?
A demographic shift refers to changes in a population's characteristics, including age, gender, birth rate, death rate, and migration patterns. These shifts happen over time and can significantly impact society by altering the demand for resources, services, and policies.
II. Key Terms and Concepts
Understanding demographic shifts requires knowing several key terms and concepts. Let's explore them:
A. Birth Rate
The birth rate is the number of live births per 1,000 people yearly.
Importance of Birth Rate:
- Population Growth: A high birth rate can lead to rapid population growth. This affects resources like food, water, and housing. It also increases the need for services such as education and healthcare.
- Economic Impact: Birth rates influence the future workforce. More births can mean a larger future workforce. But it can also strain current resources.
- Social Services: Changes in birth rates affect the demand for services like schools, pediatric healthcare, and childcare facilities.
B. Death Rate
The death rate, or mortality rate, is the number of deaths per 1,000 people yearly.
Importance of Death Rate:
- Population Decline: A high death rate can lead to population decline. This affects labor markets and economic growth.
- Healthcare Quality: Mortality rates can show a region's quality of healthcare and life expectancy. Higher death rates might mean poor healthcare services or living conditions.
- Aging Population: Lower death rates often lead to an aging population. This has implications for social services and healthcare systems.
C. Fertility Rate
The fertility rate is the average number of children a woman is expected to have during her lifetime.
Importance of Fertility Rate:
- Population Replacement: Fertility rates impact whether a population can replace itself from generation to generation. A rate of about 2.1 children per woman is generally considered the replacement rate.
- Economic Factors: High fertility rates can strain economic resources, while low rates can lead to labor shortages and an aging workforce.
- Cultural Factors: Fertility rates can reflect cultural values and norms regarding family size. Some cultures value large families, while others prefer smaller ones.
D. Migration
Migration is the movement of people from one place to another, either within a country or across borders.

Types of Migration:
- Internal Migration: Movement within a country, from rural areas to cities.
- International Migration: Movement across countries, such as immigration (moving into a country) and emigration (leaving a country).
Importance of Migration:
- Labor Markets: Migration affects labor supply and demand. Migrants can fill labor shortages and help economic growth.
- Cultural Diversity: Migration introduces cultural diversity. This enriches societies but can also pose challenges for social integration.
- Population Distribution: Migration impacts population distribution and urbanization. Large numbers of people moving to cities can lead to urban growth and sometimes overcrowding.
E. Population Pyramid
A population pyramid is a graphical representation of the age and sex distribution of a population.
Importance of Population Pyramids:
- Age Structure shows the proportion of different age groups in a population. It helps understand the age distribution and predict future trends.
- Dependency Ratios: They help identify the working-age population versus dependent populations (young and old). A high dependency ratio means more dependents per working-age person.
- Predicting Trends: Population pyramids can predict future demographic trends, such as aging populations or potential population booms.
F. Aging Population
An aging population happens when the median age of a population increases due to lower birth rates and higher life expectancy.

Importance of Aging Population:
- Healthcare Demand: Aging populations increase the demand for healthcare services. Older individuals usually need more medical care.
- Pension Systems: They put pressure on pension systems and social security as more people retire and fewer are in the workforce.
- Workforce: Aging populations can lead to labor shortages. To address this, changes in the workforce, such as later retirement ages or increased use of technology, are required.
G. Urbanization
Urbanization is when more of a population moves from rural areas to cities.
Importance of Urbanization:
- Economic Growth: Urban areas often provide more job opportunities and can drive economic growth.
- Infrastructure Strain: Rapid urbanization can strain infrastructure like transportation, housing, and sanitation systems.
- Social Services: Urbanization affects the provision of social services, including education and healthcare. They often require the expansion and adaptation of services.
H. Life Expectancy
Life expectancy is the average number of years a person is expected to live based on current mortality rates.
Importance of Life Expectancy:
- Healthcare Indicator: It is a crucial indicator of a region's healthcare quality and living conditions.
- Economic Planning: Higher life expectancy affects economic planning, especially for pensions and retirement.
- Social Impact: Longer life expectancy can change family structures and social roles with more multi-generational families.
I. Dependency Ratio
The dependency ratio is the ratio of dependents (people younger than 15 or older than 64) to the working-age population (15-64).
Importance of Dependency Ratio:
- Economic Burden: A high dependency ratio means fewer workers support more dependents, which can strain economic resources.
- Social Services: It affects the demand for social services like education and healthcare. A higher ratio often means more resources are needed for dependent care.
- Policy Making: It helps in policy-making, especially in areas like retirement age and social security.
J. Population Policies
Population policies are measures taken by governments to influence population size, growth, and distribution.
Types of Population Policies:
- Pro-Natalist Policies: Encourage higher birth rates through incentives like tax breaks and childcare support.
- Anti-Natalist Policies: Aim to reduce birth rates through family planning programs and education.
- Migration Policies: Regulate immigration and emigration to manage population size and composition.
III. How Demographic Shifts Interact
Demographic shifts do not occur alone. They interact and influence each other in many ways.
A. Birth Rate and Economic Development
Higher birth rates can lead to rapid population growth. This can strain resources like food, housing, and jobs. Lower birth rates can result in an aging population, which affects the labor market and economic growth.
B. Migration and Cultural Diversity
Migration brings cultural diversity into a population. This can enrich a society but also pose challenges for social integration. Migration can also help balance labor shortages in aging populations.
C. Aging Population and Healthcare
An aging population increases healthcare service demands. This shift requires adjustments in healthcare provision and funding. It also impacts the workforce as older individuals retire, which also means fewer young people enter the labor market.
IV. Bridge/Overlap
Understanding demographic shifts connects to various areas relevant to MCAT topics.
A. Public Health
Demographic shifts, like aging populations and migration, have significant implications for public health. They affect disease patterns, healthcare demand, and health policies.
B. Economic Implications
Demographic changes influence economic development, labor markets, and social security systems. These changes need economic planning and policy adjustments.
C. Social and Cultural Impact
Demographic shifts impact social structures and cultural norms. For example, migration brings new cultural dynamics, while aging populations change family structures and community support systems.
D. Environmental Concerns
Population growth and migration can have environmental impacts. These include urbanization and resource depletion. Understanding these connections is crucial for addressing environmental sustainability.
V. Wrap-Up and Key Terms
Understanding demographic shifts is essential for grasping broader social changes. Each concept plays a unique role but is connected to others, creating a complex web of social dynamics.
Key Terms
- Birth Rate: Number of live births per 1,000 people per year.
- Death Rate: Number of deaths per 1,000 people per year.
- Fertility Rate: Average number of children a woman is expected to have.
- Migration: Movement of people from one place to another.
- Population Pyramid: Graphical representation of age and sex distribution.
- Aging Population: Increase in the median age of a population.
- Urbanization: Movement of people from rural areas to cities.
- Life Expectancy: The average number of years a person is expected to live.
- Dependency Ratio: Ratio of dependents to the working-age population.
- Population Policies: Measures taken by governments to influence population size and growth.
VI. Practice Questions
Sample Practice Question 1
What is the average number of children a woman is expected to have during her lifetime?
A. Birth Rate
B. Fertility Rate
C. Death Rate
Ans. B
The fertility rate is the average number of children a woman is expected to have during her lifetime.
Sample Practice Question 2
Which demographic shift increases the demand for healthcare services?
A. High Birth Rate
B. Aging Population
C. High Migration
Ans. B
An aging population increases the demand for healthcare services as older individuals typically need more medical care.







 To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these
To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these 









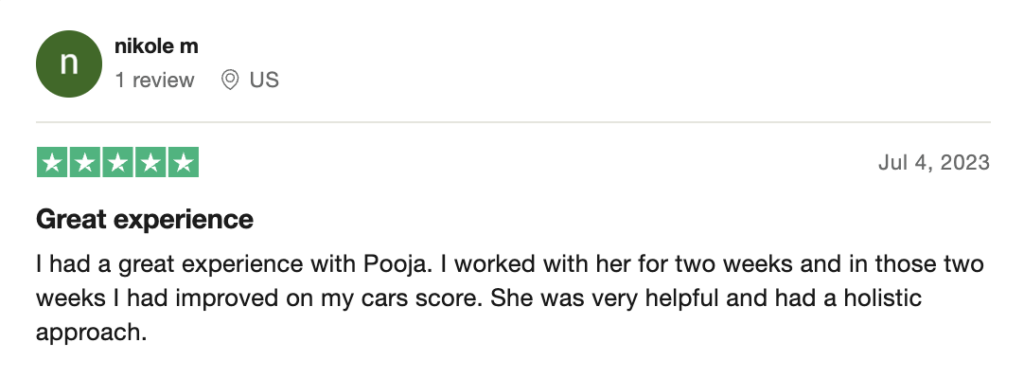
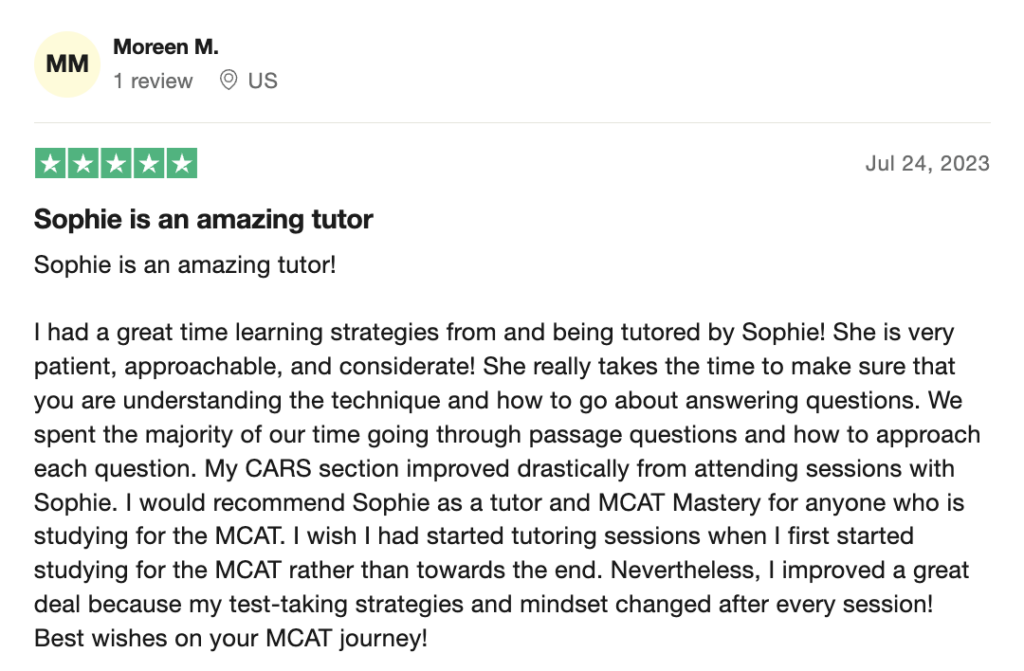

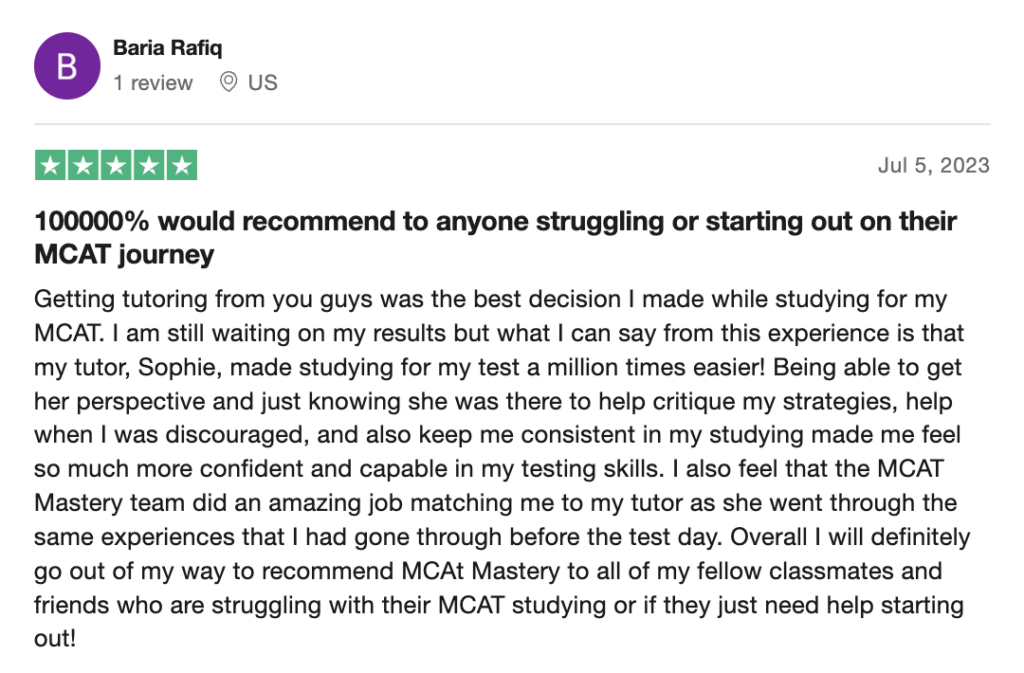
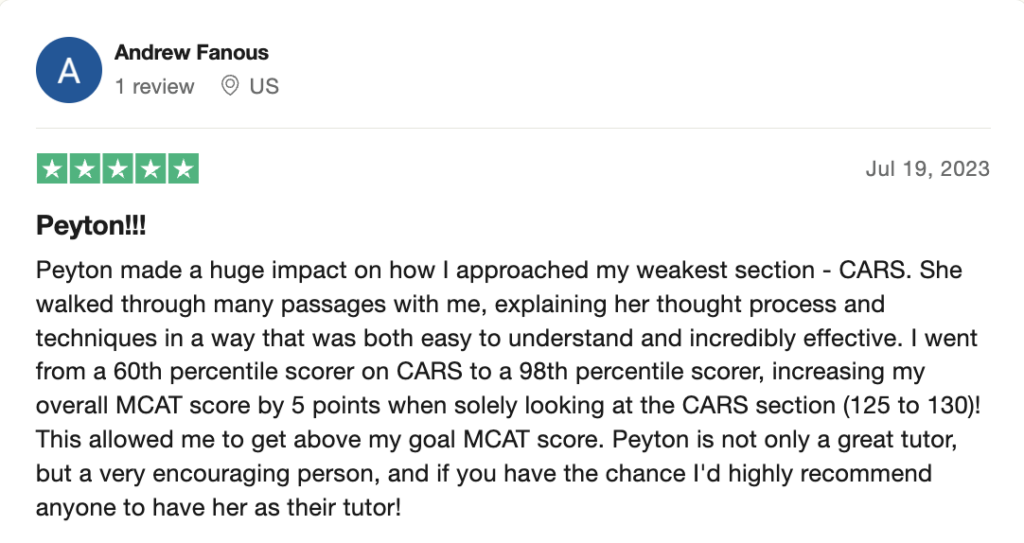
 reviews on TrustPilot
reviews on TrustPilot