Enzymatic proteins usually dominate the conversation when it comes to the topic of proteins in Biochemistry classes. However, equally as important are non-enzymatic proteins, or proteins that do not necessarily speed up chemical reactions.
Every time you do a bicep curl or run up the stairs because of the monster chasing you, non-enzymatic proteins are hard at work. In addition to maintaining the structure of cells and initiating bodily movements, non-enzymatic proteins are also involved in cell signalling, and immune function.
Now that we know the fundamental functions and importance of non-enzymatic proteins, we can dive a little further into looking at key terms, definitions, and topics that will be important for the MCAT.
Let’s get started!
Non-Enzymatic Proteins on the MCAT: What You Need to Know
Introductory biochemistry accounts for 25% of the Biological and Biochemical Foundations of Living Systems section (Bio/Biochem) and 25% of the Chemical and Physical Foundations of Biological Systems section (Chem/Phys).
Questions about non-enzymatic proteins will appear primarily in the Bio/Biochem section. Now, it is hard to say how many questions will pertain to non-enzymatic proteins, however, they have been a popular topic on stand-alone questions in the past. For these questions, it will be important to identify the structural and functional components of the various non-enzymatic proteins on the MCAT.
Luckily for you, this review will give you a concise yet comprehensive review of non-enzymatic enzymes you are required to understand!
Let’s get started!
Important Sub-Topics — Non-Enzymatic Proteins
Non-Enzymatic Function
The 3 main types of non-enzymatic proteins are:
1) Binding proteins (e.g. Hemoglobin receptors)
2) Immune proteins (e.g. Antibodies)
3) Motor proteins (e.g. myosin)
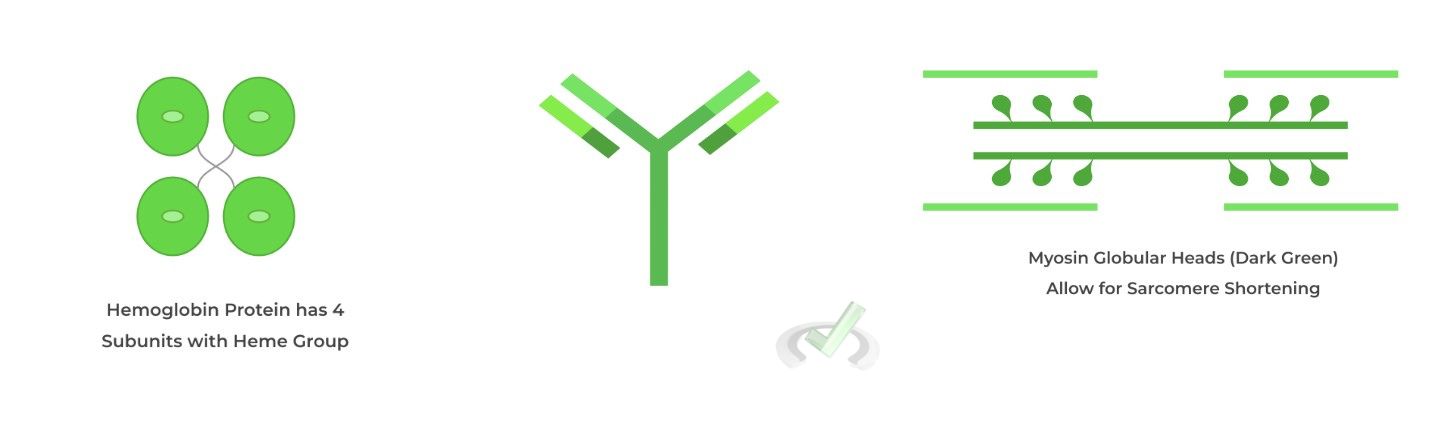
Full Study Notes : Proteins: Non-Enzymatic Function on the MCAT
For more in-depth content review on non-enzymatic function, check out these detailed lesson notes created by top MCAT scorers.
Biosignaling
Biosignaling proteins are involved in signal transduction, initiating and regulating cellular pathways. These proteins are also involved in forming intercellular (between cells) networks.
The 2 main types of biosignaling proteins are:
1) Receptors
2) Ion channels
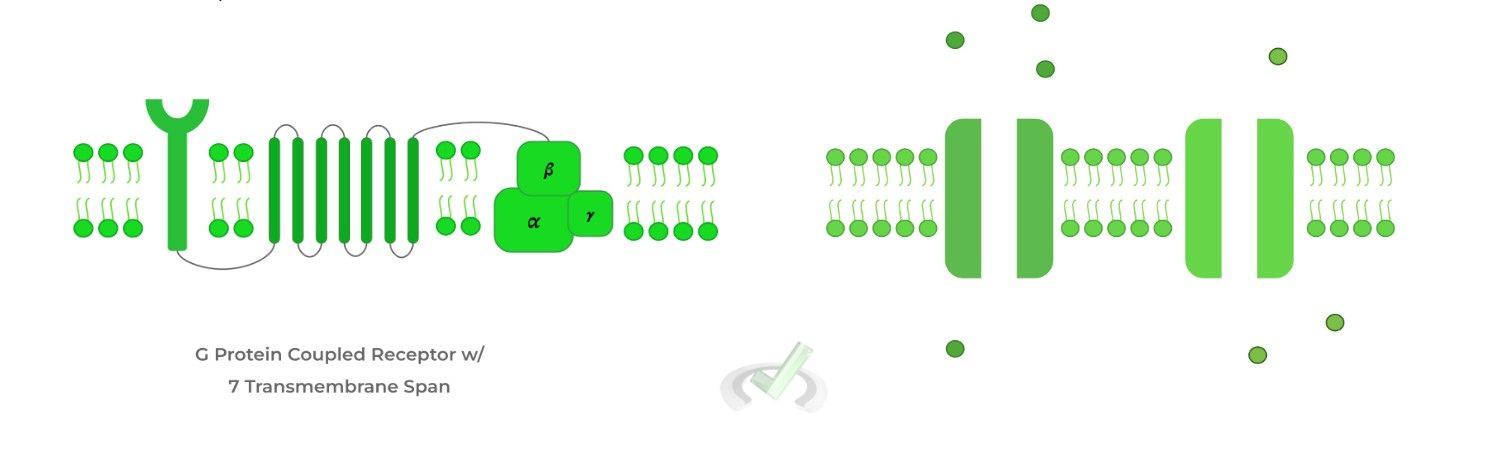
Full Study Notes : Proteins: Biosignaling on the MCAT
For more in-depth content review on biosignaling, check out these detailed lesson notes created by top MCAT scorers.
Important Definitions and Key Terms — Non- Enzymatic Proteins
Term | Definition |
|---|---|
Binding Proteins | Proteins that bind various substances for transportation or signal transduction. |
Hemoglobin | A type of binding protein that is responsible for binding oxygen molecules and transporting them in the blood to various tissues. |
DNA Binding Transcription Factors | Proteins that bind to the phosphate backbone of DNA; regulates DNA transcription. |
Antibodies | Immune proteins that are involved in binding antigens that are specific to the variable region of antibodies. |
Variable Binding Region | The region on an antibody that is specifically attracted to a distinct antigen. |
Constant Region |
The region on an antibody that is specifically attracted to a distinct antigen. |
Motor Proteins |
Proteins that are involved in transport/movement (e.g. Myosin, Kinesins/Dyneins). |
Myosin |
A motor protein that is heavily involved in muscle contraction. |
Kinesin |
A motor protein that is involved in anterograde transport (movement away from the interior of the cell, and towards the periphery of the cell). |
Dyneins |
A motor protein that is involved in retrograde transport (movement towards the interior of the cell, and away from the periphery of the cell). |
Receptors |
A biosignaling molecule that has a ligand binding domain and is responsible for signal transduction. |
Ligand Binding Domain |
A molecule that specifically attaches to a receptor to stimulate signal transduction. |
Enzyme Linked Receptor |
A receptor that, when bound to a ligand, stimulates enzymatic activity. |
G-Protein Coupled Receptor |
A heterotrimeric protein consisting of alpha, beta, and gamma subunits, and is involved in signal transduction. |
Ion Channels |
Facilitates the flow of ions. |
Ungated Ion Channels (aka. Leakage channels) |
Ion channels that are always open to facilitate the flow of ions down their concentration gradient (i.e. from high to low ion concentration). |
Ligand Gated Ion Channels |
Ion channels that bind specific ligands, which results in a conformational change and the flow of ions. |
Voltage Gated Ion Channels |
Ion channels that are sensitive to changes in voltage, resulting in a conformational change to allow ion flow through the channel. |
Additional FAQs — Non-Enzymatic Proteins on the MCAT
What are non enzymatic proteins?
What are the functions of non-enzymatic proteins?
1.) Binding ligands to regulate signal transduction/enzyme activity (Receptors).
2) Movement of molecules intracellularly (Kinesin and Dyneins).
3) Muscle contraction (Actin and Myosin).
4) Regulating DNA transcription (DNA binding transcription factors).
5) Recognizing antigens (Antibodies).
6) Facilitating the movement of ions across membranes (Ion channels).
What are the enzymatic proteins?
Are motor proteins enzymes?
Additional Reading Links – Study Notes for Non-Enzymatic Proteins on the MCAT
For more in-depth content review about non-enzymatic proteins on the MCAT, check out these detailed lesson notes created by top MCAT scorers!
Additional Reading: Biochemistry Subjects on the MCAT:
- Biological Membranes on the MCAT
- Carbohydrate Metabolism on the MCAT
- Carbohydrate Structure on the MCAT
- DNA and RNA on the MCAT
- Enzymes on the MCAT
- Lipids and Lipid Metabolism on the MCAT
- Amino Acids Peptides Proteins on the MCAT
- Regulation of Metabolism on the MCAT
- Biotechnology on the MCAT
- Bioenergetics on the MCAT







 To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these
To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these 
