What if we told you that your biological system could do much more than coordinate regular functions, such as moving your muscles when needed?
What comes to mind when you think of the term' Biotechnology'? You may think of crazy ideas like gene cloning, modified organisms, or gene therapy. These are all a significant part of biotechnology, but this term also encompasses things such as antibiotics and crop breeding!
Biotechnology refers to the use of an organism or another biological system to create a product in either a lab or real-life setting.
This guide will introduce you to the fascinating world of biotechnology, along with some key terms and definitions you should remember as you prepare for the MCAT.
Let’s get started!
Biotechnology on the MCAT: What Do You Need to Know?
Biotechnology is covered in the Biochemistry section of the MCAT.
Introductory biochemistry accounts for 25% of the Biological and Biochemical Foundations of Living Systems section (Bio/Biochem) and 25% of the Chemical and Physical Foundations of Biological Systems section (Chem/Phys).
It’s hard to predict the exact number of questions about biotechnology that will appear on the MCAT. However, you can expect it to appear in both the Bio/Biochem and Chem/Phys sections.
Important Sub-Topics – Biotechnology
We cannot stress enough the importance of biotechnology during MCAT prep since this is closely related to DNA and DNA technology, and other important MCAT topics!
Biotechnology can be complicated, so let’s break it down into important sub-topics you can concentrate on.
I. Biotechnology: Applications of DNA Technology
There are three main types of DNA technology application:
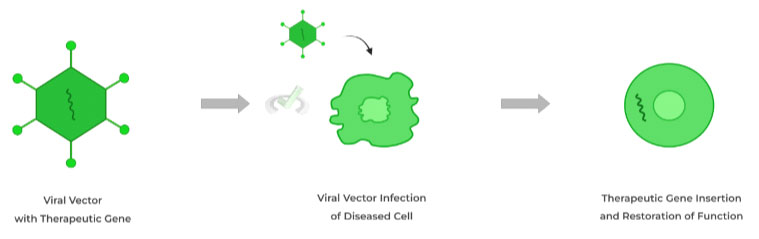
A. Viral Vector Gene Therapy
A viral vector carries the therapeutic gene to a diseased cell to restore function.
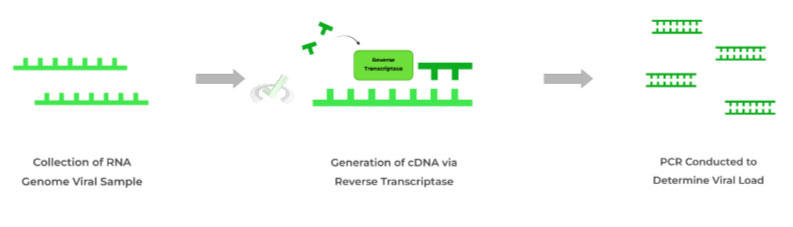
B. rt-PCR Test
This test begins with a reverse transcriptase which creates complementary DNA (cDNA) from the viral RNA genome sample. This cDNA is then amplified via numerous polymerase chain reactions to determine the viral load.
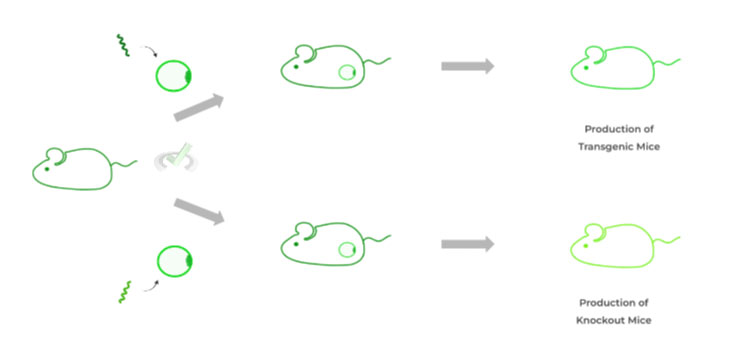
C. Transgenic and Knockout Mice
This type of DNA technology is used to study the progression of a disease, such as cancer. We can study disease progression by introducing a defective gene or by taking away a functional gene. From here, we can monitor the mice and note the outcomes!
Full Study Notes : Biotechnology: Applications of DNA Technology on the MCAT
For more in-depth content review on applications of DNA technology, check out these detailed lesson notes created by top MCAT scorers.
II. Biotechnology: Strategies for DNA Multiplication
Although there are many approaches to DNA multiplication, in this guide, we’ll be focusing on the two covered on the MCAT: Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) and Gene Cloning.
Strategy for DNA Multiplication | Description |
|---|---|
PCR | Similar to DNA replication. Three steps are involved– denaturation, annealing, and elongation. |
Gene Cloning | Using a bacterial organism to duplicate DNA. Three steps are involved– gene insertion into vector, vector uptake in bacteria, and bacterial colony growth. |
Full Study Notes : Biotechnology: Strategies for DNA Multiplication on the MCAT
For more in-depth content review on strategies of DNA multiplication, check out these detailed lesson notes created by top MCAT scorers.
III. Biotechnology: Embryonic Stem Cells
Embryonic stem cells are pluripotent, meaning they can develop into any cell type except extraembryonic cells, such as placental cells. These cells are harvested from the inner cell mass of the blastocyst and are used in many medical applications.
One example is using embryonic stem cells to determine the development of disease. This is achieved in mice by uptaking a foreign disease-causing transgene through the use of embryonic stem cells!
Another type of research utilizing embryonic stem cells and mice is called knockout mice. This occurs when the gene of interest is removed to study gene inactivation on disease progression.
Full Study Notes : Biotechnology: Embryonic Stem Cells on the MCAT
For more in-depth content review on embryonic stem cells, check out these detailed lesson notes created by top MCAT scorers.
IV. Biotechnology: Blotting
The most common technique used to identify the presence of an enzyme is blotting. There are various types of blotting, such as the Northern blot, Southern Blot, and Western Blot. Each type of blotting investigates a different molecule, which can be a DNA or RNA sequence or even a protein.
Different conclusions can be made from different blotting variations! The northern and western blot are good indicators for gene expression, while the southern blot is a good indicator for gene quantity.
Full Study Notes : Biotechnology: Blotting on the MCAT
For more in-depth content review on blotting, check out these detailed lesson notes created by top MCAT scorers.
V. Biotechnology: Safety and Ethics in Research
With research, especially in the field of DNA technology, many ethical dilemmas need to be considered.
The Belmont Report outlines three main principles that must be followed when conducting research:
The Belmont Report Principle | Description |
|---|---|
Respect for Persons | Patient autonomy and protection are met first when conducting research studies through informed consent. |
Beneficence | Assesses if the study is maximizing the potential benefits while also minimizing possible harm, also known as nonmaleficence. |
Justice | Ensures there is equal representation in the research group and that there’s a fair distribution of the benefits and risks. |
Full Study Notes : Biotechnology: Safety and Ethics in Research on the MCAT
For more in-depth content review on safety and ethics, check out these detailed lesson notes created by top MCAT scorers.
VI. Biotechnology: DNA Libraries
DNA libraries refer to the collection of DNA molecules and fragments derived from a cell. There are two main types:
A. Genomic Libraries
These consist of DNA fragments that comprise the whole genome of the cell, including both coding and noncoding DNA sequences.
B. cDNA Libraries
These are derived using mRNA templates, which oppose the central dogma. cDNA libraries are used primarily to determine gene function.
Full Study Notes : Biotechnology: DNA Libraries on the MCAT
For more in-depth content review on DNA libraries, check out these detailed lesson notes created by top MCAT scorers.
VII. Biotechnology: Gel Electrophoresis
Gel electrophoresis is a widely utilized lab technique to separate and study mixtures of nucleic acids and proteins. The technique requires a gel-like, porous matrix and an applied electric field on the matrix, where one end is termed the anode (positively charged) and the other termed the cathode (negatively charged).
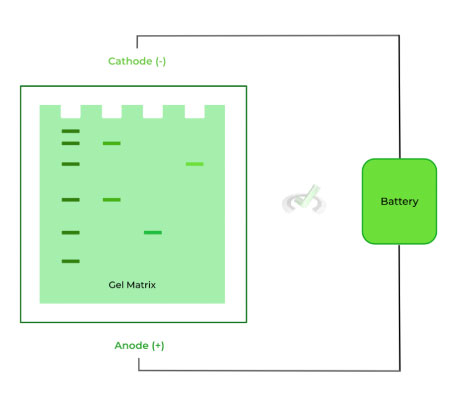
Three main factors determine how fast and far a molecule will travel in the gel – size, charge, and shape.
Various types of gel electrophoresis techniques exist. They differ in the performed experimental conditions and the characteristic that is exploited for separation:
Type of Gel Electrophoresis | Description |
|---|---|
Native PAGE | Most simple technique, the protein is run on the gel in its native form. However, the shape is a known confounding variable. |
SDS-PAGE | Detergent is used to denature proteins, making them streamlined and eliminating shape as a confounding variable. |
Reducing SDS-PAGE | Specialized version of SDS-PAGE where proteins are completely denatured with a reducing agent. |
Isoelectric Focusing | Protein matrix has a pH gradient, allowing for protein separation. |
Full Study Notes : Biotechnology: Gel Electrophoresis on the MCAT
For more in-depth content review on gel electrophoresis, check out these detailed lesson notes created by top MCAT scorers.
VIII. Biotechnology: Restriction Enzymes
These are enzymes that contain cutting mechanisms. When they are cut at recognition sites, the cut DNA can either have overhanging strands, termed sticky ends, or no overhanging strands termed blunt ends.
Full Study Notes : Biotechnology: Restriction Enzymes on the MCAT
For more in-depth content review on restriction enzymes, check out these detailed lesson notes created by top MCAT scorers.
IX. Biotechnology: DNA Sequencing
DNA sequencing is useful to determine the exact sequence of nucleotides, or bases, in a DNA molecule.
Sanger sequencing, a technique developed by Dr. Frederick Sanger, appears on the MCAT. This technique uses dideoxyribonucleotides and polymerase chain reactions in the process.
There are three main steps in Sanger sequencing:
1. Template strand isolation
Double-stranded DNA is heated to separate strands via the breaking of existing hydrogen bonds.
2. PCR and Chain Termination
The template strand then undergoes amplification via PCR, resulting in many strands of DNA of different lengths.
3. Gel electrophoresis
Gel electrophoresis is then used to differentiate the smallest strand from the largest strand. Determining the 3’ from the 5’ end!
Full Study Notes : Biotechnology: DNA Sequencing on the MCAT
For more in-depth content review DNA sequencing, check out these detailed lesson notes created by top MCAT scorers.
Key Terms and Definitions – Biotechnology
Here are some of the more important key terms and definitions to remember for this general guide to biotechnology!
Term | Definition |
|---|---|
Hybridization | The ability of DNA and RNA probes to bind with the DNA and RNA sequences, as they contain complementary, Watson-Crick base pairing. |
Endonuclease | Cleave within the nucleic acids via hydrolysis. |
Palindromic Sequence | These form recognition sites. Palindromic sequences occur when the 5’-3’ sequence on one strand is identical to the 5’-3’ sequence on the complementary, antiparallel strand. |
Electrophoresis | The use of an electrical current applied to a gel matrix to separate biological molecules. |
Viral Vector | A tool used to deliver genetic material to a cell. |
Dideoxyribonucleotides | These nucleotides lack the C3 hydroxyl group. When attached to a growing DNA strand, elongation will terminate as there is no C3 hydroxyl group to catalyze the addition of another nucleotide. This is why they’re also called terminator nucleotides. |
Additional FAQs – Biotechnology on the MCAT
Additional Reading Links – Study Notes for Biotechnology on the MCAT
For more in-depth content review about biotechnology on the MCAT, check out these detailed lesson notes created by top MCAT scorers!
Additional Reading: Biochemistry Subjects on the MCAT:
- Biological Membranes on the MCAT
- Carbohydrate Metabolism on the MCAT
- Carbohydrate Structure on the MCAT
- DNA and RNA on the MCAT
- Enzymes on the MCAT
- Lipids and Lipid Metabolism on the MCAT
- Non-Enzymatic Proteins on the MCAT
- Regulation of Metabolism on the MCAT
- Amino Acids Peptides Proteins on the MCAT
- Bioenergetics on the MCAT







 To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these
To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these 
