Cross-sectional studies are a type of observational research. They help researchers understand the characteristics of a group of people at one specific time. This guide will explain what cross-sectional studies are, how they are done, their good and bad points, and why they matter in fields like medicine, psychology, and social sciences.
I. Understanding Cross-Sectional Studies
Cross-sectional studies provide a "snapshot" of a group or event. They capture data at one specific time.
A. Definition and Purpose
A cross-sectional study is a research method that collects data from a group of people at one point in time. Unlike longitudinal studies, which follow the same people over a long period, cross-sectional studies are like taking a picture of a moment.
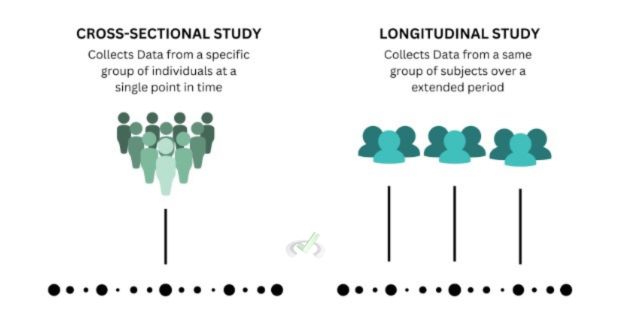
They help understand how common certain conditions, behaviors, or traits are in a group. For example, a cross-sectional study might measure the number of people with high blood pressure in a community.
B. How Cross-Sectional Studies Work
Researchers pick a sample from the group they want to study. This sample should represent the larger group to ensure the findings are accurate.
Data collection can be done through surveys, interviews, or records checks. For instance, a survey might ask people about their eating habits and exercise levels to determine the prevalence of obesity.
II. Key Parts: Elements of Cross-Sectional Studies
Each cross-sectional study involves several key parts. These include sample selection, data collection methods, and data analysis.
A. Sample Selection
Choosing the right sample is crucial for the study’s accuracy. The sample should represent the broader group.

For example, if the study aims to understand adults' eating habits, the sample should include people of different ages, genders, and backgrounds. This variety ensures that the study results apply to the whole group.
B. Data Collection Methods
Data can be collected using various methods. Common methods include:
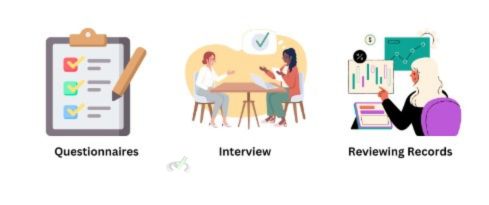
- Questionnaires: Written sets of questions that people fill out. They are efficient for collecting data from many people quickly.
- Interviews: Direct conversations between the researcher and participants. They provide detailed information.
- Reviewing Records: Analyzing existing data like medical records or past surveys.
Each method has its good and bad points. Questionnaires are quick but may not capture detailed answers. Interviews give depth but can take a lot of time. Reviewing records can offer old data but may not always be up-to-date.
C. Data Analysis
After collecting data, researchers analyze it to find patterns or trends. They use statistical tools to explore connections between different things. For example, the analysis might show a link between age and exercise levels. This could indicate that older people exercise less often.
III. Benefits and Limitations: Pros and Cons of Cross-Sectional Studies
Cross-sectional studies have several advantages but also have limitations.
A. Benefits
- Quick and Cost-Effective: These studies require less time and money than longitudinal studies, which track changes over time.
- Useful for Public Health: They help identify common diseases or health behaviors. This is valuable for public health planning. For example, knowing how many people smoke can help design anti-smoking campaigns.
- Baseline Data: Cross-sectional studies provide essential data that can guide more research or actions. For instance, if a study shows high obesity rates, it could lead to programs promoting healthier lifestyles.
B. Limitations
- Cannot Determine Cause and Effect: These studies can show links but cannot prove that one thing causes another. For example, a cross-sectional study might find that people who watch more TV also have higher obesity rates. However, it can't be prove that TV watching causes obesity.
- Snapshot Limitation: They only capture data at one point in time. This means they cannot track changes.
- Bias and Accuracy Issues: Participants might not always give accurate information, especially on sensitive topics. This can lead to response bias, where the data does not reflect the true situation.
IV. Applications: Where Cross-Sectional Studies are Used
Cross-sectional studies are used in many fields because they are flexible.
A. Medicine
In medicine, these studies help understand how common diseases are. For example, they can show how many people have diabetes or heart disease. A study might find that many people have undiagnosed high blood pressure. This information can lead to more health check-ups and treatments.
B. Psychology
Psychologists use cross-sectional studies to look at the prevalence of mental health issues like anxiety or depression. These studies can show which groups are most affected. This helps in providing the right mental health resources.
C. Social Sciences
In the social sciences, cross-sectional studies examine education levels, job rates, or income differences. For example, a study might explore the link between education and job opportunities.
V. Bridge/Overlap
Cross-sectional studies provide important data. This data can connect with other research methods and topics covered on the MCAT.
A. Comparisons with Longitudinal Studies
While cross-sectional studies give a snapshot, longitudinal studies follow the same group over time. This helps see changes and trends. For example, a cross-sectional study might show the current obesity rates. On the other hand, a longitudinal study could track weight changes over several years.
B. Integration with Experimental Research
Cross-sectional data can highlight areas for more experimental research. For example, if a study finds a link between poor diet and heart disease, experimental research could test ways to improve eating habits.
C. Real-World Implications
The findings from cross-sectional studies have real-world uses. In public health, these studies can guide policies and programs. For example, if a study shows high rates of smoking among teenagers, it could lead to targeted anti-smoking campaigns.
D. Relevant MCAT Topics
Cross-sectional studies are relevant to several MCAT topics. These include:
- Public Health and Epidemiology: Understanding how diseases spread and how common they are.
- Research Methods: Learning about different study designs and their strengths and weaknesses.
- Statistical Analysis: Analyzing data to find patterns and links.
VI. Wrap Up/Key Terms
Cross-sectional studies are valuable tools in research. They offer insights into a group's characteristics and behaviors at one time. Though they are useful in many fields, they have limits, such as not proving cause and effect.
Key Terms
- Cross-Sectional Study: A study that collects data from a group at one point in time.
- Sample: A group chosen to represent the larger group.
- Data Collection Methods: Techniques like surveys, interviews, and record reviews are used to gather information.
- Cause and Effect: The relationship between what causes something and what is caused.
- Prevalence: How common a condition is in a group.
VII. Practice
Test your understanding with these application-based questions:
Sample Practice Question 1
A cross-sectional study finds that a higher percentage of elderly people have high blood pressure than younger adults. What does this study show?
A. Elderly people will develop high blood pressure as they age.
B. There is a relationship between age and high blood pressure.
C. Young adults are immune to high blood pressure.
D. High blood pressure causes aging.
Ans. B
The study shows a link between age and high blood pressure. However, it does not prove that aging causes high blood pressure. It only shows that they are related.
Sample Practice Question 2
What can be concluded if a cross-sectional study finds a link between screen time and sleep quality among teenagers?
A. Screen time causes poor sleep quality.
B. Poor sleep quality causes increased screen time.
C. There is a relationship between screen time and sleep quality, but cause and effect cannot be determined.
D. Reducing screen time will improve sleep quality.
Ans. C
The study shows that screen time and sleep quality are related, but it does not prove that one causes the other. More research would be needed to explore cause and effect.







 To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these
To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these 










 reviews on TrustPilot
reviews on TrustPilot