Acids and bases are fundamental concepts in chemistry. They play a crucial role in various chemical reactions. Several definitions of acids and bases exist, each with its own perspective and applications. Understanding these definitions helps predict the behavior of substances in different chemical environments.
I. Introduction to Acids and Bases
Acids and bases are defined by their ability to donate or accept protons (H⁺ ions) and interact with each other in neutralization reactions. Let's explore the main definitions of acids and bases:
A. Arrhenius Definition
The Arrhenius definition focuses on the behavior of substances in water.
Acids: Substances that increase the concentration of hydrogen ions (H⁺) in aqueous solutions. For example, hydrochloric acid (HCl) dissociates in water to produce H⁺ and chloride ions (Cl⁻):
Bases: Substances that increase the concentration of hydroxide ions (OH⁻) in aqueous solutions. For example, sodium hydroxide (NaOH) dissociates in water to produce Na⁺ and OH⁻ ions:
HCl → H⁺ + Cl⁻
NaOH → Na⁺ + OH⁻
B. Brønsted-Lowry Definition
The Brønsted-Lowry definition broadens the concept to include reactions not limited to aqueous solutions.
- Acids: Proton donors. Any substance that can donate an H⁺ ion. For example, ammonia (NH₃) reacting with water: Here, NH₃ is the base accepting a proton, and H₂O is the acid donating a proton.
NH₃ + H₂O → NH₄⁺ + OH⁻
- Bases: Proton acceptors. Any substance that can accept an H⁺ ion. For example, in the same reaction, water acts as a proton donor, making NH₃ a base.
C. Lewis Definition
The Lewis definition is even more general and includes various chemical reactions.
- Acids: Electron pair acceptors. Any substance that can accept a pair of electrons to form a covalent bond. For example, aluminum chloride (AlCl₃) can accept an electron pair from chloride ions (Cl⁻):
AlCl₃ + Cl⁻ → AlCl₄⁻
Bases: Electron pair donors. Any substance that can donate a pair of electrons to form a covalent bond. For example, ammonia (NH₃) donating its lone pair of electrons to form a bond with boron trifluoride (BF₃):
NH₃ + BF₃ → NH₃BF₃
II. Examples and Chemical Equations
Understanding these definitions becomes easier with examples and chemical equations. These examples illustrate the behavior of acids and bases according to each definition.
A. Arrhenius Acid-Base Reaction
Hydrochloric acid (HCl) reacts with sodium hydroxide (NaOH) to form water and sodium chloride (NaCl):
HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H₂O
This reaction neutralizes the acid and base, forming water and salt.
B. Brønsted-Lowry Acid-Base Reaction
Acetic acid (CH₃COOH) reacting with ammonia (NH₃):
CH₃COOH + NH₃ → CH₃COO⁻ + NH₄⁺
Here, acetic acid donates a proton to ammonia, forming acetate (CH₃COO⁻) and ammonium (NH₄⁺).
C. Lewis Acid-Base Reaction
Boron trifluoride (BF₃) reacting with fluoride ion (F⁻):
BF₃ + F⁻ → BF₄⁻
In this reaction, boron trifluoride accepts an electron pair from the fluoride ion.
III. Bridge/Overlap
Understanding acids and bases connects to several other important topics in chemistry, many of which are covered on the MCAT.
A. Electrochemistry
Acids and bases play a significant role in electrochemical reactions. For example, in electrolysis, acidic or basic solutions can affect the movement of ions and the overall reaction.
B. Biochemistry
Acid-base balance is crucial in biological systems. Enzyme activity is often pH-dependent, and buffer systems in the body help maintain the pH of blood and other fluids. The Henderson-Hassel Balch equation is used to calculate the pH of buffer solutions:
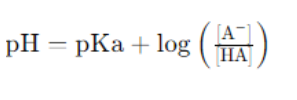
C. Organic Chemistry
Acids and bases are involved in many organic reactions, such as forming esters, amides, and other compounds. Understanding how acids and bases interact helps predict the outcomes of these reactions.
IV. Wrap-Up and Key Terms
Understanding the different definitions of acids and bases is essential for studying chemistry. These concepts help explain the behavior of substances in various reactions and environments.
Key Terms:
- Acid: A substance that can donate a proton (H⁺) or accept an electron pair.
- Base: A substance that can accept a proton (H⁺) or donate an electron pair.
- pH: A measure of the acidity or basicity of a solution.
- Titration: A technique to determine the concentration of an acid or base.
Buffer: A solution that resists changes in pH.
By understanding these fundamental concepts, you can better grasp the behavior of acids and bases in various chemical reactions.
V. Practice Questions
Sample Practice Question 1
What is Arrhenius definition of a base?
A. A substance that increases H⁺ concentration in water.
B. A substance that increases OH⁻ concentration in water.
C. A substance that donates protons.
D. A substance that accepts protons.
Ans. B
The Arrhenius definition of a base specifically refers to substances that increase the concentration of hydroxide ions (OH⁻) in aqueous solutions.
Sample Practice Question 2
Which of the following is a Lewis acid?
A. NH₃
B. H₂O
C. BF₃
D. OH⁻
Ans. C
A Lewis acid is defined as an electron pair acceptor. Boron trifluoride (BF₃) can accept an electron pair from another molecule, making it a Lewis acid.







 To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these
To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these 










 reviews on TrustPilot
reviews on TrustPilot