Do you ever wonder how we can separate a mixture of liquids into its individual components? Or how we purify chemicals for various uses?
Distillation explains the processes that are used to achieve separation and purification. Let's explore these different types of distillation and their applications in organic chemistry.
I. Introduction to Distillation
Distillation is a process used to separate liquids from a mixture. It works by heating the mixture to turn the liquid into vapor and then cooling the vapor to turn it back into liquid.
This process relies on the fact that different substances have different boiling points. Understanding distillation allows us to separate and purify different substances based on their boiling points.
II. Simple Distillation
Simple distillation separates liquids with significantly different boiling points, usually at least 25°C apart. It is ideal for purifying a liquid from non-volatile impurities or separating two liquids with a large boiling point difference.
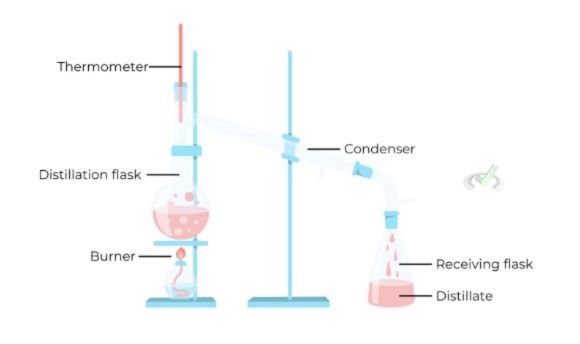
Process
In simple distillation, the mixture is heated in a distillation flask. First, the liquid with the lower boiling point turns into vapor.
The vapor rises and passes through a condenser. This is where it cools and turns back into liquid. The liquid, called the distillate, is collected in a separate container.
III. Fractional Distillation
Fractional distillation separates liquids with closer boiling points, less than 25°C apart. It is commonly used in refining petroleum and chemical labs to purify complex mixtures.
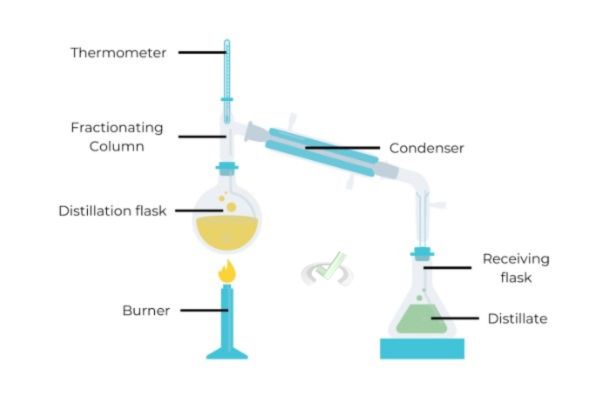
Process
The setup in fractional distillation is similar to simple distillation but includes a fractionating column filled with materials like glass beads or plates.
These materials create more surface area. It allows repeated vaporization and condensation.
As the vapor rises through the column, components with higher boiling points condense and return to the flask. Lower boiling point components continue to rise and eventually condense in the condenser.
IV. Vacuum Distillation
Vacuum distillation is used to distill compounds with very high boiling points. By reducing the pressure in the distillation apparatus, the boiling points of the compounds are lowered.
This allows distillation to occur at lower temperatures. Vacuum distillation is useful for heat-sensitive compounds that might decompose at high temperatures.
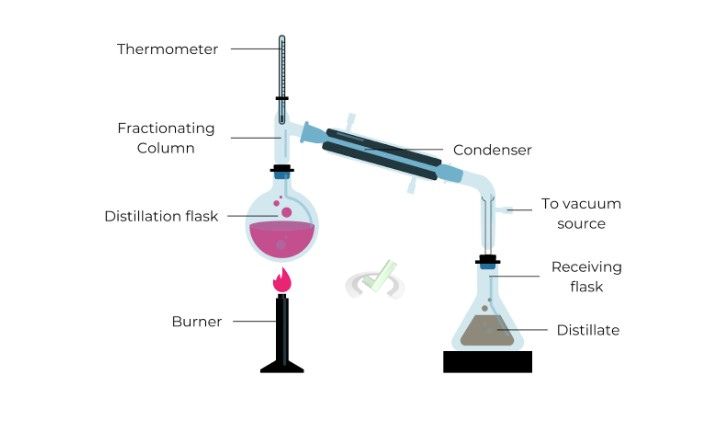
Process
In vacuum distillation, a vacuum pump reduces the pressure inside the distillation apparatus, lowering the substances' boiling points.
This makes it possible to distill compounds at lower temperatures. The rest of the process is similar to simple or fractional distillation but occurs at much lower temperatures.
V. Steam Distillation
Steam distillation separates temperature-sensitive compounds, such as natural oils and aromatic compounds. It allows the distillation of these compounds at temperatures lower than their normal boiling points by passing steam through the mixture.
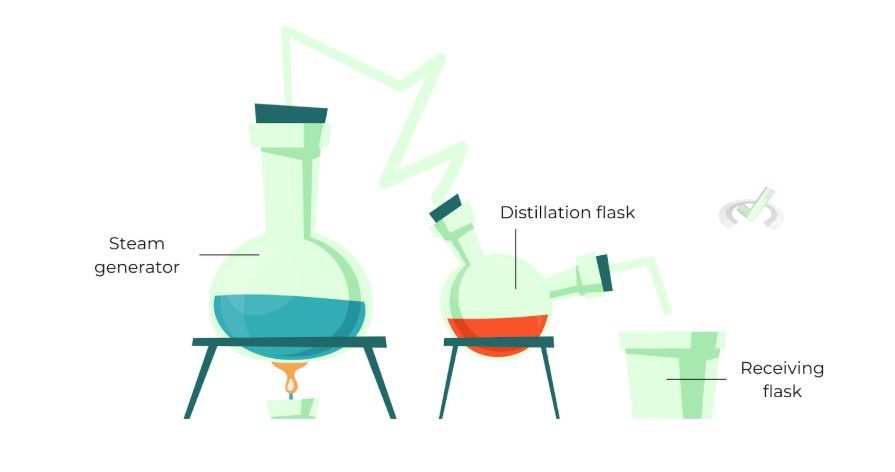
Process
In steam distillation, steam passes through the mixture containing the desired compounds, carrying the volatile compounds with it.
This steam and compound mixture is then cooled and condensed back into liquid. The resulting liquid contains the desired compound separated from the rest of the mixture.
VI. Azeotropic Distillation
Azeotropic distillation is used to separate azeotropes, which are mixtures of two or more liquids that have a constant boiling point and composition throughout distillation. This type of distillation adds another substance to create a new azeotrope with a different boiling point, allowing separation.
Process
An entertainer (another substance) is added to the mixture in azeotropic distillation. This forms a new azeotrope with a different boiling point. The new azeotrope can then be distilled, separating the original components.
VII. The Broader Impact of Distillation
In Organic Synthesis
Distillation is essential in organic synthesis for purifying reactants and products. It helps obtain the pure compounds needed for further reactions.
In Pharmaceutical Chemistry
Distillation is used in the production of pharmaceuticals to ensure the purity of drug components. This is crucial for the safety and effectiveness of medications.
In Petrochemical Industry
The petrochemical industry relies heavily on fractional distillation to refine crude oil into valuable products like gasoline, diesel, and jet fuel. Each fraction contains hydrocarbons of different boiling ranges.
Environmental Applications
Distillation is also used in environmental chemistry to purify water and treat waste. It helps remove contaminants and recover valuable substances from waste streams.
Laboratory Applications
In chemistry labs, simple distillation is often used to purify solvents. Fractional distillation is used to separate complex mixtures during organic synthesis.
Safety Considerations
When performing distillation, it is important to use proper glassware and handle heat sources carefully. Also, to prevent accidents, always ensure the setup is secure.
VIII. Wrap-Up and Key Terms
Understanding the different types of distillation is crucial for mastering organic chemistry techniques. Let's review the key terms and concepts:
Key Terms
- Distillation: A process used to separate mixtures based on differences in boiling points.
- Simple Distillation: Used for separating liquids with significantly different boiling points.
- Fractional Distillation: A fractionating column separates liquids with closer boiling points.
- Vacuum Distillation: Used for distilling high boiling point compounds at reduced pressures.
- Steam Distillation: Used for distilling temperature-sensitive compounds using steam.
- Azeotropic Distillation: Used for separating azeotropes by adding an entrainer to form a new azeotrope.
IX. Practice Questions
Sample Practice Question 1
Which type of distillation is best for separating liquids with very high boiling points?
A. Simple Distillation
B. Fractional Distillation
C. Vacuum Distillation
D. Steam Distillation
Ans. C
Vacuum distillation reduces the pressure inside the apparatus, lowering the substances' boiling points. This allows distillation to occur at lower temperatures, which is ideal for high-boiling-point compounds.
Sample Practice Question 2
How does fractional distillation differ from simple distillation?
A. It uses a vacuum pump.
B. It uses a fractionating column.
C. It uses steam.
D. It uses an entrainer.
Ans. B
Fractional distillation uses a fractionating column. It provides a larger surface area for repeated vaporization and condensation, allowing better separation of liquids with close boiling points.



 To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these
To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these